the wavelength emitted by the source
This means, as emitted by the source if it were in a stationary laboratory.
\(\Delta \lambda=\left(\lambda_{lab}-\lambda_{observed}\right)\)
So \(\frac{\Delta \lambda}{\lambda}\) is the percent change in wavelength.
Similar expressions exist for frequencies \(f_{lab}\) and \(f_{observer}\)
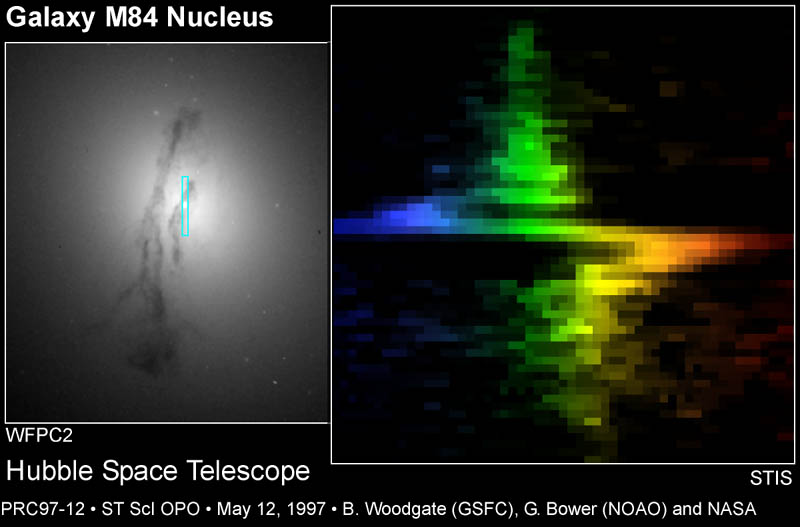












 Cf.,
Cf., 
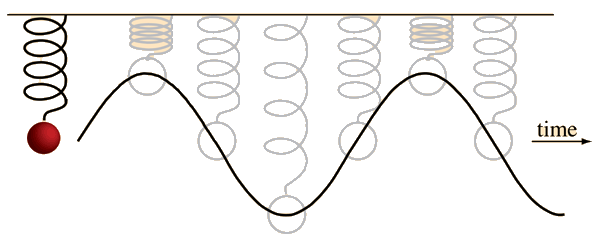 That is, what is simple to learn about spring/mass systems becomes widely applicable in other oscillatory systems like a beating heart, a particle inside an atom's nucleus, a light wave, a tsunami etc.
That is, what is simple to learn about spring/mass systems becomes widely applicable in other oscillatory systems like a beating heart, a particle inside an atom's nucleus, a light wave, a tsunami etc. knowing that a regular sinus rhythm is a very specific oscillatory system, whereas fibrillation, tachycardia etc. are NOT oscillatory. Cf., G.Koulaouzidis, S. Das et al. "Prompt and accurate diagnosis of ventricular arrhythmias with a novel index based on phase space reconstruction of ECG" International Journal of Cardiology, 2015-03-01, Volume 182, Pages 38-43. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.12.067
knowing that a regular sinus rhythm is a very specific oscillatory system, whereas fibrillation, tachycardia etc. are NOT oscillatory. Cf., G.Koulaouzidis, S. Das et al. "Prompt and accurate diagnosis of ventricular arrhythmias with a novel index based on phase space reconstruction of ECG" International Journal of Cardiology, 2015-03-01, Volume 182, Pages 38-43. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.12.067