- Dec 2020
-
-
Biology h
Test
-
- Nov 2020
-
dickinsonstate.smartcatalogiq.com dickinsonstate.smartcatalogiq.com
-
For all degree programs within the Department of Natural Sciences, no on-line classes will be accepted in place of face- to-face courses with laboratories. Students can file for an exception with the Department Chair if it can be demonstrated that all 3 of the following conditions have been met: The required science class was not offered at least TWO times over the course of a standard eight-semester college experience. The student can provide documentation of the conflict(s) that prevented enrollment in the face-to-face course when it was offered. The student can provide evidence that they have met with and followed the recommendations of their appropriate, assigned post-freshman advisor prior to the required course offerings.
Online Course Policy
-
-
catalog.csc.edu catalog.csc.edu
-
BIOL 138& 138LGENERAL BIOLOGY: BOTANYand GENERAL BIOLOGY: BOTANY LABORATORY4 BIOL 139& 139LGENERAL BIOLOGY: ZOOLOGYand GENERAL BIOLOGY: ZOOLOGY LABORATORY4
At Chadron State: BIOL 139 are called General Biology. They serve the same purpose as Gen Biol I, II, Zoology, and Botany at DSU
-
-
und-public.courseleaf.com und-public.courseleaf.com
-
BIOL 315. Genetics. 3 Credits. An introduction to genetics, with emphasis on classical genetic analysis and the biochemistry of gene transmission, expression and regulation. Prerequisites: BIOL 150, BIOL 150L, BIOL 151, and BIOL 151L or an equivalent approved by the department. F.
UND genetics does not have a lab. They don't even offer a lab.
-
-
dickinsonstate.smartcatalogiq.com dickinsonstate.smartcatalogiq.com
-
Students who wish to challenge the rejection of credit for course equivalency, general education, or program credit may request an additional review by the Office of Academic Records or the appropriate department chair. Students requesting an additional review are responsible for providing supporting evidence.
-
- Sep 2020
-
onlinelibrary.wiley.com onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
if turnover is fast the accumulation of respiring biomass is low and respiration depends primarily on photosynthesis; while if turnover is slow the accumulation of respiring biomass is high and respiration depends primarily on biomass
For small plants, respiration rates depend upon photosynthesis. In larger plants, respiration is dependent upon biomass.
Idea is that respiration rates are controlled by photosynthates.
-
- Dec 2019
-
dickinsonstate.smartcatalogiq.com dickinsonstate.smartcatalogiq.com
-
Students are required to take one additional course of three or more credits from the General Education curriculum
Caution: Three Credits in Citizenship List D cannot be used to satisfy this requirement.
-
-
-
Institutional Specific (must be chosen from one of the following four categories: communication, social sciences, arts and humanities, and/or mathematics/science & technology)
- 3 or more credits more in General Education Elective
- 3 Credits in Citizenship, global perspectives.
NB: These general education credits must be from Citizenship Lists A, B, and C, or Critical and Creative Thinking Lists A, B, C, D, and E.
Citizenship list D cannot be used to satisfy the institutional specific requirements.
-
Mathematics, Science & Technology
- 3 Credits in Citizenship, Technology List
- 4 Credits in Critical and Creative Thinking, Natural Sciences List
- 3 Credits in Critical and Creative Thinking, Mathematics List
-
Arts & Humanities
- 3 Credits of Critical and Creative Thinking Creative, Expressions List
- 3 Credits of Critical and Creative Thinking, Literature List.
-
Communications
9 DSU Credits in Communication Group
-
Social Sciences
- 3 Credits in Citizenship; Human Behavior and Governance.List
- 3 Credits in Critical and Creative Thinking, Social Sciences List
-
403.7 Common General Education Requirement and Transfer of General Education Credits
-
- Aug 2019
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
A stomatal safety-efficiency trade-off constrains responses to leaf dehydration
Possibly a good paper for undergraduates.
-
-
help.photosynq.org help.photosynq.org
-
Accessing a Single Value from Variables
@n for a single variable2n<array><value>
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
help.photosynq.org help.photosynq.org
-
Photosystem I that is ready to accept electrons
-
One or all of the acceptors of Photosystem I have no electron(s).
-
All the acceptor side of Photosystem I are occupied by electrons and cannot accept any more electrons. Kanazawa et al. Front. Plant Sci. (2017)
-
Active Photosystem I that is operational to receive/pass electrons.
-
-
www.frontiersin.org www.frontiersin.org
-
PSIox i
PhotosynQ
-
PSI over-reduced (PSIor),
PhotosynQ
-
PSIopen
PhotosynQ
-
The total active PSI centers (PSIact) in the leaves under a certain condition is proportional to PM, the maximal absorption difference between dark and the second saturation pulse taken after application of far red light to oxidize electron carriers. It was assumed that all PSI centers in dark adapted material (before light treatments) were active, so the all parameters were normalized to the Po, PM value measured in dark adapted leaves prior to illumination with a full complement of active PSI centers. Thus, for example, the fraction of active PSI, PSIact is expressed as the ratio of PM/P0, where P0, is the PM value measured in dark adapted leaves prior to illumination with a full complement of active PSI centers.
