- Aug 2022
-
-
While it is a fundamental principle that workscontemporary with an event are presumably more authenticthan later ones, it should be borne in mind that the morerecent secondary works are frequently based on more ma-terials and present new interpretations.
-
-
howaboutthis.substack.com howaboutthis.substack.com
-
Below is a two page spread summarizing a Fast Company.com article about the Pennebaker method, as covered in Timothy Wilson’s book Redirect:
Worth looking into this. The idea of the Pennebaker method goes back to a paper of his in 1986 that details the health benefits (including mental) of expressive writing. Sounds a lot like the underlying idea of morning pages, though that has the connotation of clearing one's head versus health related benefits.
Compare/contrast the two methods.
Is there research underpinning morning pages?
See also: Expressive Writing in Psychological Science https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1745691617707315<br /> appears to be a recap article of some history and meta studies since his original work.
-
-
berkeley-defi.github.io berkeley-defi.github.io
-
Question 1 (Incentive Security). Is there mutually profitable con-tinued participation across all required parties?
EDU content should have "reflection" segments with these kind of questions to help guide reader's curiosity and knowledge --> socratic method
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Neurath claimed that magic was unfalsifiable and therefore disenchantment could never be complete in a scientific age.[18]
- Josephson-Storm, Jason (2017). The Myth of Disenchantment: Magic, Modernity, and the Birth of the Human Sciences. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-226-40336-6.
-
- Jul 2022
-
go.dev go.dev
-
Pointer receivers You can declare methods with pointer receivers. This means the receiver type has the literal syntax *T for some type T. (Also, T cannot itself be a pointer such as *int.) For example, the Scale method here is defined on *Vertex. Methods with pointer receivers can modify the value to which the receiver points (as Scale does here). Since methods often need to modify their receiver, pointer receivers are more common than value receivers. Try removing the * from the declaration of the Scale function on line 16 and observe how the program's behavior changes. With a value receiver, the Scale method operates on a copy of the original Vertex value. (This is the same behavior as for any other function argument.) The Scale method must have a pointer receiver to change the Vertex value declared in the main function.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
An Index is something you must physically create asyou add cards in a physical note system.
Watch closely to see how Allosso's description of an index comes to the advice of John Locke versus the practice of Niklas Luhmann.
Alternately, is it closer to a commonplace indexing system or a shallowly linked, but still complex zettelkasten indexing system?
In shared digital systems, I still suspect that densely indexed notes will have more communal value.
Link to: - https://hypothes.is/a/nrk0vgoCEe2y3CedssHnVA
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
But online information has a very weak link to memory.
Why is memory for online pieces weaker for most?
Is it the lack of sense of "physical" location for helping to store it? What about the seemingly ephemeral character of online data?
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Professor Ernst Bernheim, of the University ofGreifswald, has worked through nearly all themodern works on historical method, and the fruitof his labours is an arrangement under appropriateheadings, most of them invented by himself, of agreat number of reflections and selected references.His Lehrhuch der historischen Methode^ (Leipzig, 1894,8vo) condenses, in the manner of German Lehrhiicher,the special literature of the subject of which ittreats.
These French authors are specifically aware of Ernst Bernheim's 1894 text which also has sections on note taking methods. Should be interesting to see how this differs at least for the brief portion of Bernheim I read on the topic.
Link to: - https://hyp.is/RJ-6-AekEe268sOEeQ79Yw
-
The best work that has hitherto been published (in French) onhistorical method is a pamphlet by MM. Ch. and V. Mortet, LaScience de Vhistoire (Paris, 1894, 8vo), 88 pp., extracted from vol. xx.of the Grande Encyclopidie
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Bernheim, Ernst. Lehrbuch der historischen Methode und der Geschichtsphilosophie: mit Nachweis der wichtigsten Quellen und Hilfsmittel zum Studium der Geschichte. Leipzig : Duncker & Humblot, 1908. http://archive.org/details/lehrbuchderhist03berngoog.
Title translation: Textbook of the historical method and the philosophy of history : with reference to the most important sources and aids for the study of history
A copy of the original 1889 copy can be found at https://digital.ub.uni-leipzig.de/mirador/index.php
-
Ein grofer Teil der Regestenarbeit wird neuerdings demForscher durch besondere Regestenwerke abgenommen, nament-lich auf dem Gebiet der mittelalterlichen Urkunden. Daf diesebevorzugt werden, hat zwei Griinde: erstens sind die Urkundenfur die Geschichte des Mittelalters gewissermafen als festesGerippe von besonderer Wichtigkeit; zweitens sind sie so ver.streut in ihren Fund- und Druckorten, da8 die Zusammen-stellung derselben, wie sie ftir jede Arbeit von neuem erforder-lich wire, immer von neuem die langwierigsten und mtthsamstenVorarbeiten n&tig machen wiirde. Es ist daher von griéStemNutzen, da8 diese Vorarbeiten ein fir allemal gemacht und demeinzelnen Forscher erspart werden.
Ein großer Teil der Regestenarbeit wird neuerdings dem Forscher durch besondere Regestenwerke abgenommen, namentlich auf dem Gebiet der mittelalterlichen Urkunden. Daß diese bevorzugt werden, hat zwei Gründe: erstens sind die Urkunden fur die Geschichte des Mittelalters gewissermafen als festes Gerippe von besonderer Wichtigkeit; zweitens sind sie so verstreut in ihren Fund- und Druckorten, daß die Zusammenstellung derselben, wie sie ftir jede Arbeit von neuem erforderlich wire, immer von neuem die langwierigsten und mtthsamsten Vorarbeiten nötig machen würde. Es ist daher von größtem Nutzen, daß diese Vorarbeiten ein fir allemal gemacht und dem einzelnen Forscher erspart werden.
Google translation:
A large part of the regesta work has recently been relieved of the researcher by special regesta works, especially in the field of medieval documents. There are two reasons why these are preferred: first, the documents are of particular importance for the history of the Middle Ages as a solid skeleton; Secondly, they are so scattered in the places where they were found and printed that the compilation of them, as would be necessary for each new work, would again and again necessitate the most lengthy and laborious preparatory work. It is therefore of the greatest benefit that this preparatory work should be done once and for all and that the individual researcher be spared.
While the contexts are mixed here between note taking and historical method, there is some useful advice here that while taking notes, one should do as much work upfront during the research phase of reading and writing, so that when it comes to the end of putting the final work together and editing, the writer can be spared the effort of reloading large amounts of data and context to create the final output.
-
nennt man Regesten, Regesta, eine Ableitung von dem Verbumregerere, das schon bei Quintilian in der Bedeutung ,abschreiben,eintragen“ vorkommt. Spezielle Zusammenstellungen der Auf-enthaltsorte historischer Persinlichkeiten aus den Quellen nenntman Itinerare.
Derartige geordnete Eintragungen historischer Materialien nennt man Regesten, Regesta, eine Ableitung von dem Verbum regerere, das schon bei Quintilian in der Bedeutung ,abschreiben, eintragen“ vorkommt. Spezielle Zusammenstellungen der Aufenthaltsorte historischer Persönlichkeiten aus den Quellen nennt man Itinerare. (p 556-557)
Google translation:
Such ordered entries of historical material are called regesta, regesta, a derivation of the verb regerere, which already occurs in Quintilian in the meaning "to copy, to enter". Special compilations of the whereabouts of historical figures from the sources are called itineraries.
Regesta in this context are complete copies of ordered entries of historical material. One might also translate this as historical copies or entries.
While Bernheim is talking about historical records and copies thereof in his discussion of regesta, he does bring up a useful point about manual note taking practice: one needn't completely copy the original context, just do enough work to create context for yourself so as not to be overburdened with excess material later. Some working in digital contexts may find it easy to simply copy and paste everything from an original document, but capturing just the useful synopsis may be enough, particularly when the original context can be readily revisited.
-
3. Regesten.Da wir gesehen haben, wieviel auf tibersichtliche Ordnungbei der Zusammenstellung des Materials ankommt, muff manauf die praktische Einrichtung seiner Materialiensammlung vonAnfang an bewufte Sorgfalt verwenden. Selbstverstindlichlassen sich keine, im einzelnen durchweg gtiltigen Regeln auf-stellen; aber wir kinnen uns doch tiber einige allgemeine Ge-sichtspunkte verstindigen. Nicht genug zu warnen ist vor einemregel- und ordnungslosen Anhiufen und Durcheinanderschreibender Materialien; denn die zueinander gehérigen Daten zusammen--gufinden erfordert dann ein stets erneutes Durchsehen des ganzenMaterials; auch ist es dann kaum miglich, neu hinzukommendeDaten an der gehirigen Stelle einzureihen. Bei irgend gréferenArbeiten muff man seine Aufzeichnungen auf einzelne loseBlatter machen, die leicht umzuordnen und denen ohne Unm-stinde Blatter mit neuen Daten einzuftigen sind. Macht mansachliche Kategorieen, so sind die zu einer Kategorie gehérigenBlatter in Umschligen oder besser noch in K&sten getrennt zuhalten; innerhalb derselben kann man chronologisch oder sach-lich alphabetisch nach gewissen Schlagwiértern ordnen.
- Regesten Da wir gesehen haben, wieviel auf tibersichtliche Ordnung bei der Zusammenstellung des Materials ankommt, muß man auf die praktische Einrichtung seiner Materialiensammlung von Anfang an bewußte Sorgfalt verwenden. Selbstverständlich lassen sich keine, im einzelnen durchweg gültigen Regeln aufstellen; aber wir können uns doch über einige allgemeine Gesichtspunkte verständigen. Nicht genug zu warnen ist vor einem regel- und ordnungslosen Anhäufen und Durcheinanderschreiben der Materialien; denn die zueinander gehörigen Daten zusammenzufinden erfordert dann ein stets erneutes Durchsehen des ganzen Materials; auch ist es dann kaum möglich, neu hinzukommende Daten an der gehörigen Stelle einzureihen. Bei irgend größeren Arbeiten muß man seine Aufzeichnungen auf einzelne lose Blätter machen, die leicht umzuordnen und denen ohne Umstände Blätter mit neuen Daten einzufügen sind. Macht man sachliche Kategorieen, so sind die zu einer Kategorie gehörigen Blätter in Umschlägen oder besser noch in Kästen getrennt zu halten; innerhalb derselben kann man chronologisch oder sachlich alphabetisch nach gewissen Schlagwörtern ordnen.
Google translation:
- Regesture Since we have seen how much importance is placed on clear order in the gathering of material, conscious care must be exercised in the practical organization of one's collection of materials from the outset. It goes without saying that no rules that are consistently valid in detail can be set up; but we can still agree on some general points of view. There is not enough warning against a disorderly accumulation and jumble of materials; because to find the data that belong together then requires a constant re-examination of the entire material; it is also then hardly possible to line up newly added data at the appropriate place. In any large work one must make one's notes on separate loose sheets, which can easily be rearranged, and sheets of new data easily inserted. If you make factual categories, the sheets belonging to a category should be kept separate in covers or, better yet, in boxes; Within these, you can sort them chronologically or alphabetically according to certain keywords.
