incomplete dominance


English — incomplete dominance (thorough explanation)
1) What incomplete dominance means (core idea)
Incomplete dominance is an inheritance pattern in which neither allele is completely dominant, so the heterozygous phenotype is an intermediate (blended) form of the two homozygous phenotypes.
Incomplete dominance = blending of traits in heterozygotes
2) How incomplete dominance works
- Two different alleles affect the trait
- In a heterozygous individual, both alleles partially influence the outcome
- The result looks like a mix, not one trait hiding the other
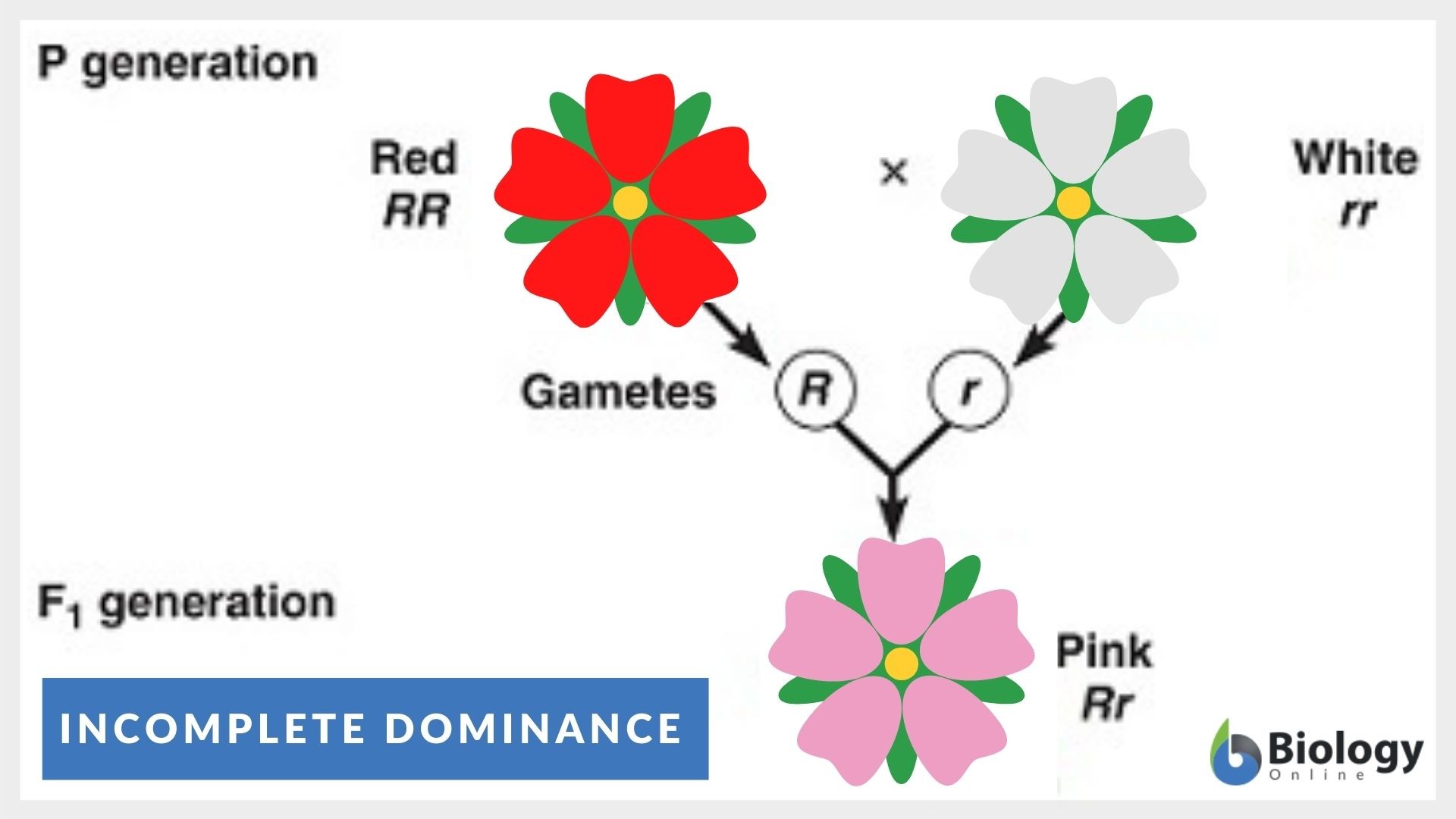
3) Classic example (Science 10 favorite): flower color
Let:
- R = red flowers
- W = white flowers
Cross: RR × WW
Offspring:
- RW → pink flowers
📌 Pink is not a new allele; it’s the intermediate phenotype.