PhotosynQ
-
- May 2019
-
science.halleyhosting.com science.halleyhosting.com
-
Variety collinsii: Stem leaves with heart-shaped bases that often clasp the stem. Petals less than 7 mm long. Pedicels bent sharply downwards at their base. The siliques are more or less straight. Found from Washington to Alberta, Wyoming and east through he Dakotas and Manitoba to Quebec.
Identification features of B. collinsii
-
- Apr 2019
-
craigwhippo.github.io craigwhippo.github.io
-
Grading Rubric
A total of 16 points is possible, but students only need to earn 12 points to earn a perfect score. This gives students some flexibility in deciding how they want to go about annotating the text.
-
- Feb 2019
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
100
~ 2mg
-
- Jan 2019
-
www.plantphysiol.org www.plantphysiol.org
-
phyB
-
- Nov 2018
-
photosynq.org photosynq.org
-
"protocolrepeats"
should be "
set_repeats"
-
-
photosynq.org photosynq.org
-
"protocols": 12,
Repeat the protocols 12 times
-
"protocols_delay": 300000
5 minute delay between measurements.
-
-
photosynq.org photosynq.org
-
300000
5 minutes
-
"environmental": [
-
-
photosynq.org photosynq.org
-
e "averages",
-
-
photosynq.org photosynq.org
-
wiki on github
Dead link
-
-
www.cell.com www.cell.comAlgae1
-
Such losses have also occurred in embryophytes, adding to the complexity of trying to define these lineages in functional terms. While oxygenic photosynthesis is monophyletic, the eukaryotic algae are polyphyletic.
What are examples?
-
- Oct 2018
-
www.jstor.org www.jstor.org
-
10-pin point
-
-
bio-protocol.org bio-protocol.org
-
0.3 mM CaCl2
33 mg/L
-
-
-
The Gibberellin Signalling Pathway

-
The Brassinosteroid Perception Pathway

-
The Auxin Response Pathway
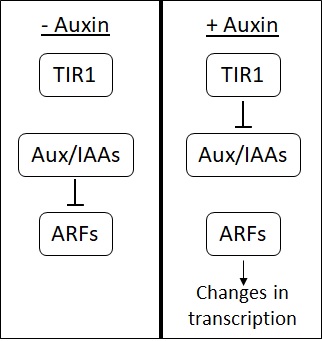
-
Figure 1Examples of auxin, gibberellin or brassinosteroid involvement in growth phenomena across the plant life cycle.

Justify this figure:
-
only cytokinin, auxin, gibberellins and brassinosteroids are considered to be essential for growth.
Brassinosteroids & Gibberllins: Cell Elongation Cytokinins: Cell division Auxin: Cell elongation & Cell Division
-
abscisic acid, auxin, brassinosteroids, cytokinins, ethylene, gibberellins, jasmonates and strigolactones
-
-
www.plantphysiol.org www.plantphysiol.org
-
To demonstrate that P deficiency in plants is highly reversible and that disruptions in electron transport can be recovered rapidly, we infiltrated P-deficient leaf segments with a Pi-containing solution by immersion for 60 min.
Good idea.
-
The objective of this study was to develop a comprehensive biological model of how photosynthesis is affected by P deficiency under physiologically relevant conditions.
-
This obviously low P use efficiency is unsustainable.
Phosphate deficient soils are common. Fertilization with phosphate results in eutrophication
-
Multiple sets of barley plants (Hordeum vulgare ‘Quench’) were hydroponically cultivated using three different treatments:
Why barley?
-
It has been estimated that 30% of the world’s arable soils are deficient in P and require P fertilization to improve yields (MacDonald et al., 2011).

Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
To test this hypothesis we conducted a detailed study on the root architecture of these crops using SimRoot (Postma and Lynch, 2011a, b), a functional–structural plant model, and estimated competition for nitrate, potassium and phosphorus among roots of maize, bean and squash plants grown in monoculture or polyculture.
-
Maize, bean and squash differ strongly in root architecture (Weaver and Bruner, 1927) and we hypothesize that these differences in root architecture allow these crops to explore different soil domains with variable intensity
-
Root architecture, however, has been overlooked in intercropping studies despite the recognition that root placement may be more important for competition than root physiology (Schwinning and Weiner, 1998).