In a pre-digital era, Ernst Bernheim warns against "a disorderly accumulation and jumble of materials" (machine translation from German) as it means that one must read through and re-examine all their collected materials to find or make sense of them again.
In digital contexts, things are vaguely better as the result of better search through a corpus, but it's still better practice to have things with some additional level of order to prevent the creation of a "scrap heap".
link to: - https://hyp.is/i9dwzIXrEeymFhtQxUbEYQ
In 1889, Bernheim suggests making one's notes on separate loose sheets of paper so that they may be easily rearranged and new notes inserted. He suggested assigning notes to categories and keeping them separated, preferably in boxes. Then one might sort them in a variety of different ways, specifically highlighting both chronological and alphabetical order based on keywords.
(This quote is from the 1903 edition, but presumably is similar or the same in 1889, but double check this before publishing.)
Link this to the earlier section in which he suggested a variety of note orders for historical methods as well as for the potential creation of insight into one's work.
-
Man sieht, die stoffliche Ordnung setzt bereits bestimmteGesichtspunkte voraus und ist daher durch die ,Auffassung“bedingt; allein bei tibersichtlicher Materialordnung werden wirauch umgekehrt oft genug durch sich anhtufende Daten einergewissen von uns anfangs nicht erwarteten Art auf ganz neueGesichtspunkte unseres Themas aufmerksam gemacht.
Google translation:
One sees that the material order already sets certain ones points of view ahead and is therefore conditional; only with a clear arrangement of the material will we also vice versa often enough due to accumulating data in a way that we didn't expect at first, in a completely new way points of view of our topic.
While discussing the various orders of research material, Ernst Bernheim mentions the potential of accumulating data and arranging it in various manners such that we obtain new points of view in unexpected ways. This sounds quite similar to a process of idea generation similar to combinatorial creativity, though not as explicit.
The process creates the creativity, but isn't necessarily used to force the creativity here.
While he doesn't point out a specific generative mechanism for the creation of the surprise, it's obvious that his collection and collation method underpins it.
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Ernst Bernheim (19 February 1850 – 9 July 1942) was a German historian who is best known for an influential Lehrbuch der historischen Methode (1889) on historical method.
-
-
drive.google.com drive.google.com
-
Many of the workers reported that first thing in themorning, or after any interruption in their thought(like a ‘phone call), they have the “where was 1?”problem in a complex and ill-defined space of ideas.The layout of physical materials on their desk givesthem powerful and immediate contextual cues torecover a complex set of threads without difilcultyand delay, “this is my whole context, these are mypersonal piles”
Following interruptions by colleagues or phone calls at work, people may frequently ask themselves "where was I?" more frequently than "what was I doing?" This colloquialism isn't surprising as our memories for visual items and location are much stronger than actions. Knowledge workers will look around at their environments for contextual clues for what they were doing and find them in piles of paper on their desks, tabs in their computer browser, or even documents (physical or virtual) on their desktops.
-
- Jun 2022
-
www.scientificamerican.com www.scientificamerican.com
-
Instead of hiking the trail yourself, the trees, rocks and moss move past you in flashes with no trace of what came before and no way to see what lies ahead.
Just as there are deficits like dyslexia in the literate world, are there those who have similar deficits relating to location in the oral world? What do these look like? What are they called specifically?
There are definitely memory deficits withing cognitive neuropsychology. Is there a comprehensive list one could look at?
Some people aren't as good at spatial orientation as others. Women are stereotyped as being less good at direction and direction finding.
-
Both anecdotally and in published studies, people report that when trying to locate a particular piece of written information they often remember where in the text it appeared.
How does location affect our reading? Is it similar to methods of location and memory within oral traditions?
-
-
www.kcet.org www.kcet.org
-
If a guy got lucky at a restaurant, it got included.” Jauregui waxes poetic about The Address Book, calling it “sexual memory…told by spaces.”
Something interesting here about a "gossipy collaboration" of an address book that crystallized a "sexual memory...told by spaces".
-
-
Local file Local file
-
You can download this chapter at Buildingasecondbrain.com/bonuschapter.
Come be a part of my sales funnel!!!
ugh... This should generally be sacrilege, but it's even worse when having a solid index (which is roughly the purpose that tags support) is an important part of any commonplace book, especially since John Locke, which a resource Forte has cited elsewhere in his book.
-
When a few of his friends became interested in thetopic, he took eight minutes to progressively summarize the bestexcerpts before sharing the summarized article with them. The timethat he had spent reading and understanding a complex subject paidoff in time savings for his friends, while also giving them a newinterest to connect over.
To test one's own understanding of a topic one has read about and studied, it can be useful to discuss it or describe one's understanding to friends or colleagues in conversations. This will help you discover where the holes are based on the person's understanding and comprehension of what you've said. Can you fill in all the holes where they have questions? Are their questions your new questions which have exposed holes that need to be filled in your understanding or in the space itself.
I do this regularly in conversations with people. It makes the topics of conversation more varied and interesting and helps out your thinking at the same time. In particular I've been doing this method in Dan Allosso's book club. It's almost like trying on a new idea the way one might try on a piece of clothing to see how it fits or how one likes it for potential purchase. If an idea "fits" then continue refining it and add it to your knowledge base. These conversations also help to better link ideas in my thought space to those of what we're reading. (I wonder if others are doing these same patterns, Dan seems to, but I don't have as good a grasp on this with other participants).
Link to :<br /> - Ahren's idea of writing to expose understanding<br /> - Feynman technique<br /> - Socratic method (this is sort of side or tangential method to this) <- define this better/refine
-
How to Resurface and Reuse Your Past Work
Coming back to the beginning of this section. He talks about tags, solely after-the-fact instead of when taking notes on the fly. While it might seem that he would have been using tags as subject headings in a traditional commonplace book, he really isn't. This is a significant departure from the historical method!! It's also ill advised not to be either tagging/categorizing as one goes along to make searching and linking things together dramatically easier.
How has he missed the power of this from the start?! This is really a massive flaw in his method from my perspective, particularly as he quotes John Locke's work on the topic.
Did I maybe miss some of this in earlier sections when he quoted John Locke? Double check, just in case, but this is certainly the section of the book to discuss using these ideas!
-
As powerful as search can be, studies5 have found that in manysituations people strongly prefer to navigate their file systemsmanually, scanning for the information they’re looking for. Manualnavigation gives people control over how they navigate, with foldersand file names providing small contextual clues about where to looknext.6
The studies quoted here are in the mid 80s and early 90s before the rise of better and easier UI methods or more powerful search. I'd have to call this conclusion into question.
There's also a big difference in what people know, what people prefer, and what knowledgeable people can do most quickly.
Cross reference this with Dan Russell's research at Google that indicates that very few people know how to use ctrl-f to find or search for things in documents. - https://hyp.is/7a532uxjEeyYfTOctQHvTw/www.youtube.com/channel/UCh6KFtW4a4Ozr81GI1cxaBQ
Relate it to the idea of associative (memory) trails (Memex), songlines, and method of loci in remembering where things are -- our brains are designed to navigate using memory
Tags
- Feynman Technique
- commonplace books
- file navigation
- fashion
- idea links
- sales funnels
- indices
- ctrl-f
- Memex
- method of loci
- associative memory
- testing understanding
- search
- oral folders
- subject headings
- conversations
- memory trails
- Dan Russell
- Socratic method
- writing for understanding
- John Locke indexing method
- folders
- associative trails
- songlines
- metaphors
- understanding
Annotators
-
-
hybridpedagogy.org hybridpedagogy.org
-
Groups in arts education rail against the loss of music, dance, and art in schools and indicate that it's important to a balanced education.
Why has no one embedded these learning tools, for yes they can be just that, into other spaces within classrooms? Indigenous educators over the millennia have done just this in passing on their societal and cultural knowledge. Why have we lost these teaching methods? Why don't we reintroduce them? How can classrooms and the tools within them become mnemonic media to assist both teachers and learners?
Perhaps we need to bring back examples of how to do these things at the higher levels? I've seen excercises in my daughter's grade school classrooms that bring art and manipulatives into the classroom as a base level, but are they being done specifically for these mnemonic reasons?
Michael Nielsen and Andy Matuschak have been working at creating a mnemonic medium for areas like quantum mechanics relying in part on spaced repetition. Why don't they go further and add in dance, movement, art, and music to aid in the process. This can be particularly useful for creating better neurodiverse outcomes as well. Education should be more multi-modal, more oral, and cease it's unending reliance on only literacy as it's sole tool.
How and where can we create a set of example exercises at various grade levels (similar to rites of knowledge initiation in Indigenous cultures, for lack of specific Western language) that embed all of these methods
Link to: - Ideas in The Extended Brain about movement, space, etc. - Nielsen/Matuschak mnemonic media work
-
-
-
The box makes me feel connected to a project. It is my soil. I feel this evenwhen I’ve back-burnered a project: I may have put the box away on a shelf, but Iknow it’s there. The project name on the box in bold black lettering is a constantreminder that I had an idea once and may come back to it very soon.
Having a physical note taking system also stands as a physical reminder and representation of one's work and focus. It may be somewhat out of the way on a shelf, but it takes up space in a way that digital files and notes do not. This invites one into using and maintaining it.
Link to - tying a string on one's finger as a reminder - method of loci - orality
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
*The compass*
I too have seen this before, though the directions may have been different.
When thinking about an idea, map it discretely. North on the compass rose is where the idea comes from, South is where it leads to, West leads to things similar to the idea while East are ideas that are the opposite of it.
This is useful in situating information, particularly with respect to the similarities and opposites. One must generally train themselves to think about the opposites.
Many of the directions are directly related to putting information into a zettelkasten, in particular where X comes from (source), where it leads (commentary or links to other ides), what's similar to x are links to either closely related ideas or to an index. The opposite of X is the one which is left out in this system too.
<script async src="https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js" charset="utf-8"></script>*The compass*: <br>Saw that one before. Ugh, didn't like it.<br><br>Thinking about it though, it's a fitting metaphor to look at a note from different directions. I'm going to add this to my notes template(Just to try). All my notes have North & could use some other perspectives 🎉<br><br>🧶4/4 pic.twitter.com/CJctmC5Y39
— Alex Qwxlea (@QwxleaA) June 14, 2022Link to - Indigenous map conceptualizations - direction finding - method of loci
-
-
www.revolutionaryplayers.org.uk www.revolutionaryplayers.org.uk
-
https://www.revolutionaryplayers.org.uk/the-scope-and-nature-of-darwins-commonplace-book/
Erasmus Darwin's commonplace book
It is one of the version(s?) published by John Bell based on John Locke's method and is a quarto volume bound in vellum with about 300 sheets of fine paper.
Blank pages 1 to 160 were numbered and filled by Darwin in his own hand with 136 entries. The book was started in 1776 and continued until 1787. Presumably Darwin had a previous commonplace book, but it has not been found and this version doesn't have any experiments prior to 1776, though there are indications that some material has been transferred from another source.
The book contains material on medical records, scientific matters, mechanical and industrial improvements, and inventions.
The provenance of Erasmus Darwin's seems to have it pass through is widow Elizabeth who added some family history to it. It passed through to her son and other descendants who added entries primarily of family related topics. Leonard Darwin (1850-1943), the last surviving son of Charles Darwin gave it to Down House, Kent from whence it was loaned to Erasmus Darwin House in 1999.
