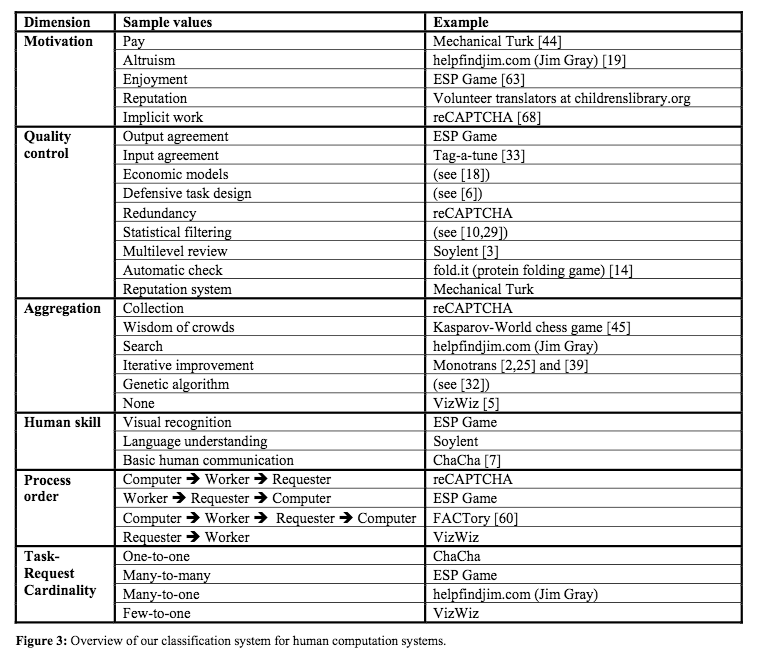
Another way to use a classification system is to consider if there are other possible values that could be used for a given dimension.
Future direction: Identify additional sample values and examples in the literature or in situ to expand the options within each dimension.