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
The presence of highly pitted lignified tissue in the mesophyll of gymnosperms leaves has been formally noted in the conifer family Podocarpaceae and the cycad genus Cycas (Griffith, 1957; Hu and Yao, 1981). We found that similar tissues are present in conifers from all families including Sciadopitys and Amentotaxus (T. Brodribb, unpublished data) and in each case they were associated with leaf widths in excess of those achievable with unmodified mesophyll tissue (Fig. 1B). Indeed it appears that terrestrial plants have adopted two different systems to overcome the intrinsically low hydraulic conductivity of the leaf mesophyll. The most common of these is to branch the vein system such that a high volume apoplastic flow pathway (the xylem) is allowed to approach very close to the sites of evaporation. This is the means of water distribution in most angiosperm leaves. The second system, identified here, is to modify the mesophyll by directing the lignification and apoptosis (Griffith, 1957) of a proportion of mesophyll cells, thereby greatly increasing its conductivity to water. This fascinating divergence in leaf water distribution systems appears to have arisen in the gymnosperm clade, as there have been no reports of lignified mesophyll cells in any plant groups basal to gymnosperms.
-
We found that the photosynthetic capacity of leaves in terrestrial plants is strongly correlated with proximity of veins to the evaporative surfaces of the leaf.
-
yet the response of Kleaf to mean maximum mesophyll path length (Dm) fell into two distinct groups.
Two groups
- highly signficant regression
- Conifers and cycads with schrieds.
-
an intimate association between light-saturated net CO2 assimilation rate (Amax) and the hydraulic conductance (Kleaf) of whole leaves was found
-
B, Dm from the end of the vein xylem to the gas-exchange epidermis plotted against 1/Kleaf. Means for both parameters are shown for single-vein (white circles) and multivein (red triangles) leaves plotted together, excluding the species with lignified sclereids in the mesophyll.
- white circles = single vein leaves
- red triangles = multi-vein leaves
-
A, Kleaf versus Amax in leaves of bryophytes (black), lycopods (white), ferns (green), conifers (red), angiosperms (blue), and gymnosperms with lignified sclereids in the mesophyll (brown).
- Black = bryophytes
- White = lycopods
- Green - ferns
- Red = conifers
- Blue = angiosperm
-
In this study we examine how the water transport and photosynthetic carbon assimilation rates of leaves are related to the spatial arrangement of veins in the leaf mesophyll.
-
Our a priori hypothesis was that the length of mesophyll tissue that must be traversed as the transpiration stream passes from a vein ending to site of evaporation will reflect both the hydraulic and coupled photosynthetic performance of any leaf.
-
While our knowledge of the molecular and developmental processes that guide leaf vein development and patterning grows at an ever-increasing rate (Kang and Dengler, 2004; Fleming, 2005; Scarpella et al., 2006; Sieburth and Deyholos, 2006), the underlying physical principles that connect vein pattern with leaf productivity remain unresolved.
-
Leaves have sustained virtually all terrestrial ecosystems over the last 400 million years
-
-
-
Live- stock may be given access to the largest of these two mesas in the near future. Attempts had previously been made to construct a stock trail to its top; these efforts were being renewed in 1956
-
- Sep 2018
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Knowing that other animals are as smart as us means we can appreciate them more, which could also help us to help them.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.genetics.org www.genetics.org
-
Selective Use of the Primary Literature Transforms the Classroom Into a Virtual Laboratory
This is an important paper for guiding how to teach scientific literacy skills to students. It also provides some ideas about how to go about annotating a scientific article.
-
Think of the next experiment:
- Diagram two additional experiments in cartoons.
- Mock grant review panels to select the best experiment.
-
Analyze and interpret the data:
- Ask students to compare and contrast elements within an inscription.
- Class discussion like a lab meeting.
- Make a summary concept map
-
http://www.genetics.org/supplemental/)
-
Elucidate the hypotheses:
Use cartons, figures, and rewritten figure/tables to define the hypothesis or questions.
-
Read:
Students:
- Draw a carton that illustrates the methods.
- Annotate figures by adding labels
- Write titles for each carton and figures
-
Consider
Concept Mapping of the Introduction
- Defining key terms
- Define the issues
- Define the relationships between terms and issues
I would also add having the students determine the motive, objective, and general approach of the paper.
-
-
photosynq.org photosynq.org
-
-0.660
Can we annotate data on photosynQ?
-
-
irma.nps.gov irma.nps.gov5664275
-
Seedlings of these species require large amounts of light and moisture to survive. Typically these requirements are met only in locations disturbed and irrigated by the river (Scott et al. 1996). S
How does the Earth stay green?
-
Flow and Climate
Snow melt earlier. Northward flow unusual. Low summer precipitation causes dry growing seasons.
-
Although cottonwood forests dominate river floodplains in dryregions of North America, Asia, Europe and Africa, naturally reproducing examples like the forest at THRO are increasingly rare.
- Reservoir construction
- Invasive trees.