-
- May 2022
-
via3.hypothes.is via3.hypothes.is
-
Thus, the sensitive seismographer of avant-garde develop-ments, Walter Benjamin, logically conceived of this scenario in 1928, of communicationwith card indices rather than books: “And even today, as the current scientific methodteaches us, the book is an archaic intermediate between two different card indexsystems. For everything substantial is found in the slip box of the researcher who wroteit and the scholar who studies in it, assimilated into its own card index.” 47
- Walter Benjamin, Einbahnstra ß e, in Gesammelte Schriften, vol. 4 (Frankfurt am Main: Suhrkamp Verlag, 1928/1981), 98 – 140, at 103.
Does Walter Benjamin prefigure the idea of card indexes conversing with themselves in a communicative method similar to that of Vannevar Bush's Memex?
This definitely sounds like the sort of digital garden inter-communication afforded by the Anagora as suggested by @Flancian.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
Where has Scott gotten the phrase "memory castle" which he repeats many times here?
-
the memory castle that jordan peter peterson described i think it has potentially a risk of inducing 00:58:28 confirmation bias
Jordan Peterson apparently has described using a memory palace (castle?) he used with 12 spaces for writing his book (presumably 12 Rules for life?).
-
-
Local file Local file
-
S-)$+"#$91*+$+H-$0#&+=)'#*$*0"-81)*$"1(#$0-&0#9+=18'O#4$+"#$4"#$%"&3"("$9)'C1)'8,$1*$1&$-7Z#0+Y$4)1H'&2$0-C91)I'*-&*$7#+H##&$1$*"##+$-.$919#)$1&4$-+"#)$-7Z#0+I$71*#4$C#+19"-)*$+"1+$8'@#&$+"#$C'&4$+-$1$017'&#+Y$1$+"#1+#)Y$1$)--CY$-)$1$"-=*#Vf
Most of the object-based metaphors for the mind over the past two centuries are spaces or location-based: a cabinet, a theater, a room, or a house. This would seem to show a close association of our prior uses of mnemotechniques, particularly the method of loci, for remembering anything with the mind.
Are there any non-object/non-location based metaphors other than the tabula rasa mentioned by Matthew Daniel Eddy?
-
-
www.exurbe.com www.exurbe.com
-
When chatting with my father about the proton research he summed it up nicely, that two possible responses to hearing that how we measure something seems to change its nature, throwing the reliability of empirical testing into question, are: “Science has been disproved!” or “Great! Another thing to figure out using the Scientific Method!” The latter reaction is everyday to those who are versed in and comfortable with the fact that science is not a set of doctrines but a process of discovery, hypothesis, disproof and replacement. Yet the former reaction, “X is wrong therefore the system which yielded X is wrong!” is, in fact, the historical norm.
-
- Apr 2022
-
-
The connections will still make it easier to remember and understand.
Linking one's ideas together is a means of contextualizing them as well as situating them in a particular location with respect to your other knowledge. This creation of structure and place (loci) helps to quicken one's memory of not on the new item, but the items to which it is attached.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Dr Ellie Murray, ScD. (2021, September 19). We really need follow-up effectiveness data on the J&J one shot vaccine, but not sure what this study tells us. A short epi 101 on case-control studies & why they’re hard to interpret. 🧵/n [Tweet]. @EpiEllie. https://twitter.com/EpiEllie/status/1439587659026993152
-
-
www.covid-19-mobility.org www.covid-19-mobility.org
-
Schlosser, F. (2021, November 29). Omicron—Import Risk. Covid-19 Mobility Project. https://www.covid-19-mobility.org/reports/importrisk_omicron/
-
-
www.facetsjournal.com www.facetsjournal.com
-
Caulfield, T., Bubela, T., Kimmelman, J., & Ravitsky, V. (2021). Let’s do better: Public representations of COVID-19 science. FACETS, 6, 403–423. https://doi.org/10.1139/facets-2021-0018
-
-
-
In this way the pressures of the multitude and diversity of authorita-tive opinion, already articulated in the previous century by Peter Abelard (1079–1142), were heightened by the development of reference books, from indexes and concordances that made originalia searchable and to the large compilations that excerpted and summarized from diverse sources.
Prior to the flourishing of reference materials, Peter Abelard (1079-1142) had articulated the idea of "the multitude and diversity of authoritative opinion" to be found in available material. How was one to decide which authority to believe in a time before the scientific method?
-
Even if the Speculum was copied only in parts, Vincent of Beauvais exposed the reader to multiple opinions on any topic he discussed. Neither the concordance nor the encyclo-pedic compendium resolved the textual difficulties or contradictions that they helped bring to light. Vincent explicitly left to the reader the task of reaching a final conclusion amid the diversity of authoritative opinions that might exist on a question: “I am not unaware of the fact that philosophers have said many contradictory things, especially about the nature of things. . . . I warn the reader, lest he perhaps be horrified, if he finds some contradictions of this kind among the names of diverse authors in many places of this work, especially since I have acted in this work not as an author, but as an excerptor, that I did not try to reduce the sayings of the philosophers to agreement but report what each said or wrote on each thing; leaving to the judgment of the reader to decide which opinion to prefer.”161
Interesting that Vincent of Beauvais indicates that there were discrepancies between the authors, but leaves it up to the reader to decide for themself.
What would the reader do in these cases in a culture before the scientific method and the coming scientific revolutions? Does this statement prefigure the beginning of a cultural shift?
Are there other examples of (earlier) writers encouraging the the comparison of two different excerpts from "expert" or authoritative sources to determine which should have precedence?
What other methods would have encouraged this sort of behavior?
-
-
www.ema.europa.eu www.ema.europa.eu
-
EMA. (2020, October 27). COVID-19 vaccines: Development, evaluation, approval and monitoring [Text]. European Medicines Agency. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/public-health-threats/coronavirus-disease-covid-19/treatments-vaccines/vaccines-covid-19/covid-19-vaccines-development-evaluation-approval-monitoring
-
-
super-memory.com super-memory.com
-
You should avoid such items whenever possible due to the high cost of retaining memories based on sets.
Piotr Wozniak recommends against avoiding memorizing sets and prefers enumerations.
Is this a result of his not knowing the method of loci as a means of travelling through sets and remembering them easily? It's certainly evidence he wasn't aware of the as a general technique.
He does mention peg techniques, mind maps, and general mnemonic techniques.
-
- Mar 2022
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci on Twitter: ‘@alexdefig are you really going to claim that responses to the introduction of passports on uptake across 4 other countries are evidentially entirely irrelevant to whether or not passports are justified or not?’ / Twitter. (n.d.). Retrieved 31 March 2022, from https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1444358068280565764
-
-
twitter.com twitter.comTwitter1
-
James Heathers. (2021, October 26). Perish the thought I would be as peremptory as @GidMK. No, I’m going to hector, mock, or annoy those replies, THEN ask for money, THEN block you when I get bored. See, these aren’t rebuttals. No-one’s said anything about the actual work. Nothing. Not a sausage. [Tweet]. @jamesheathers. https://twitter.com/jamesheathers/status/1452980059497762824
-
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
Heathers, J. (2021, October 23). The Real Scandal About Ivermectin. The Atlantic. https://www.theatlantic.com/science/archive/2021/10/ivermectin-research-problems/620473/
-
-
www.elizabethfilips.com www.elizabethfilips.com
-
MY LECTURE NOTES
Elizabeth Filips has digital versions of medical school notes online. She's drawn them (in software) by hand with color and occasional doodles in them (there's an image of Einstein's head with an E=mc^2 under it on one page) which makes them more memorable for having made them in the first place, but with the color and the pictures, they act as a memory palace.
I've found no evidence (yet) that she's using direct mnemonics or that she's been specifically trained in the method of loci or other techniques. This doesn't, however, mean that she's not tangentially using them without knowing about them explicitly.
One would suspect that this sort of evolutionary movement towards such techniques would have been how they evolved in the first place.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Topic A topic was once a spot not a subjecttopic. to ̆p’ı ̆k. n. 1. The subject of a speech, essay, thesis, or discourse. 2. A subject of discussion or con-versation. 3. A subdivision of a theme, thesis, or outline.*With no teleprompter, index cards, or even sheets of paper at their disposal, ancient Greek and Roman orators often had to rely on their memories for holding a great deal of information. Given the limi-tations of memory, the points they chose to make had to be clustered in some meaningful way. A popular and quite reliable method for remembering information was known as loci (see Chapter 9), where loci was Latin for “place.” It involved picking a house you knew well, imagining it in your mind’s eye, and then associating the facts you wanted to recall with specifi c places inside of that house. Using this method, a skillful orator could mentally fi ll up numerous houses with the ideas he needed to recall and then simply “visit” them whenever he spoke about a particular subject. The clusters of informa-tion that speakers used routinely came to be known as commonplaces, loci communes in Latin and koinos topos in Greek. The great Greek philosopher Aristotle referred to them simply as topos, meaning “places.” And that’s how we came to use topic to refer to subject or grouping of information.**
Even in the western tradition, the earliest methods of mnemonics tied ideas to locations, from whence we get the ideas of loci communes (in Latin) and thence commonplaces and commonplace books. The idea of loci communes was koinos topos in Greek from whence we have derived the word 'topic'.
Was this a carryover from other local oral traditions or a new innovation? Given the prevalence of very similar Indigenous methods around the world, it was assuredly not an innovation. Perhaps it was a rediscovery after the loss of some of these traditions locally in societies that were less reliant on orality and moving towards more reliance on literacy for their memories.
-
-
www.science.org www.science.org
-
Contents | Science 375, 6586. (n.d.). Science. Retrieved 23 March 2022, from https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/science.2022.375.issue-6586
-
-
-
These ways of knowinghave inherent value and are leading Western scientists to betterunderstand celestial phenomena and the history and heritage thisconstitutes for all people.
The phrase "ways of knowing" is fascinating and seems to have a particular meaning across multiple contexts.
I'd like to collect examples of its use and come up with a more concrete definition for Western audiences.
How close is it to the idea of ways (or methods) of learning and understanding? How is it bound up in the idea of pedagogy? How does it relate to orality and memory contrasted with literacy? Though it may not subsume the idea of scientific method, the use, evolution, and refinement of these methods over time may generally equate it with the scientific method.
Could such an oral package be considered a learning management system? How might we compare and contrast these for drawing potential equivalencies of these systems to put them on more equal footing from a variety of cultural perspectives? One is not necessarily better than another, but we should be able to better appreciate what each brings to the table of world knowledge.
-
- Feb 2022
-
niklas-luhmann-archiv.de niklas-luhmann-archiv.de
-
9/8g Hinter der Zettelkastentechnik steht dieErfahrung: Ohne zu schreiben kann mannicht denken – jedenfalls nicht in anspruchsvollen,selektiven Zugriff aufs Gedächtnis voraussehendenZusammenhängen. Das heißt auch: ohne Differenzen einzukerben,kann man nicht denken.
Google translation:
9/8g The Zettelkasten technique is based on experience: You can't think without writing—at least not in contexts that require selective access to memory.
That also means: you can't think without notching differences.