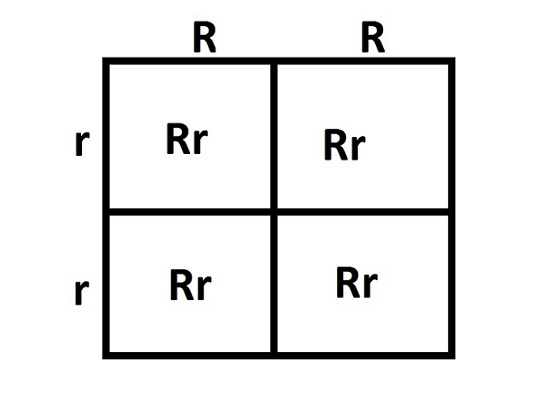
4) Incomplete dominance in Punnett squares
Parents: RW × RW
Possible offspring:
- RR → red
- RW → pink
- RW → pink
- WW → white
Phenotype ratio: 1 red : 2 pink : 1 white
📌 Notice: phenotype ratio = genotype ratio in incomplete dominance.
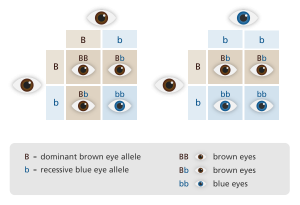
5) Incomplete dominance vs other patterns (very important)
| Pattern | Heterozygous result | Example | | ------------------------ | ------------------------- | ------------------ | | Dominant–recessive | Dominant trait only | Brown eyes | | Incomplete dominance | Blended trait | Red × white → pink | | Codominance | Both traits fully visible | AB blood type |
6) Why incomplete dominance matters
Incomplete dominance:
- Explains traits that don’t follow simple dominance
- Increases visible variation in populations
- Is common in plants, animals, and humans (for some traits)
One-sentence exam summary
Incomplete dominance occurs when heterozygous individuals show an intermediate, blended phenotype.
中文 — incomplete dominance(不完全显性) 详细解释
1) 什么是不完全显性(核心概念)
不完全显性是指: 两个等位基因中没有一个完全显性,杂合体表现为中间型性状。
不完全显性 = 性状混合表现
2) 不完全显性的表现特点
- 显性不能完全压制另一等位基因
- 杂合体表现为中间状态
- 性状不是“要么这个,要么那个”
3) 经典例子(考试常考)
花的颜色:
- 红花(RR)
- 白花(WW)
杂交后:
- RW → 粉红色花
📌 粉红不是新基因,而是红和白的中间表现。
4) 潘尼特方格中的不完全显性
父母:RW × RW
后代比例:
- 1 红(RR)
- 2 粉(RW)
- 1 白(WW)
👉 表现型比例 = 基因型比例
5) 不完全显性 vs 共显性(重点区分)
| 遗传方式 | 表现结果 | | ----- | ---------- | | 不完全显性 | 中间型(混合) | | 共显性 | 两种性状同时清楚出现 |
一句话考试版总结
不完全显性指杂合体表现为两种性状的中间型。
如果你愿意,我可以把 dominant / recessive / incomplete dominance / codominance 整理成 Science 10 中英对照对比表、潘尼特方格练习或互动闪卡,非常适合系统复习与教学。
不完全显性(incomplete dominance) EN: A condition in which neither allele for a gene completely conceals the presence of the other, resulting in an intermediate expression of a trait. Example: In four o’clock plants, red flowers crossed with white flowers produce pink offspring, an intermediate phenotype. 中文:两种等位基因互不完全掩盖对方,从而产生介于双亲之间的中间型表现。 例子:紫茉莉红花与白花杂交产生粉红花,就是不完全显性的例子。