-
This report summarizes research conducted by the U.S. Geological Survey from 2003 through 2016 on factors controlling reproduction and survival of plains cottonwood at the North and South Units of THRO (Figure1), and is relevant to management of cottonwood-dominated forests throughout the western United States.
-
An outstanding feature of Theodore Roosevelt National Park (THRO) is the exceptionally old and undisturbed gallery forest of plains cottonwood (Populus deltoidessubsp. monilifera) along the Little Missouri River. THRO protects the oldest known plains cottonwoods in the world, established as early as the year 1641 and growing up to 1.66 m (5.45 ft) in diameter. As the largest and most abundant tree in theriparian ecosystem, cottonwoods provide important habitat for many other species (Brinson et al. 1981).
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Aug 2018
-
nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
Our results suggest that tooth size, shape, and number within some, but not all, species are sensitive to climate.
-
The average area of individual teeth increases with warmer temperatures in both species (Tables 2 and 3); this is opposite to the site mean observations of Royer et al. (2005).
-
The patterns for Q. kelloggii are more complex.
- Still fewer teeth in warmer climates.
- Larger leaves in warmer climates.
- Correlations are stronger with elevation.
- No correlation of leaf traits to MAP
-
There are many significant correlations in A. rubrum between MAT and leaf physiognomy
- Colder climates more teeth, larger teeth.
- Colder leaves are larger.
- MAP and leaf physiogony are weakly correlated.
-
Quercus kelloggii
-
Acer rubrum
-
in an effort to more firmly ascertain the influence of climate on leaf physiognomy within species, we report results from a large data set that includes two North American woody plants (A. rubrum and Q. kelloggii) whose native ranges span large MAT gradients and are not closely related to each other.
-
Investigating the role of intraspecific variation in leaf–climate relationships is important for at least three reasons
- phenotypic platsiticty
- Paleobotanists use leaf-climate relationships to estimate paleoclimate.
- Find better patterns to study leaf-paleoclimate connections.
-
how tooth size, shape, and number respond to climate within species.
-
Hydathodes
-
However, intraspecific patterns also provide useful information
-
In this study, we examined the strength of correlation between leaf size and shape (physiognomy) and climate for two North American species with broad climatic ranges, Acer rubrum (red maple, Sapindaceae) and Quercus kelloggii (California black oak, Fagaceae). We sampled Q. kelloggii across a large elevation gradient (146–2362 m) but restricted sampling of A. rubrum to lowland areas (< 250 m).
-
-
www2.palomar.edu www2.palomar.edu
-
Araucaria heterophylla
-
-
academic.oup.com academic.oup.com
-
. The dynamic response of stomata or gs to fluctuations in light intensity has been studied in several understorey forest-dwelling species, but relatively few reports have studied crop species (Chazdon and Pearcy, 1986; Chazdon, 1991; Tinoco-Ojanguren and Pearcy, 1993; Leakey et al., 2005; McAusland et al., 2016).
-
Efforts to develop a big data approach to photosynthetic phenomics by recruiting many researchers into online cloud-based initiatives (Kuhlgert et al., 2016) may be promising because not only can they assay many genotypes but they can also do so under the diverse conditions which plants experience in nature.
-
However, the importance of the dynamic responses of photosynthesis raises a key problem that has not been adequately addressed: it is difficult to capture photosynthetic responses within (rapidly) fluctuating environments, especially in the field.
The Challenge
-
Whilst morphological adaptations to such extreme temperature fluctuations are well documented, the physiological adjustments are not (Hedberg, 1970).
Gap in knowledge
-
Indeed, it is particularly important that light is accurately tracked by the plant for optimal photosynthetic performance
This would suggest that chloroplast movement, which is relatively slow, could be a limiting factor of photosynthesis.
-
‘photosynthome’
Phenome of photosynthesis
-
Indeed, we are beginning to understand that the way in which photosynthesis is regulated in response to fluctuations in the environment is perhaps a more important determinant of plant productivity than its performance under steady-state or temporarily steady-state conditions
Other ways of measuring photosynthesis are needed.
-
-
www.jstor.org www.jstor.org
-
Wemeasure leaf-margin photosynthesis and transpiration througha growing season for two groups of native woody speciesfrom Pennsylvania and North Carolina.
-
Why are leaves more likelyto have teeth in colder climates?
-
Given the wide application of this proxy, calledleaf-margin analysis, it is surprising that the selective mecha-nisms driving the response of leaf margins to temperature areonly poorly known
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Apr 2018
-
-
Precipitation is limited in southwestern North Dakota
-
High Plains has been estimated at $38 million annually
~$91 million in 2018
-
- Mar 2018
-
academic.oup.com academic.oup.com
-
Citizen Science and Climate Change: Mapping the Range Expansions of Native and Exotic Plants with the Mobile App Leafsnap
-
-
onlinelibrary.wiley.com onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
An Arabidopsis rbcs1a rbcs2b mutant (double mutant 1a2b) was generated by crossing T-DNA insertion lines GABI_608F01 (At1g67090) and GABI_324A03 (At5g38420). The 1a3b mutant (GABI_608F01 (At1g67090); SALK_117835 (At5g38410)) was provided by Hiroyuki Ishida, Department of Applied Plant Science, Tohoku University, Japan.