There's something interesting about the translation here of "notching" occurring on an index card about ideas which can be linked to the early computer science version of edge-notched cards. Could this have been a subtle and tangential reference to just this sort of computing?
The idea isn't new to me, but in the last phrase Luhmann tangentially highlights the value of the zettelkasten for more easily and directly comparing and contrasting the ideas on two different cards which might be either linked or juxtaposed.
Link to:
- Graeber and Wengrow ideas of storytelling
-
Shield of Achilles and ekphrasis thesis
-
https://hypothes.is/a/I-VY-HyfEeyjIC_pm7NF7Q With the further context of the full quote including "with selective access to memory" Luhmann seemed to at least to make space (if not give a tacit nod?) to oral traditions which had methods for access to memories in ways that modern literates don't typically give any credit at all. Johannes F.K .Schmidt certainly didn't and actively erased it in Niklas Luhmann’s Card Index: The Fabrication of Serendipity.
-
-
materchristi.libguides.com materchristi.libguides.com
-
To create trails When we are studying a text we need to take the time to understand more than just the storyline. During your second reading, any comments made during the first reading (marginal comments or summaries) will quickly give you the gist of your first reading, so that you can take advantage of your second.
While multiple readings of a text in antiquity may have been rarer, due to the cheap proliferation of books, one can more easily "blaze a trail" through their reading to make it easier or quicker to rebuild context on subsequent readings.
Look at history of reading to see which books would have been more likely re-read, particularly outside of one's primary "area" of expertise.
Link to the trails mentioned by Vannevar Bush in As We May Think.
-
-
www.zhihu.com www.zhihu.com
-
苏轼给的建议是,一本史书,要读很多遍,每一遍都只专注于一个层面,所谓“每书数过,一意求之”。想研究政治政策,就着重于书中的奏章言论;想搞懂典章制度,就着重于书中官职升迁礼仪往来,想看明白地理建制,就着重于书中的地名沿革山河变动。
苏东坡八面受敌读书法
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
Local file Local file
-
The linear process promoted by most study guides, which insanelystarts with the decision on the hypothesis or the topic to write about,is a sure-fire way to let confirmation bias run rampant.
Many study and writing guides suggest to start ones' writing or research work with a topic or hypothesis. This is a recipe for disaster to succumb to confirmation bias as one is more likely to search out for confirming evidence rather than counter arguments. Better to start with interesting topic and collect ideas from there which can be pitted against each other.
-
-
www.scibeh.org www.scibeh.org
-
SciBeh Virtual Workshop 2021: Science Communication as Collective Intelligence. (n.d.). SciBeh. Retrieved 14 February 2022, from https://www.scibeh.org/events/workshop2021/
-
-
-
Neue Studie: Wie gut schützen FFP2-Masken vor Corona? (2021, December 4). ZDFheute. https://www.zdf.de/uri/6f2f3223-fd82-4dc3-a6bf-24e8dc6eb648
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Smith, G. C. S., & Pell, J. P. (2003). Parachute use to prevent death and major trauma related to gravitational challenge: Systematic review of randomised controlled trials. BMJ : British Medical Journal, 327(7429), 1459–1461.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Deepti Gurdasani. (2022, January 29). Going to say this again because it’s important. Case-control studies to determine prevalence of long COVID are completely flawed science, but are often presented as being scientifically robust. This is not how we can define clinical syndromes or their prevalence! A thread. [Tweet]. @dgurdasani1. https://twitter.com/dgurdasani1/status/1487366920508694529
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Deepti Gurdasani. (2022, January 30). Have tried to now visually illustrate an earlier thread I wrote about why prevalence estimates based on comparisons of “any symptom” between infected cases, and matched controls will yield underestimates for long COVID. I’ve done a toy example below here, to show this 🧵 [Tweet]. @dgurdasani1. https://twitter.com/dgurdasani1/status/1487578265187405828
-
-
threadreaderapp.com threadreaderapp.com
-
- Jan 2022
-
towardsdatascience.com towardsdatascience.com
-
Generally, bootstrap involves the following steps:
- A sample from population with sample size n.
- Draw a sample from the original sample data with replacement with size n, and replicate B times, each re-sampled sample is called a Bootstrap Sample, and there will totally B Bootstrap Samples.
- Evaluate the statistic of θ for each Bootstrap Sample, and there will be totally B estimates of θ.
- Construct a sampling distribution with these B Bootstrap statistics and use it to make further statistical inference, such as:
- Estimating the standard error of statistic for θ.
- Obtaining a Confidence Interval for θ.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Retraction Watch. (2022, January 7). Our list of retracted COVID-19 papers is up to 206. For context and denominators, please see the post. Https://retractionwatch.com/retracted-coronavirus-covid-19-papers/ [Tweet]. @RetractionWatch. https://twitter.com/RetractionWatch/status/1479599196089077766
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Survivals of this spatially oriented technique still mark our language when we say “in the first place” and “passing on to the next point.”
The use of mnemonic techniques through history have been crystalized into our language with phrases like "in the first place" and "passing on to the next point".
-
-
-
The effect was beautifully suggested by Victor Hugo in a familiar passage in Notre-Dame de Paris (183 1) when the scholar holding his first printed book turns away from his manuscripts, looks a t the cathedral, and says "This will kill that" (Ceci tuera cela). Print also destroyed "the invisible cathedrals of memory." For the printed book made it less nec- essary to shape ideas and things into vivid images and then store them in Memory-places.
In Notre-Dame de Paris (1831) Victor Hugo depicts a scholar holding his first printed book. He turns away from his manuscripts to look at the cathedral and says "This will kill that" (Ceci tuera cela). Similarly the printed book made it far less necessary to store one's knowledge into cathedrals of memory.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
後來藉由Reading note的方式,發現能讓閱讀後的記憶持續更久,忘記時也能藉由筆記迅速找到需要的資訊
-
文章篇幅長就比較容易有看了就忘的情況,常常一個段落要重複看幾次才能掌握其中的訊息,抑或是在文獻綜述階段閱讀的參考文獻等到要實際寫論文時記憶已經模糊
-
看這類句子先看動詞部分,能夠更理解句子的主要意思而非糾結於專業單字上,閱讀速度也有所提升
-
在大學以前所閱讀的英文文章大多是考試時的短文抑或是詞彙較日常的小說,而學術型論文中有大量不同專業領域的單字,若還是保持著以往邊看邊查單字的的習慣,閱讀速度則大幅降低,也比較難記住文章的重點內容
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Spinney, L. (2022, January 9). Are we witnessing the dawn of post-theory science? The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2022/jan/09/are-we-witnessing-the-dawn-of-post-theory-science
-
- Dec 2021
-
learn-us-east-1-prod-fleet01-xythos.content.blackboardcdn.com learn-us-east-1-prod-fleet01-xythos.content.blackboardcdn.com
-
Hobbes and Rousseau told their contemporaries things that werestartling, profound and opened new doors of the imagination. Nowtheir ideas are just tired common sense. There’s nothing in them thatjustifies the continued simplification of human affairs. If socialscientists today continue to reduce past generations to simplistic,two-dimensional caricatures, it is not so much to show us anythingoriginal, but just because they feel that’s what social scientists areexpected to do so as to appear ‘scientific’. The actual result is toimpoverish history – and as a consequence, to impoverish our senseof possibility.
The simplification required to make models and study systems can be a useful tool, but one constantly needs to go back to the actual system to make sure that future predictions and work actually fit the real world system.
Too often social theorists make assumptions which aren't supported in real life and this can be a painfully dangerous practice, especially when those assumptions are built upon in ways that put those theories out on a proverbial creaking limb.
This idea is related to the bias that Charles Mathewes points out about how we treat writers as still living or as if they never lived. see: https://hypothes.is/a/VTU2lFvZEeyiJ2tN76i4sA
-
-
sciencebasedmedicine.org sciencebasedmedicine.org
-
Loud Silenced Doctors | Science-Based Medicine. (2021, December 19). https://sciencebasedmedicine.org/muzzled/
-
-
danallosso.substack.com danallosso.substack.com
-
Every serious (academic) historical work includes a conversation with other scholarship, and this has largely carried over into popular historical writing.
Any serious historical or other academic work should include a conversation with the body of other scholarship with which argues for or against.
Comparing and contrasting one idea with another is crucial for any sort of advancement.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Replicating scientific results is tough—But essential. (2021). Nature, 600(7889), 359–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03736-4
-
-
-
Object of the study is the case of urban planning and policyexperiments in land management and reuse, food productionand local procurement in the city of Cleveland.
The authors use "situated and articulated qualitative research strategies" (p. 241) through a case study approach to analyze experimentation with land management, food production and procurement strategies in Cleveland, Ohio, through the lens of post-capitalism and social -innovation theories, and offered up by traditional community development actors, city administrators and anchor institutions.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Tom Moultrie. (2021, December 12). Given the comedic misinterpretation of the South African testing data offered by @BallouxFrancois (and many others!) last night ... I offer some tips having contributed to the analysis of the testing data for the @nicd_sa since April last year. (1/6) [Tweet]. @tomtom_m. https://twitter.com/tomtom_m/status/1469954015932915718
-
-
-
Drexel, for instance, held those teach-ers ridiculous who taught students to build up houses and rooms by means of imagination and stock them with images of memorable subjects (imagines agentes).16 According to the German Jesuit, the effort was not only huge but students wasted their time because images escape from these artificial places
much as prisoners escape from jails without guards.17 16 Drexel, Aurifodina, 258 17 Drexel, Aurifodina, 3–4.
Jeremias Drexel (1581 – 1638) recommended against the method of loci during the explosion of information in the late 16th and early 17th centuries.
Add Drexel to the list of reformers against the ars memoria in the early 1600s.)
While dealing with the information overload, educators may have inadvertently thrown out the baby with the bath water. While information still tends to increase and have increased complexity, some areas also show compression and concatenation and new theories subsume old information into their models. This means that one might know and understand Einstein which means that memorizing Newton's work is no longer needed at some point. Where should one draw the line of memorization for subsuming the knowledge of their culture? Aren't both old and new methods for memory usable? Keep the ars memoria while also using written methods.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
The analysis pro-vides a picture of how to measure success and sustainability. Table 3 demon-strates one option for how to translate the findings from this study into ameasurement framework that can be tested in other cases of local-to-nationalalliances.
Dependent variables and their operationalization
-
The study was developed in collaboration with the organization’s seniorleadership to examine its practices of alliance building,
Co-research design
-
-
www.newyorker.com www.newyorker.com
-
Cox, a classically trained British stage actor, has a “turn it on, turn it off” approach to acting, and his relationship with Strong recalls a famous story about Laurence Olivier working with Dustin Hoffman on the 1976 film “Marathon Man.” On learning that Hoffman had stayed up partying for three nights before a scene in which he had to appear sleep-deprived, Olivier said, “My dear boy, why don’t you try acting?”
Brian Cox
-
-
-
Foucault proclaimed in a footnote: “ Appearance of the index card and development of the human sciences: another invention little celebrated by historians. ”
from Foucault 1975, p. 363, n. 49; see Foucault 1966, pp. XV and passim for discourse analysis.
