Let 𝑧=𝑓(𝑥,𝑦)=−𝑥2−12𝑦2+𝑥𝑦+10
When you move by infinitely small amount, you are moving through a straight line. Also f_x(2,1) and f_y(2,1) are different because they are slopes and they are in different direction.
f(2,1) is the total slope.
Let 𝑧=𝑓(𝑥,𝑦)=−𝑥2−12𝑦2+𝑥𝑦+10
When you move by infinitely small amount, you are moving through a straight line. Also f_x(2,1) and f_y(2,1) are different because they are slopes and they are in different direction.
f(2,1) is the total slope.
Crystal lattices can be classified by their translational and rotational symmetry.
Translational symmetry means, if you move say two units distance in x direction, you would get the same arrangement as you got when you started. Rotational symmetry is pretty much self explanatory.
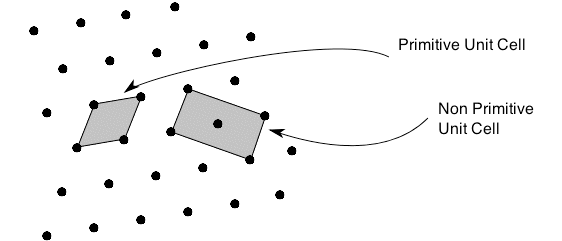
Of course this definition means that there are an infinite number of possible unit cells. So, in general, the unit cell is chosen such that it is the smallest unit cell that reflects the symmetry of the structure. There are two distinct types of unit cell: primitive and non-primitive. Primitive unit cells contain only one lattice point, which is made up from the lattice points at each of the corners. Non-primitive unit cells contain additional lattice points, either on a face of the unit cell or within the unit cell, and so have more than one lattice point per unit cell. It is often the case that a primitive unit cell will not reflect the symmetry of the crystal structure. A suitable non-primitive unit cell will be picked in such cases.
Primitive vs Non-Primitive Unit cell
Quartz crystals are birefringent , so they exhibit optical anisotropy. Consider plane polarised light passing through a birefringent crystal. Inside the crystal, the light is split into two rays travelling along permitted vibration directions (p.v.d.s). The two rays are subject to different refractive indices, so the light travelling along each p.v.d. reaches the opposite side of the crystal at a different time. When the two rays recombine, there is a phase difference between the two rays that causes the polarisation state of the transmitted light to be different from that of the incident light.
birefringent means having two different refractive indices. Anisotropy means the properties are direction dependent.
Gypsum can be cleaved along particular crystallographic planes using a razor blade. The bonding perpendicular to these cleavage planes is weaker than that in other directions, and hence the crystal breaks preferentially along these planes. Quartz and diamond do not have such distinct cleavage planes, and so cleaving these crystals requires much more effort and care.
I didn't know that. Single Crystals
A polycrystalline solid or polycrystal is comprised of many individual grains or crystallites. Each grain can be thought of as a single crystal, within which the atomic structure has long-range order. In an isotropic polycrystalline solid, there is no relationship between neighbouring grains. Therefore, on a large enough length scale, there is no periodicity across a polycrystalline sample
We consider the short ordered segments of poly crystalline solids as grains or crystallites.
Amorphous solids have the tendency to flow like liquid, but it is a very slow process. Therefore, sometimes they are called pseudo solids or super cooled liquids.
Amorphous solids can be also called pseudo solids or super cooled liquids
The faces of crystals can intersect at right angles, as in galena (PbS) and pyrite (FeS2), or at other angles, as in quartz.(Right) Cleavage surfaces of an amorphous solid. Obsidian, a volcanic glass with the same chemical composition as granite (typically KAlSi3O8), tends to have curved, irregular surfaces when cleaved.
Does this mean, they can only interject at right angles to each other. Like the diagram printed in Kittel's book, 
Amorphous solids have two characteristic properties. When cleaved or broken, they produce fragments with irregular, often curved surfaces; and they have poorly defined patterns when exposed to x-rays because their components are not arranged in a regular array. An amorphous, translucent solid is called a glass.
is called a glass? I mean, are we not talking about the glass made from Silica oxides anymore?