-
-
-
Information as a critical
Test
-
-
onlinelibrary.wiley.com onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
WALLACE: GUI for R scripted species modeling.
-
-
onlinelibrary.wiley.com onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
These same leaves exhibited a reactivation of photosynthesis in spring,
MM states that they cut off leaves and took them back to the laboratory for measurements. Are these really the same leaves?
-
- Feb 2018
-
onlinelibrary.wiley.com onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
In the present study, the levels of photosynthetic down-regulation as well as the engagement and nature of the two different dissipation processes are examined in bearberry, which is a species that occurs over a wide range of conditions.
-
How does bearberry cope with this wide range of environmental conditions, coupled with high levels of solar radiation?
-
-
umwdtlt.com umwdtlt.com
-
My Open Textbook: Pedagogy and Practice
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
elifesciences.org elifesciences.org
-
Enabling scientific discussion on eLife with Hypothesis
These discussions are going to be interesting.
-
- Jan 2018
-
github.com github.com
-
Python filter support for Pandoc: on a Windows command prompt, type pip install pandocfilters
In windows command prompt:
cd C:\Python27python -m pip install pandocfilters
-
-
elifesciences.org elifesciences.org
-
- Direct Defenses
- Indirect Defenses
-
However, we have not had conclusive evidence that releasing these volatile compounds increased the fitness of the plant in the Darwinian sense of increasing reproductive success.
-
Manduca sexta,

Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
craigwhippo.github.io craigwhippo.github.io
-
Annotating
This is an anotation.
-
-
h5p.com h5p.com
-
H5P as a Service coming Q1 2018
Worth keeping an eye on. It could be a good way to embed questions for students to answer on hypothes.is.
-
-
www.authorea.com www.authorea.com
-
Bookdown site
A github site does similar thing. I write my syllabi in Rmarkdown and render it as an html and push it my github repo. The syllabi contains the hyperlinks to the reading assignments. Students use hypothes.is to annotate.
-
Moreover, the class' Hypothesis activities were synced into a dedicated Slack channel named "Hypo Feed" via the Hypothesis' API; as such, social annotations containing the course hashtag (made by both formal or open participants) were notified on Slack as well, and Slack participants could react to a Hypothesis annotation by following a link provided in the notification (Goals 2, 3 & 4).
Cool. Where can I learn more about this?
-
-
news.orvis.com news.orvis.com
-
Pink Squirrel Nymph
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
- Whiting Farms soft hacle with chickabou cdl
- Lightingn strike streamer/nymph SN1 size 8
- 6/0 olive danville
- pearl krystal flash
- Whiting Farms soft hackle with chickabou cdl salmon
- Whiting Farms soft hackle with chickabou cdl burnt orange
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Cable Tie Craw
- Do-It Wacky Jig Hook. Size 2 or 6
- Cyclops beads 5/32 Black Nicklel (EYC5100)
- .02 Lead Free Wire
- 140 denier light olive
- Pine squiral zonker brown olive
- 4 inch long cable tie -black
- krysal flash -amber
- Fly rattle -micro size
- Whiting farms full soft hackle coq de leon/ Chichaboue speckled golden Olive
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
- Hook Dai-Riki - 700 size
- Cone head -smooth staper, large, nickle.
- 0.20 lead-free wire
- UTC 140 denier brown olive
- Chartreuse ultra wire
- Sparkle braid silver SB252
- pine squirle zonker strip -chartreuse
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
- Hook: Dai-Riki #270 Size 8, Natural Bend 3x long
- 140 Denier Yellow Thread
- Red chenille
- Yellow, Blue, and Red Craft foam
- Yellow rubber legs
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Mop 'N Glo 2.0
- Dai-Riki 135 size 14
- 140 denier yellow thread
- Mop tenticles
- Clown egg material
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Dumb Bunny Streamer
- Do- it Wacky Jig Hook Size 6 or 2 (6216)
- 140 Denier ultra thread chartreuse
- Rabbit Zonker -Dark Olive (RH901)
- Rabbit Zonker - FL Chartruese (RH 509)
- X-small 1/60 oz. lead eyes
- Hard as nails -white
- Hard as nails -black
- Hard as nails -clear
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
- Hook: Dai-Riki 700 size 8
- Cone Head: Gold 4.5 mm
- .02 lead free wire
- 140 denier thread -yellow
- strung marabou -yellow
- Krystal flash -gold
- Yellow pearl chenille
- yellow rubber legs
- Orange grizzle saddle hackle
- head cemment
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Dec 2017
-
hypothesis-h5p.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com hypothesis-h5p.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com
-
for
<iframe allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" frameborder="0" height="226" src="https://h5p.org/h5p/embed/157632" width="1090"></iframe><script charset="UTF-8" src="https://h5p.org/sites/all/modules/h5p/library/js/h5p-resizer.js"></script>
-
-
www.lifescied.org www.lifescied.org
-
However, these faculty members are also of the opinion that it is very time-consuming to teach these skills
This is an example of a unicorn.