Is he talking here about the invention of the index card about the same time as the rise of the scientific method? With index cards one can directly compare and contrast two different ideas as if weighing them on a balance to see which carries more weight. Then the better idea can win while the lesser is discarded to the "scrap heap"?
-
- Nov 2021
-
Local file Local file
-
Grimmer & Stewart (2013) - Text as Data: The Promise and Pitfalls of Automatic ContentAnalysis Methods for Political Texts
- urn:x-pdf:5bb906b65a58358ba98fbc3ee72836f9
- https://is.gd/rBVTEI
-
-
scholarlykitchen.sspnet.org scholarlykitchen.sspnet.org
-
tack towards discovery, towards truth
This sailing metaphor is a useful one. Buffeted on all sides by distraction. Constantly shifting pressures, but generally going in the same direction. There maybe an ideal path forward, but the variables are too numerous to know where the ideal path lies.
-
-
countryoftheblind.blogspot.com countryoftheblind.blogspot.com
-
http://countryoftheblind.blogspot.com/2012/01/mnemonics-for-pronouncing-chinese.html
The Marilyn method is a means of creating associated characters and places to sounds/tones in Chinese for memorizing kanji.
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Lynne Kelly</span> in Foreign Languages – a call for opinions – Lynne Kelly (<time class='dt-published'>11/22/2021 12:44:51</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
drive.google.com drive.google.com
-
qualitative research method,
qualitative research method,
-
-
-
imited in itspractical utility
Limits of method
-
-
Local file Local file07Murray1
-
if the scholar wishes to understand the actions of people it is necessary forhim to see their objects as they see them’
A method of symbolic interactionism...
-
-
drive.google.com drive.google.com
-
a series of online meetings(through the Zoom platform) to complement the written stories, and guide
method
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
2. MethodFour scales of parenting styles and other psychosocial adjustment measures were administered to 118 gifted (38 males and 77 females) and 115 normal (36 males and 82 females) adolescents between 11 and 14 years old. The study was conducted in three academic grades (sixth, seventh and eighth and ninth) of students' junior high school in Amol city. In the gifted children's school to which they had been admitted, the gifted subjects were administered an IQ test by the Ministry of Education, while the normal subjects were administered the text from the normal children's school.
The method
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
wn oral cultures the sorting function canbe performedW for exampleW by integration into a narrative Sstorytelling orbardic poetryTY
The sorting function is also done by mental links from one space to another similar to the method of loci in Western culture. cross reference the idea of songlines
-
- Oct 2021
-
Local file Local fileUntitled1
-
Contingent valuation has become very prevalent in the last decade or so as method of assigning monetary values to non-market ‘goods and services so that those values can be included in a benefit cost or other policy analysis (Mitchell and Carson 1989).
Discusses contingent valuation as an alternative to Cost-benefit analysis because it allows for the assignment of monetary values to non-market goods and services, such as ecosystem services.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
rank correlation analysis, using Kendall's tau-c. For this purpose the three urban renewal status classes are assumed to constitute a scale. Evidence that such an assumption is reasonable is present in Tables 1 and 3.
Kendall's tau-c
a non-parametric measure of relationships between columns of ranked data. The Tau correlation coefficient returns a value of 0 to 1, where: 0 is no relationship, 1 is a perfect relationship. source: https://www.statisticshowto.com/kendalls-tau/)
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
@lakens: I’m interested to hear which COVID studies by psychologists you think have had a measurable positive effect on the world. E.g.… [Tweet]. https://twitter.com/lakens/status/1427856489990004741?s=20
-
-
www.science.org www.science.org
-
Mateus, J., Dan, J. M., Zhang, Z., Rydyznski Moderbacher, C., Lammers, M., Goodwin, B., Sette, A., Crotty, S., & Weiskopf, D. (n.d.). Low-dose mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine generates durable memory enhanced by cross-reactive T cells. Science, 0(0), eabj9853. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abj9853
-
- Sep 2021
-
Local file Local file
-
Institutional Post-Secondary Educational Data System (IPEDS) to identify a population of eligible universities.
Sampling of existing data - to ID universities likely to be involved in revitalization because of problematic urgan conditions + the orga capacity. Accredited Non-profit four-year, degree Urban pop >100K
FRAME 2 referenced the literature and cross referenced with Carnegie Classifiaction fo rCommunity engagement , Anchor Instition Task Force and Coalition of Urban Serving Univesities.
Self-identification by the universities. For accuracy.
22/65 response rate. Covering every region in US but under represented in the South and West. Even dispersal amount city pop size.
-
This study uses these frameworks to consider the normative question posed by the lit-erature: what are and/or what should anchor institutions be pursuing?
Their framework borrows on the concept of redistribution of university wealth talent etc to neighborhood
-
This study uses contemporary anchor institution frameworks
What is the contemporary anchor institutional framework??
-
-
-
three major categories of indicators.
Indicators: demographic trends - pop and race; 2) socioeconomic trends (Pov, media hh income; 3) housing trens (units, vacancy, tenure, values.
-
two subareas (Figure 1). The first is comprised of the 10 block groups located in the Sadie Tanner Mossell Alexander University of Pennsylvania Partnership School catchment area, more commonly referred to as the Penn Alexander School (PAS). These 10 block groups received the full array of WPI interventions, including access to enrollment in the Penn-sponsored neighborhood public school. The second subarea includes the portions of University City outside of the PAS catch-ment, defined as all block groups located in the University City boundary, exclusive of those groups also in the PAS catchment. These block groups received most of the WPI interventions, excluding access to the PAS
Catchment definition in ACS five-year And Outside the Catchment
-
five-year estimates from the ACS provide continuity in the socioeconomic indicators.
five-year ACS at block group level has a wide margin of error. The census blocks and tracts may not accurately reflect the actual catchment area of the school. (approximate)
-
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn)
Why UPenn as the point of examination? Previous research: cass on UPenn's WPI 0 West Philadelphia Initiatives. But NON have looked at the neighborhood impacts Etienne - Among most sign qual research - but narrow subset - not comprehensive - no stats or measures of broader NH Change.
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
The difficulties of estimating long Covid | David Spiegelhalter and Anthony Masters | The Guardian. (n.d.). Retrieved September 28, 2021, from https://www.theguardian.com/theobserver/commentisfree/2021/sep/26/the-difficulties-of-estimating-long-covid
-
-
Local file Local file
-
It draws upon material from a significant number of interviews that the author has conducted with this group in a variety of economic sectors and
-
-
Local file Local file
-
articipant observation and 30 interviews conducted over three yearsfrom 2011 until 2014 on and around the High Line with visitors, FHL staff and volunteersand local business owners.
Qualitative
-
-
Local file Local fileUntitled1
-
snowball sample of quali- tative researchers and sent them an informal survey, asking them about methods of qualitative data analysis they had been using, and inviting them to send specific examples, B. The Nature of This Book =» 3 exhibits, and suggestions. Many of the ideas from these 126 colleagues have been included.
Asked other researchers by informal survey about qual methods of analysis that they use and to send examples.
-
-
inst-fs-iad-prod.inscloudgate.net inst-fs-iad-prod.inscloudgate.net
-
Methodology
where the data came from
-
This survey looked at the 20 largestcities in America and focused on thetop 10 private firms in each (see Table1). T
Survey of 20 top US cities - 10p 10 private firms.
-
-
sakai.duke.edu sakai.duke.edu
-
Voice is lost
Can we, like Shepherds, tell a merry Tale? Stephen Duck, The Thresher's Tale (poem)
There's a link here to shepherds and a bardic tradition. In some sense, shepherds have lots of time to kill during the day and thus potentially tell stories. But they're also moving around their environment which also makes it easier for them to have used songline-like methods for attaching their memories to their environment.
How far back might this tradition go in our literate culture?
I also wonder at the influence of time on oral traditions as the result of this. Lynne Kelly describes calendrical devices in a variety of indigenous settings in Knowledge and Power in Prehistoric Societies for potential use in annual spaced repetition. What about the spaced repetition within daily cycles of regular work as described in this paper with respect to shepherds, fishing communities, and crofting?
The daily cycle of life may have been a part of the spaced repetition for memory.
How might we show this?
A quick example that comes to mind is the French children's song Alouette, Gentille Alouette which details how one kills, cleans, and dresses a chicken for cooking.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
Local file Local file
-
he term 'partic
Participatory research - make the research useful for the community of focus and involve them in its design and execution.
-
s. However, in regard to outcomes, I would add two more bench-marks, namely whether (v) the research enables both researchers and respondents to be more fully aware of the issues being investigated; (vi) the poor use the research findings for their own purpose
Outcomes criteria.
-
i) they (the poor) define the issues to be researched; (ii) they contribute to deciding how the topic should be researched; (iii) they participate in collecting the research material; (iv) they interpr
Criteria for judging if research benefits the vulnerable.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
While itis important to recognize the value of respondents’ time andcontributions to our research, inappropriate levels of remunera-tion can be either coercive or extractive (Paradis, 2000).
Renumeration of interviewees for time can be extractive.
-
remuneration. Weargue that it can be unethical to ask low-income workers tointerrupt their work to participate in research activities withoutcompensating them for their time.
Pay low-wage people for their time.
-
en exploitative in terms of the time andenergy requested of low-i
Design research based on community priorities so as to avoid exploitation and be authentically engaged
-
Ethnography as a method2 is suitable for use in doublyengaged social science research because of one important fea-ture: Researchers must embed themselves in the communitiesthey study, and this immersive approach gives scholars a better,clearer, and more in-depth view of the particular policy chal-lenges facing those populations.
Embedding research - immersive approach - good for descovering policy challenges.
-
Ethnography: A Doubly Engaged SocialScience Research Method Suited toVulnerable Populations?
Theoretic Context begins here.
-
-
finiteeyes.net finiteeyes.net
-
Bigger is better.
Research shows that high-resolution monitors make thinking easier. This also seems true of classrooms which use large posters and maps as teaching aids at lower grades.
Why don't we use these methods as we grow older?
When used in mnemonic traditions, one can use vast spaces to create memory palaces that become thinking vistas within the brain. How can we better leverage these effects while still maintaining the effectiveness of focused journeys?
-
Valorize motion, not sitting still.
I wonder how much of our genetic programming is based on centuries of evolution with humans moving around their landscapes and attaching their memories to them?
Within Lynne Kelly's thesis about stone circles, henges, etc. most of the locations have roads and entryways into them which require movement much less the idea of dancing and singing attached to memory performance as well.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
At the same time that we were trying to find some fruitful categories in which to group our inter- viewees, we were analysing issues or themes in the in- terviews.
iterative methodological process.
-
This attempt to make sense out of our information by placing the women into categories of ‘changers’ and ‘non-chang
Categorization of womens' roles ignored complexities of their situations.
-
However, we recognized a usually unarticulated tension between friendships and the goal of research.3 The researcher’s goal is always to gather information; thus the danger always exists of manipulating friendships to that end.
Mentions weakness of the method of the study - manipulation.
-
is As we pointed out, our commitment to minimizing the power differentials of the relationship in the research was further confounded when it came to the analysis. We found that we had to assume the role of the people with the power to define. The act of look- ing at interviews, summarizing another’s life, and placing it within a context is an act of objectification.