-
scientific argumentation model (SAM), a heuristic consisting of a set of seven moves (unpublished data) that play an important role in an author's argument as given in research articles.
Could be a starting point for annotating a scientific manuscript.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Oct 2017
-
www.nejm.org www.nejm.org
-
We report results from randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials of antibiotic therapy inseropositive and seronegative patients who had chron-ic symptoms after treatment for Lyme disease.
Experimental study with correct experimental design.
-
it is important to determine the efficacy of suchtherapy.
Does this treatment work?
-
In view of thesubstantial morbidity and even death5 associated withprolonged parenteral antibiotic treatment of Lyme dis-ease
Prolonged treatment with antibiotics has risks, which justifies this study.
-
- Lyme disease
- Borrelia burgdorferi
- Treatment for seronegative B. burddorferi
-
- Sep 2017
-
-
We hypothesized that introductory textbooks under-represent the processes of scientific investigation and discovery.
Reasonable hypothesis given that reforms are focused on correcting this problem.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.coursesource.org www.coursesource.org
-
Duncan (16) found that less than 5% of the figures in a typical textbook contain data. It is no wonder that students using a traditional and passive textbook do not know how to support their answers with data.
Absolutely. The question is how to bridge the Perry Scheme so that students are more focused on evidence than the conclusion.
-
However, if reading the book is a key component of class time and tests, students will use the text to help them construct their own understanding of the material.
I agree. The text should be the organizing factor.
-
Second, students must come to class prepared for classroom activities, which also facilitates studying for exams as the semester progresses.
Hypothes.is also helps with this too
-
First, student work outside of class needs to be intentionally and effectively structured.
Hypothes.is is one tool that I use to achieve this goal.
-
-
dev.biologists.org dev.biologists.orgdev0106.q10
-
Our results also discourage modelsof guidance by default that involve repulsive guidance cuesfrom non-target cells, which has been shown to play a signifi-cant role in neural path finding (Dodd and Schuchardt, 1995).
Counter argument based on these results is uncertain.
-
Whatever the details of molecular basis of theguidance process is, there are two ways by which the femalegametophyte may accomplish this. (1) The gametophyte maydirectly change the surface characteristics of the epidermalcells lining the ovule stalk and the outer integument byproducing a surface-localized signal (Fig. 6B). (2) An alter-native mechanism would be, a signal from the gametophyteindirectly causing changes in the surface properties of thesporophytic cells along which the pollen tube tracks (Fig. 6C).This latter model demands that the primary gametophyticsignal is passed from the adjacent sporophytic cells to furtherneighboring sporophytic cells by the same or a differentsignaling mechanism.
-
A support for the second model (Fig. 6C) comes from theobservation that the abnormal ovules of the inner-no-outer(ino)mutants are defective in the final stages of pollen tube guidance(Baker et al., 1997).
-
These results convincingly demon-strate that pollen tube guidance by an ovule requires a func-tional female gametophyte, and excludes the model presentedin Fig. 1B
-
The resultsreported here allow us to conclusively reject the possibilitythata group of sporophytic cells of the ovule are responsiblefor guiding the pollen tube as well as controlling the femalegametophyte development.
-
The results are sum-marized in Table 4. Of the 184 morphologically normal ovulesscored, 124 ovules were associated with a pollen tube at themicropylar end. By contrast, none of the 189 ovules without anormal female gametophyte had a pollen tube guided to themicropylar end. The morphology of 137 ovules could not beunambiguously scored in these flowers because these wereeither squashed too hard or were occluded by the surroundingopaque tissues; however, approximately half of these had somepollen tube association.
Support for the findings can be found in table 4.
67% of normal ovules were able to interact with a pollen tube.
0% of the abnormal ovules interact with pollen tubes.
-
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Missing Data Processing Procedures
-
Therefore, at least the finalphase of pollen tube guidance to the ovule is controlled by thefemale gametophyte.
-
In this communication, we describe an explicit genetic testthat distinguishes between the above two models.
-
The above results forced us to entertain two alternativemodels (Fig. 1) that could not be distinguished in the previousstudy. One model proposes that the gametophyte produces asignal that directly, or indirectly through its effects on sporo-phytic cells, causes pollen tube guidance to the ovule (Fig. 1A).
The motive of this study is to distinguish between two models of pollen tube guidance to the ovule. In model 1, the female gametophyte produces a signal that guides the pollen tube to the micropyle. In the second, model sporophytic signals control both megagametophyte development and produces a signal.
-
-
dev.biologists.org dev.biologists.org
-
In this study, we identified an earlier adhesion event thatallows plants to capture appropriate pollen.
-
To investigate the nature and role of cell adhesion in plants,we analyzed the initial step of pollination in Arabidopsis: thebinding of pollen grains to female stigma cells.
Motive of these study
-
Pollen-stigma adhesion in Arabidopsis: a species-specific interactionmediated by lipophilic molecules in the pollen exine
How do plants of the same species recognize each other?
-
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
“You might be able to get more lycopene out because the heat starts to break down the cell matrix and that actually allows some of the tied-up carotenoids to be released from the cell walls,”
I would have stated it differently. Heating will help break down the cell walls, which facilitates the release of lycopene from the chromoplasts.
-
- Mar 2017
-
bookdown.org bookdown.org
-
We hope to integrate these themes and styles into bookdown, so authors do not have to dive into the details of how to use a certain LaTeX class or how to configure CSS for HTML output.
I'm looking forward to this.
-
-
bookdown.org bookdown.org
-
Can readers interact with examples in our book as they read it?
Yes, if they are using web annotation. The potential connections between bookdown, shiny, html widgets and hypothesi.is are cool
-
certain figures float to a random page,
Controlling figure placement is a problem with Rmarkdown to generate a PDF.
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
his work led to the recognition that most enzymes are in fact proteins and in 1946 Sumner was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Cool, I never knew that plant biology was so seminal in biochemistry.
-
- Feb 2017
-
www.cell.com www.cell.com
-
3,000-fold concentration differences between varieties
This variation is important. Could be a good GWAS study.
-
tomato flavor now seems to be a cherished ‘lost virtue’ of a recent but bygone era.
This may be the result of breeding for yield, sugar, and disease resistance. Tomato breeders have not selected for the volatiles that are important for flavor.
-
-
www.lifescied.org www.lifescied.org
-
Course Structure
Four Articles used to teach critical analysis:
- Flawed paper
- Exemplary
- Conflicting Paper #1
- Conflicting Paper #2
Class Meeting Agenda:
- Identification of Background, terminology, and methodology
- Explanation of unfamiliar background, terminology, and methodology
- Data interpretation
- Author's conclusion and unanswered questions
- Follow up experiments
-
FIGURE 1.

Title: Number of papers read by undergraduates and Masters Students
Specific Question: How many scientific papers have students carefully analyzed?
Analysis:
2/3 students have carefully read fewer than 20 papers.
Prediction: Most undergraduates read about 1 primary literature article each semester. This is probably not enough to learn how to read the primary literature.
-
, instructors have detected that students struggle with some of its aspects
- Connecting background information to specific research questions
- The logical linkage of hypothesis with testing methods
- Data interpretation
- Evaluating strength of conclusions based on evidence
- Identification of implications
- Relating data between articles.
- Jargon and writing style
-
In their report Scientific Foundations for Future Physicians, the American Association of Medical Colleges and Howard Hughes Medical (AAMC-HHMI) Institute listed the ability of critical reading and evaluation of scientific papers as one of the competencies that students should possess before entering medical school (AAMC-HHMI, 2009, p. 26).
Motivating statement for why students should want to learn how to read scientific papers.
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
8-10 quanta
8-10 photons
-
In fact the photosynthetic rate achieved with the two light qualities combined could be 30–40% higher than the sum of the rates in far-red or shorter red when measured separately (Emerson et al. 1957).
This could be an important experiment to use as a case study.
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
Carotenoids are accessory pigments that also function to dissipate excess energy.
-
In low light, ChlB will increase and the chla/b ratio will be lower.
-
Chl a/b ratios commonly range from 3.3 to 4.2 in well-nourished sun-adapted species, but can be as low as 2.2 or thereabouts in shade-adapted species grown at low light.
This is an important phenotype because it tells gives you some idea about how light harvesting is optimized.
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
Chloroplast Structure
- Stroma (carbon reactions, nitrogen and sulfur metabolism, and plastid genome.
- Inner membrane (phosphate and metabolite transporters, lipid synthesis.
- Thlakoid membranes (light reactions)
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
biochemical aspects of photosynthetic carbon reduction (Calvin cycle) are now comprehensively understood. The transduction of light energy into chemical potential energy is not so well understood, while events surrounding photosynthetic electron flow are defined in some detail and are described here, biophysical processes within the water-splitting apparatus of chloroplasts, and indeed the manner in which photons are captured and their quantum energy harnessed for photolysis, remain something of an enigma and fall outside the scope of our present account.
This is an interesting perspective on the state of the field. I've never thought about it this way.