Weakness of method in upholding feminist ideals - the fundamental objectification of the participants during the analysis. What is objectification.. depersonalization of women, perpetuating historical harms?
-
er part of the attempt to deal with the subject-object problem was to try to establish some reciprocity by offering, at the end of the first inter- view, to tell the women something about ourselves if we had not done so earlier. Often we didn’t have to offer - it was a request made to us. We always responded as honestly as we could, talking about aspects of our lives that were similar to the things we had been discussing about the experience of the inter- viewee - our marriages, our children, our jobs, our parents. Often this meant also that our relationship was defined as something which existed beyond the limits of the interview situation. We formed friend- ships with many of the women in the study.
"Subject-object problem" addressed.
-
The women were interviewed in their own homes by one of the three of us as investigators. We had in- terviews with 65 women and followed a sub-group of 30 women for four to five years. We tried not to im- pose our ideas about what was important; our inten- tion was to let the concepts, explanations and inter- pretations of those participating in the study become the data we would analyse (Glazer and Strauss, 1973). While we tried to avoid determining what was to be considered in the content of consciousness, we were still aware of our own theoretical ideas. In our continual process of analysis we had to confront discrepancies between our ideas and interpretations and those of the women we interviewed. As the inter- view process proceeded, we decided to bring up cer- tain questions if they did not emerge in the inter- views.
65 women interviewed in their own home... HOW WERE THEY SELECTED?
-
e decided to look at the experiences of women who had been primarily mothers and wives and were attempting to move into the labor market.
Research sample: Women who were first mother's and wives entering the job market.
-
We chose repeated, unstructured, individual interviews as well as some group interviews.
Unstructed interviews of individuals and group interviews. (sampling structure???)
-
The following is an account of our research process and the problems we encountered. The feminist critique of social
Methods section begins here - an account of the research process.
-
n this analysis, we use a dialectical method, in order to arrive . . . ‘at adequate descrip- tion and analysis of how it actually works. Our methods cannot rest in procedures for deciding among different formalized “opinions” about the world’ (Smith, 1977). Rather, this is a method of ex- ploration and discovery, a way to begin to search for understandings that may contribute to the goals of liberation. E
Dialectical method? Qual research method aimed at finding the "truth"through interrogation of complex ideas, perspectives or arguments. Not about a hypothesis, rather, an attempt to generate a new understanding. Works with ideas rather than data. Applications: organizational processes, or to understand the philosophy of a movement. (WIKI)
In this case, it's about understanding the goals of liberation.
-
-
www.medrxiv.org www.medrxiv.org
-
Aleta, A., Blas-Laína, J. L., Anglés, G. T., & Moreno, Y. (2021). Unraveling the COVID-19 hospitalization dynamics in Spain using publicly available data (p. 2021.09.03.21263086). https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.09.03.21263086v1
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Bracher, J., Wolffram, D., Deuschel, J., Görgen, K., Ketterer, J. L., Ullrich, A., Abbott, S., Barbarossa, M. V., Bertsimas, D., Bhatia, S., Bodych, M., Bosse, N. I., Burgard, J. P., Castro, L., Fairchild, G., Fuhrmann, J., Funk, S., Gogolewski, K., Gu, Q., … Xu, F. T. (2021). A pre-registered short-term forecasting study of COVID-19 in Germany and Poland during the second wave. Nature Communications, 12(1), 5173. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25207-0
-
- Aug 2021
-
medievalbooks.nl medievalbooks.nl
-
Then there are the really exotic hands, which are turned into a visual feast. Fig. 7 shows and an arm that was turned into the body of a dragon, while the hands in Fig. 8 (which look like ladies’ gloves) are attached to the wrong location on the human body. These hands are not just meant to point out an important passage, they must also have been intended to bring a smile on the reader’s face.
Far beyond this, they're most likely used as mnemonic devices to associate the important information with a more memorable image for storing in one's memory palace.
-
-
forum.artofmemory.com forum.artofmemory.com
-
I'd start with the basics of 0-9 of the Major System and then introduce the method of loci. Once they've got those two basics down reasonably I'd expand their Major system up to 99 at a minimum.
The tougher part then is expanding your pedagogy to build these tools into the curriculum so that you're actively using them with your content.
You might appreciate the experience from Lynne Kelly here: https://www.lynnekelly.com.au/?p=4794. Her excellent book Memory Craft also has some interesting examples and stories for children including the use of what she calls rapscallions for use in multiplication tables, languages, and other educational applications. Her book also has a wealth of other methods and potential applications depending on the subjects you're teaching.
I'd love to hear your experiences as you progress with your class.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
commonplace tabulae effectively functioned as memory aids to beused in conjunction with other texts and the direct observation of objects.
The commonplace tabulae created by Linnaeus used spatial layout which also served as memory aids.
-
This connection between the topical space of book pages andcabinet interiors was reinforced by the very word, loculus, which Linnaeus generally used to referto cabinet compartments. This term was diminutive of locus, that is, the word employed by clas-sical orators to denote a ‘place’ in the mind reserved for related ideas or concepts. Early modernhumanists drew direct analogies between the label assigned to such places in the mind and theheads that they used to gloss the content of quotations and personal observations. This relationshipbetween the ‘space’ of the mind and space on the page facilitated the logic of commonplacing all
the way through the eighteenth century.
Direct linguistic analogies for commonplacing one's notes and the placing of ideas into the memory via the word locus.
-
-
forum.artofmemory.com forum.artofmemory.com
-
It was today as I was doing Chinese vocabulary that it struck me. I tried to add words using the locations from memory because it was cold, and I didn’t want to go out. I know each of the houses in the songline, but adding vocabulary is way way easier when I walk and do the learning in the physical space. I couldn’t do it from home.
I seem to recall reading anecdotes of aboriginal peoples who knew areas and water holes in places they'd never visited in their lives. I'm wondering how they may have encoded these in songlines for places they'd never been to and physically seen.
It would seem that it's better to use a physical space when you have access to it, but I don't think I have as much issue adding things to pre-existing palaces/songlines as Kelly describes here. I wonder how this works out for others?
-
I am beginning to think that the significant difference is that with songlines, learning is always done in the physical ‘memory palace’ which is constantly revisited. It can be recalled from memory, but is encoded in place. For me, that is way more effective, but I have aphantasia and very poor visualisation, so it may not be as big a factor for others. So recalling your childhood home can be a memory palace, but not a songline.
Lynne Kelly is correct here that we need better delineations of the words we're using here.
To some of us, we're taking historical methods and expanding them into larger super sets based on our personal experiences. I've read enough of Kelly's work and her personal experiences on her website (and that of many others) that I better understand the shorthand she uses when she describes pieces.
Even in the literature throughout the middle ages and the Renaissance we see this same sort of picking and choosing of methods in descriptions of various texts. Some will choose to focus on one or two keys, which seemed to work for them, but they'd leave out the others which means that subsequent generations would miss out on the lost bits and pieces.
Having a larger superset of methods to choose from as well as encouraging further explorations is certainly desired.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Anecdotal mention here of someone using sketchnotes or doodling as a mnemonic device.
Sketchnotes could be a means of implementing visual method of loci in one's note taking. Like creating a faux memory palace. Also somewhat similar, expecially in the case of the leaf doodle mentioned above, to the idea of drolleries, but in this case, they're not taking advantage of the memory's greater capacity of imagination to make things even more memorable for long term retention.
-
-
www.nwo.nl www.nwo.nl
-
Science is like competitive sports | NWO. (n.d.). Retrieved 11 August 2021, from https://www.nwo.nl/en/science-competitive-sports
-
-
-
https://www.reddit.com/r/commonplacebook/comments/jb8x3d/what_does_your_indexing_system_look_like/
Brief discussion of indexing systems for commonplace books. Locke's system is mentioned. Another person uses a clunky system at the bottom of pages to create threaded links.
Intriguingly, one person mentions visiting theirs often enough that they remember where things are. (spaced repetition with a bit of method of loci going on here)
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
McIntyre, L. (2021). Talking to science deniers and sceptics is not hopeless. Nature, 596(7871), 165–165. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-02152-y
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Murphy, C., Laurence, E., & Allard, A. (2021). Deep learning of contagion dynamics on complex networks. Nature Communications, 12(1), 4720. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24732-2
-
-
Local file Local file
-
After a long and influential career, commonplace books lost their influence in the late seventeenth century. Classical passages were relegated to the anti- quarian scholar; they no longer molded discourse and life. Men who sought confirmation in empirical evidence and scientific measurement had little use for commonplace books.
I believe that Earle Havens disputes the idea of the waning of the commonplace book after this.
I would draw issue with it as well. Perhaps it lost some ground in the classrooms of the youth, but Harvard was teaching the idea during Ralph Waldo Emerson's time during the 1800s. Then there's the rise of the Zettelkasten in Germany in the 1700s (and later officially in the 1900s).
Lichtenberg specifically mentions using his commonplace as a scientific tool for sharpening his ideas.
Can we find references to other commonplacers like Francis Bacon mentioning the use of them for science?
Tags
Annotators
-
- Jul 2021
-
-
https://ideas.ted.com/how-you-can-use-the-power-of-celebration-to-make-new-habits-stick/
B=MAT
behavior = motivation + ability + trigger
-
Psychologist BJ Fogg is the founder and director of the Behavior Design Lab at Stanford University — he’s coached over 40,000 people in his behavior change methods and influenced countless more. His Tiny Habits method states that a new behavior happens when three elements come together: motivation, ability and a prompt.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Inasaridze, K. (2021). Behavioral activation method for depression therapy [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/ge8s3
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Nan, X., Wang, Y., & Thier, K. (2021). Health Misinformation. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/jt3ur
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
‘Trust the science’ is the mantra of the Covid crisis – but what about human fallibility? | Margaret Simons | The Guardian. (n.d.). Retrieved July 27, 2021, from https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2021/jul/24/trust-the-science-is-the-mantra-of-the-covid-crisis-but-what-about-human-fallibility?CMP=Share_iOSApp_Other
-
-
developer.mozilla.org developer.mozilla.org
-
The difference between PUT and POST is that PUT is idempotent: calling it once or several times successively has the same effect (that is no side effect), whereas successive identical POST requests may have additional effects, akin to placing an order several times.
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
> I should have used "side-effect-free" instead of "idempotent" in my tweetsThe HTTP term is "safe method".
-
-
wordtothewise.com wordtothewise.com
-
So long as the filters are only using GET requests to pull down links, there’s nothing fundamentally wrong with them. It’s a basic (though oft-ignored) tenet of web development that GET requests should be idempotent; that is, they shouldn’t somehow change anything important on the server. That’s what POST is for. A lot of people ignore this for convenience’s sake, but this is just one way that you can get bitten. Anyone remember the Google Web Accelerator that came out a while ago, then promptly disappeared? It’d pre-fetch links on a page to speed up things if you clicked them later on. And if one of those links happened to delete something from a blog, or log you out… well, then you begin to see why GET shouldn’t change things. So yes, the perfect solution to this is a 2-step unsubscribe link: the first step takes to you a page with a form on it, and that form then POSTs something back that finalizes the unsubscribe request.