-
- Jan 2017
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
Photosynthetic capacity of leaves varies widely according to light, water and nutrient availability and these differences in capacity usually reflect Rubisco content.
Sun leaves allocate more N to rubisco. Shade leaves allocate more N to chlorophyll.
-
. In part, this gentle transition reflects the fact that a leaf is a population of chloroplasts which have different photosynthetic properties depending on their position within that leaf.
Interesting example of collective properties of individual chloroplasts having a predictable outcome.
-
For most leaves, 80–85% of 400–700 nm light is absorbed and it is only in leaves produced under severe nitrogen deficiency where there is less than 0.25 mmol Chl m–2 that absorptance falls below 75%.
Relationship between NUE and LUE.
-
Expressed in terms of absorbed quanta, sun and shade leaves have virtually identical quantum efficiencies for CO2 assimilation.
This is interesting. I always had the misconception that shade leaves were more efficient.
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
Section 1.1 encompasses anatomy, light interception and leaf gas exchange and includes a case study on development of a process-based model for photosynthetic CO2 assimilation using A:Ci curves.
I am interested in how variation in leaf anatomy, light interception, and gas exchange allows for plants to optimize light interception and carbon fixation.
-
variation
This variation could be a powerful tool for studying photosynthesis.
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
concept of function
Structure-function relationships are central to biology.
-
m. In effect, we need to know collective behaviour (e.g. PV = nRT) before we can ask pertinent questions about the parts (e.g. how can we best summarise the behaviour of a legion of elastically colliding molecules).
This is interesting because the organization of the book starts at a smaller level than the end of the book.
-
rare exceptions
-
Osmond and Chow 1988
Each box represents a "black box" that spans about three orders of magnitude. Each box represents a different aspect of photosynthesis. What would this diagram look like for other physiological processes?
-
Accountability, philosophy and plant physiology
-
A plant science manifesto
During the Spring 2017 semester, students taking a plant physiology course at Dickinson State University will be publicly annotating chapters from this online textbook.
-
-
bio.libretexts.org bio.libretexts.org
-
satellite DNA
Microsatellite DNA is used to study genetic variation in a population.
-
2.1.2 Levels of compaction
-
spool
DNA has a negatively charged backbone. The histones surface has positively charged amino acids.
-
tightly DNA is packaged
I wonder what are the molecular controls that control chromosome condensation.
-
compaction makes it easier to transport DNA within a dividing cell, it also makes DNA less accessible for other cellular functions such as DNA synthesis and transcription.
Trade off between untangling DNA fibers for cell replication and accessibility for transcription and translation.
-
-
bio.libretexts.org bio.libretexts.org
-
Knowledge of these hereditary properties has been of significant value in the history of human development.
This is an understatement. Plant and animal domestication was required for the development of agrarian societies.
-
Genetics
Genetics also studies the flow and regulation of hereditary biological information.
-
- Dec 2016
-
journal.disruptivemedia.org.uk journal.disruptivemedia.org.uk
-
very hard to quantify that datum
It may be a challenge, but it shouldn't be very hard. The hypothe.is R package is a good start in creating a data science workflow. This workflow would have a clear advantage in higher education... especially in academic disciplines that use R.
-
-
www.genetics.org www.genetics.org
-
marginalia
Mendel's marginalia allows us to read "Experiments on Plant Hybrids" in a new way.
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
synthesis mapping,
Synthesis mapping is concept/mind mapping 2.0. For subjects like biology, the ability to show connections between scale levels is an important skill for students to develop. Using this approach in teaching may help students understand the concept of emergent properties better.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
As CO2 molecules diffuse inwards they encounter an opposite flux of H2O molecules rushing outwards that is three to four orders of magnitude stronge
Water has a lower molecular mass than carbon dioxide. The concentration gradient is also steeper for water exiting the cell.
-
cuticle
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
The lower half of a leaf absorbs about 25% of incoming light, but is responsible for about 31% of a leaf’s total CO2 assimilation.
How does photorespiration play into this scenario?
-
Overall, absorption of visible light by mesophyll tissue is complex due to sieve-effects and scattering
Sieve effect decreases absorption due to packaging of pigments within chloroplasts. Scattering increases absorption due to reflection and refraction (mostly by spongy mesophyll).
-
weak absorption around 550 nm, which corresponds to green light.
Absorption around 550 nm is relatively weak. Not weak in absolute terms.
-
-
plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au plantsinaction.science.uq.edu.au
-
of sections cut parallel to the leaf surface are shown for palisade
I've never seen cross sections like this. Interesting.
-
A thicker leaf in sunny environments is energy effective because enough photons reach chloroplasts in lower cell layers to keep their Rubisco gainfully employed.
This is because chloroplasts move to the cell walls perpendicular to the light. Allowing more light to reach lower cell layers.
-