-
Idempotent just means that following a link twice has exactly the same effect on persistent state as clicking it once. It does not mean that following the link must not change state, just that after following it once, following it again must not change state further. There are good reasons to avoid GET requests for changing state, but that’s not what idempotent means.
https://hyp.is/JTNJ6uaLEeuFtzvtkXWaeA/developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/Safe/HTTP confirms this claim and states it even more clearly.
-
-
security.stackexchange.com security.stackexchange.com
-
Arguably any link that performs such an action via GET is fundamentally broken. A proper unsubscribe should direct to a page with a form that requires a POST submission. (Of course, in the real world, few things are proper.)
-
-
softwareengineering.stackexchange.com softwareengineering.stackexchange.com
-
This is not advice. A GET is defined in this way in the HTTP protocol. It is supposed to be idempotent and safe.
-
-
-
developer.mozilla.org developer.mozilla.org
-
An HTTP method is safe if it doesn't alter the state of the server. In other words, a method is safe if it leads to a read-only operation.
-
All safe methods are also idempotent, but not all idempotent methods are safe. For example, PUT and DELETE are both idempotent but unsafe.
-
-
developer.mozilla.org developer.mozilla.org
-
Each of them implements a different semantic, but some common features are shared by a group of them: e.g. a request method can be safe, idempotent, or cacheable.
Which ones are in each group?
Never mind. The answer is in the pages that are being linked to.
-
request method can be safe, idempotent, or cacheable.
-
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Park, A., & Velez, C. (2021). A mixed methods study of the psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on American life. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/tjz32
-
-
-
How a memory palace works When we’re learning something new, it requires less effort if we connect it to something we already know, such as a physical place. This is known as elaborative encoding. Once we need to remember the information, we can “walk” around the palace and “see” the various pieces. The idea is to give your memories something to hang on to. We are pretty terrible at remembering things, especially when these memories float freely in our heads. But our spatial memory is actually pretty decent, and when we give our memories some needed structure, we provide that missing order and context. For example, if you struggle to remember names, it can be helpful to link people you meet to names you already know. If you meet someone called Fred and your grandmother had a cat called Fred, you could connect the two. Creating a multisensory experience in your head is the other part of the trick. In this case, you could imagine the sound of Fred meowing loudly. To further aid in recall, the method of loci is most effective if we take advantage of the fact that it’s easiest to remember memorable things. Memory specialists typically recommend mentally placing information within a physical space in ways that are weird and unusual. The stranger the image, the better.
This notion of using spatial memory to encode other concepts - or even the P-A-O sytem where a 2 digit number encodes a person performing an action is an interesting idea for someone like me who forgets quite a bit.
-
-
www.jayeless.net www.jayeless.net
- Jun 2021
-
-
Simon DeDeo and Elizabeth Hobson on equality and hierarchy | Santa Fe Institute. (n.d.). Retrieved 30 June 2021, from https://www.santafe.edu/news-center/news/simon-dedeo-and-elizabeth-hobson-equality-and-hierarchy
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Soderberg, C. K., Errington, T. M., Schiavone, S. R., Bottesini, J., Thorn, F. S., Vazire, S., Esterling, K. M., & Nosek, B. A. (2021). Initial evidence of research quality of registered reports compared with the standard publishing model. Nature Human Behaviour, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01142-4
-
-
www.health.gov.au www.health.gov.au
-
Health, A. G. D. of. (2021, March 13). COVID-19 vaccines – Is it true? [Text]. Australian Government Department of Health; Australian Government Department of Health. https://www.health.gov.au/initiatives-and-programs/covid-19-vaccines/is-it-true
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Derrick, G. (2021). A year after lockdowns began, has research got any kinder? Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-01579-7
-
-
asaobinoue.blogspot.com asaobinoue.blogspot.com
-
We just cannot know all that life will throw at us, and if we want our grading contract to be fair and equitable for everyone, we need to reexamine it, reflect on how it has been working for each of us, and perhaps adjust it.
This idea of re-evaluating at regular time points can be a very useful and powerful tool in more areas than just writing.
Society as a whole needs to look carefully at where it is do do this same sort of readjustment as well.
It's the same sort of negative feedback mechanism which is at work in the scientific method and constantly improving the state-of-the art.
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
WHO voices concerns over Sputnik V Covid vaccine plant. (2021, June 23). The Guardian. http://www.theguardian.com/society/2021/jun/23/who-voices-concerns-over-sputnik-v-covid-vaccine-plant
-
-
blogs.lse.ac.uk blogs.lse.ac.uk
-
Lynne Kelly's observation that oral cultures revised useful knowledge into their memories appears to me to be a simple precursor to annotation and the idea of the scientific method all in one...
-
Scholars are likely familiar with the so-called “Great Conversation,” or the idea in Western thought that we collectively participate in an iterative process of knowledge production through reference, review, and refinement. As our conversation continues over time, an ever-expanding network of annotation–through notation, citation, links, and data–traces an interconnected lineage of ideas and insight.
Again, Dr. Lynne Kelly discusses this sort of process in non-Western and primarily oral cultures as well. Songlines has some interesting discussion of this in the Australian aboriginal cultures.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Yet even thisdecline is followed by an unexpected resurgence in mnemonics in the 1800s, when Connors claimsthat writing was replacing speaking in school settings (127).
I would question this statement, as annotated separately in this article. I have a feeling that the mnemonic tradition into the 1800's was more heavily influenced by the rise of the idea of the major system and not so much by the memory palace or the method of loci. This definitely seems to be the case in the United States based on my readings.
-
Ong puts it this way:“Ramus can adopt memory intodialectic because his entire topically conceived logic is itself a system of local memory”(Ramus280).However, it is a simplified systemunlike the classical one: The ancient precepts about images and theirfacilitation of invention have been dropped.
What is gained and lost in the Ramist tradition versus the method of loci?
There is some simplicity to be sure and structure/organization aid in the structured memory.
We lose the addition work, creativity, and invention. We also loose some of the interest that students might have. I recently read something to the effect that we always seem to make education boring and dull. (cross reference this, which I haven't read: https://daily.jstor.org/why-school-is-boring/)
How does this interact with Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi's idea of flow? Does Ramism beat out the fun of flow?
How also, is this similar to Kelly's idea of the third archive as a means of bringing these all back together?
-
Ramist method does away withimaginesand architecturalloci, replacing them with asystem of abstract, logical arrangement.
Similar to Yates' theory.
-
Memory treatises published in Europe, by half-century.
In looking at this, I immediately wonder about the nature of the treatises. I would suspect there's a slow decline of treatises on the method of loci while the 1800's sees an increase of those writing about the major system and which I've found generally aren't aware of the method of loci or earlier methods.
-
Todate, however, no scholar has taken advantage of bibliographic resources to verify whether or notmemory treatises did in fact decline in England in the latter sixteenth and early seventeenthcenturies, a period that coincides with the continuing influence of iconoclasm and the risinginfluence of English Ramism. In this article I provide such bibliographic evidence, demonstratingthat the publication of memory treatises abated in England following Henry VIII’s reforms andduring the English Civil War
When reading Yates and thinking about the disappearance of these traditions in the West, I've wanted to delve into this exact question!
Glad to see the work has already been done for me.
-
- May 2021
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Agarwal, A. (2021). Ripple Effect of a Pandemic: Analysis of the Psychological Stress Landscape during COVID19. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/dm5x2
-
-
www.eventbrite.com www.eventbrite.com
-
Data Collection and Integration to Enhance Public Health Registration, Thu, Jun 10, 2021 at 1:00 PM | Eventbrite. (n.d.). Retrieved May 28, 2021, from https://www.eventbrite.com/e/data-collection-and-integration-to-enhance-public-health-registration-156146370999
-
-
carmattu.com carmattu.com
-
Ezgi. (n.d.). SIOP/CARMA Open Science Virtual Summer Series. Consortium for the Advancement of Research Methods and Analysis (CARMA). Retrieved May 28, 2021, from https://carmattu.com/siop-carma-open-science-virtual-summer-series/
-
-
journals.plos.org journals.plos.org
-
-
This study reveals several subtle, but important advantages for teaching of the Australian Aboriginal memorization method as compared to the more widely known memory palace technique. In particular the Australian Aboriginal method seems better suited to teaching in a single, relatively short instruction period. This is evidenced by the increased probability of obtaining complete recall of the target list after a 20 minute teaching period, and the pronounced improvement in correct sequencing of information which was observed compared to the memory palace approach.
Here's the tl;dr version of the study:
Australian Aboriginal memorization methods >> Western method of loci methods
-
Both methods of loci improved upon the already high level of recall among medical students relative to those who received no memory training.
I'm saddened to see the erasure of the Australian Aboriginal approach (possibly better termed Songlines or Dreaming for specificity) here only to have it lumped into the Western method. This is worse when their general results show the Australian approach to be significantly better.
This may be due to over-familiarity with the techniques which are broadly similar, but for rigor and respect they should remain separate in this paper.
-
A full description of the classical memory palace technique can be found in [12].
A full one, but not necessarily a good one, particularly for beginners.
-
-
forum.artofmemory.com forum.artofmemory.com
-
As someone who knows both methods and has likely practiced them in reasonable depth, I'm curious what Dr. @LynneKelly thinks. I'd love to see this same study done to include song, dance, painting, etc. to expand the potential effects.
If nothing else, it's good to see some positive research on the methods which will hopefully draw more attention to the pedagogy and classroom use.
Dr. Reser said the Monash School of Rural Health is considering incorporating these memory tools into the medical curriculum once teaching returns to a post-COVID normal. “This year we hope to offer this to students as a way to not only facilitate their learning but to reduce the stress associated with a course that requires a lot of rote learning,” he said. —https://scitechdaily.com/ancient-australian-aboriginal-memory-tool-superior-to-memory-palace-learning-technique/
-
-
scitechdaily.com scitechdaily.com
-
Great news on Memory. Was song and art used too?
-
-
brainbaking.com brainbaking.com
-
My wife taught me to add some color after some pages are filled and the more I do that, the more I like browsing through the journal. Watercolor is still too heavy for most notebooks and I don’t bother to bring colored pencils on location. That’s a relaxing activity to do at home.
Color also adds creativity and additional loci to one's pages which also can help to make them more memorable.
-
-
newrepublic.com newrepublic.com
-
Long before Vannevar Bush, Francis Bacon cited Seneca to describe a similar ambition for his scientific method, which he hoped would “abridge the infinity of individual experience ... and remedy the complaint of vita brevis, ars longa.”
-
Blair’s previous work demonstrated that the practices of literary reading and writing were central to the rise of scientific method. Focusing on the lawyer and scientist Jean Bodin in the sixteenth century, she meticulously examined how Bodin collected commonplace reading notes and then stored and analyzed them as scientific evidence.
I really do need to create a historical timeline for commonplace books already.
Georg Christoph Lichtenberg also did this in the late 1700's and became famous for it after his death and the publication of his Waste Books. Worth looking into who his influences may have been?
-
-
doctorow.medium.com doctorow.medium.com
-
Cringing at your own memories does no one any good. On the other hand, systematically reviewing your older work to find the patterns in where you got it wrong (and right!) is hugely beneficial — it’s a useful process of introspection that makes it easier to spot and avoid your own pitfalls.
This idea is far from new and is roughly what Georg Christoph Lichtenberg was doing with the science portions of his Waste Books in the late 1700's where he was running experiments, noting wins, losses, and making progress using the scientific method.
-
-
www.learnbayesstats.com www.learnbayesstats.com
-
The ‘Learning Bayesian Statistics’ podcast. (n.d.). Retrieved 13 May 2021, from https://www.learnbayesstats.com
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
The scrapbooks reveal a critical and analytical way of thinking and emphasis on experimental evidence in physics, through which he became one of the early founders and advocates of modern scientific methodology. The more experience and experiments are accumulated during the exploration of nature, the more faltering its theories become. It is always good though not to abandon them instantly. For every hypothesis which used to be good at least serves the purpose of duly summarizing and keeping all phenomena until its own time. One should lay down the conflicting experience separately, until it has accumulated sufficiently to justify the efforts necessary to edifice a new theory. (Lichtenberg: scrapbook JII/1602)
Georg Christoph Lichtenberg used his notebooks as thinking tools with respect to scientific methodology.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Daly, M., & Robinson, E. (2020). Psychological distress and adaptation to the COVID-19 crisis in the United States [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/79f5v
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
(20) ReconfigBehSci on Twitter: ‘RT @martikagv: New book “Urban Informatics”, #OpenAccess https://t.co/wp45uWU9Mi Edited by @jmichaelbatty @CUHKofficial Michael Goodchild,…’ / Twitter. (n.d.). Retrieved 21 April 2021, from https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1384411081456582662
-
-
open.lnu.se open.lnu.se
-
Niemeyer, H., Aert, R. C. M. van, Schmid, S., Uelsmann, D., Knaevelsrud, C., & Schulte-Herbrueggen, O. (2020). Publication Bias in Meta-Analyses of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Interventions. Meta-Psychology, 4. https://doi.org/10.15626/MP.2018.884
-
-
-
This approach also splits email development for modern email clients and older clients in two. You can use Safari/Chrome to test and develop modern techniques for WebKit-supported clients while using Firefox for your baseline experience for older clients like Outlook.
-
-
www.mcgill.ca www.mcgill.ca
-
Epidemiology 101 for Journalists. (n.d.). Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Occupational Health. Retrieved 23 February 2021, from https://www.mcgill.ca/epi-biostat-occh/epidemiology-101-journalists
-
- Apr 2021
-
www.bmj.com www.bmj.com
-
Evaluating computerised health information systems: hard lessons still to be learnt
The article used a Qualitative study design method as it only highlights the problems within the health system in South Africa which is posing threat to the use of health information system in our healthcare centres.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.thelancet.com www.thelancet.com
-
Ten scientific reasons in support of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2—The Lancet. (n.d.). Retrieved April 19, 2021, from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)00869-2/fulltext
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
When Should You Start a New Note?
note taking suggestions
-
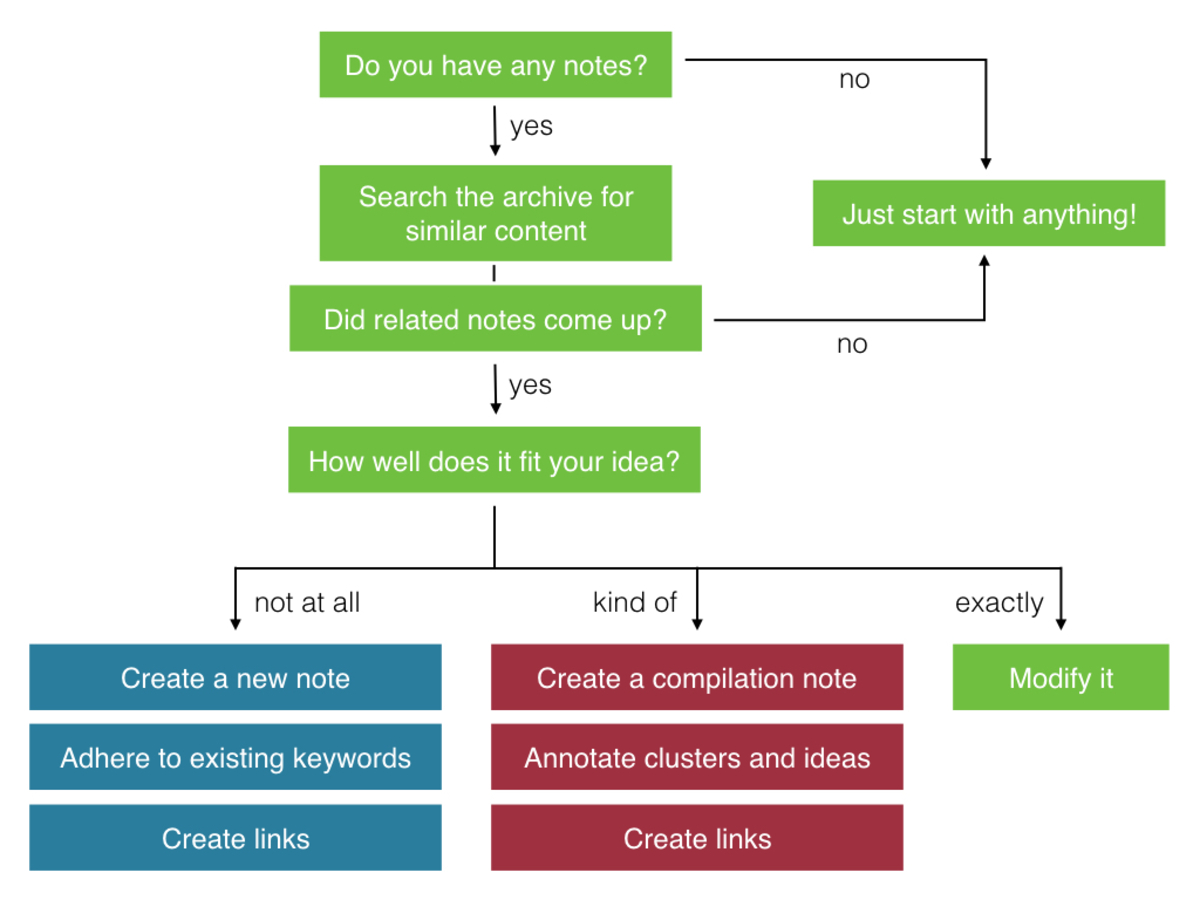
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
Goal, is to figure out if I can do this with Notion.

The zettel is the smallest unit, a note entered into the system. It requires a unique identifier, the body/content for the note, and footer/references.



Actively include citations to other Zettels.

Two types of structures depicted graphically

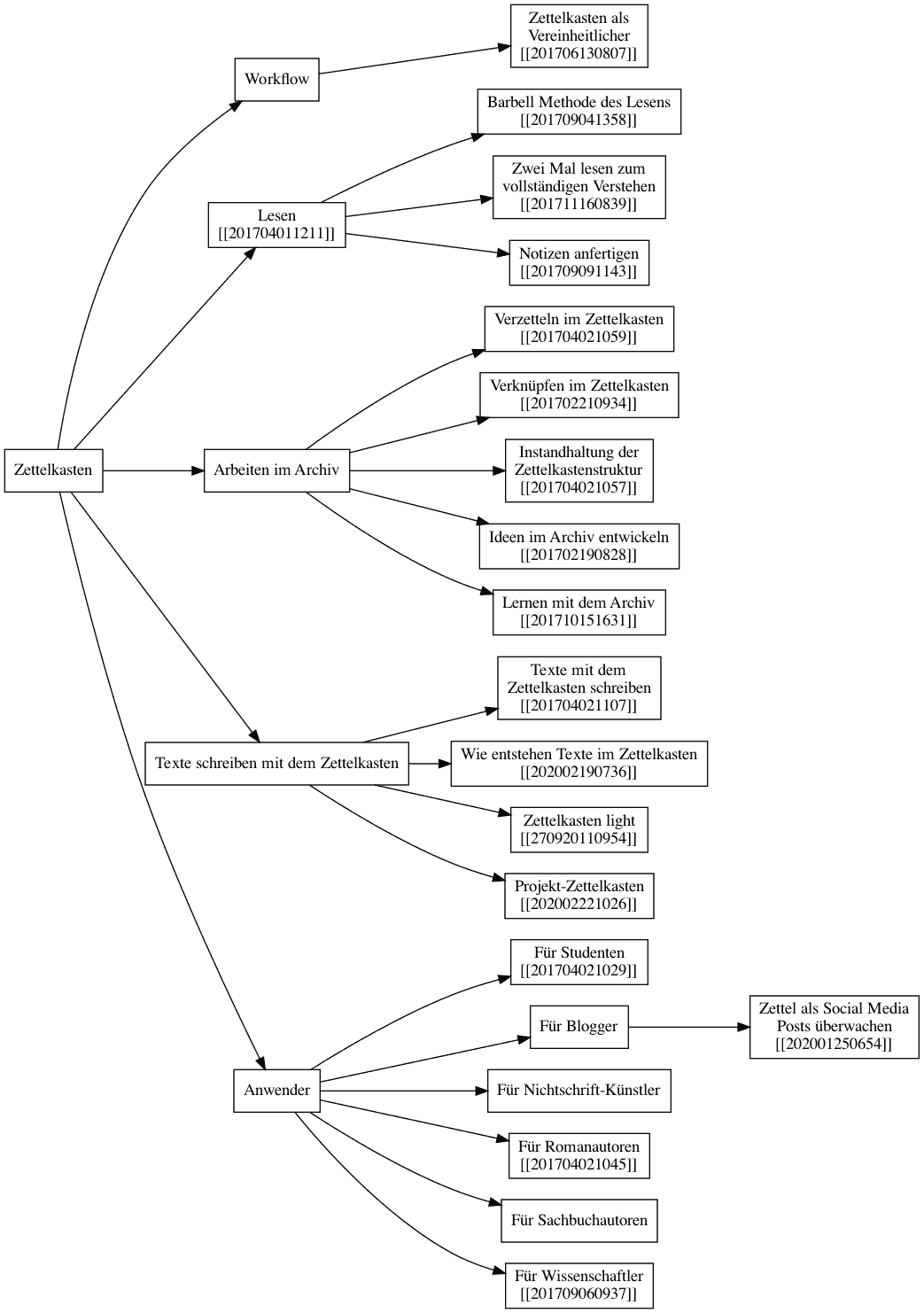
-
To make the most of a connection, always state explicitly why you made it. This is the link context. An example link context looks like this:
So ACTIVELY include the equivalent of citations to other ZETTELS.
-
The most important aspect of the body of the Zettel is that you write it in your own words. There is nothing wrong with capturing a verbatim quote on top. But one of the core rules to make the Zettelkasten work for you is to use your own words, instead of just copying and pasting something you believe is useful or insightful. This forces you to at least create a different version of it, your own version. This is one of the steps that lead to increased understanding of the material, and it improves recall of the information you process. Your Zettelkasten will truly be your own if its content is yours and not just a bunch of thoughts of other people.
If you enter the content in your own words you take active ownership. Also, as a grad student, you don't want the extra work of not only finding the reference you'd like to allude to but additionally having to rephrase it at the time of writing a paper or book.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-