How to Read a Book by Shaykh Hamza Yusuf, Part 1
Amazing series by Shaykh Hamza Yusuf on Adler and van Doorns How to Read a Book. Part 2 is here: . How to Read a Book, Part 2 by Shaykh Hamza Yusuf
How to Read a Book by Shaykh Hamza Yusuf, Part 1
Amazing series by Shaykh Hamza Yusuf on Adler and van Doorns How to Read a Book. Part 2 is here: . How to Read a Book, Part 2 by Shaykh Hamza Yusuf
The third reading should again be a slow reading,
relationship to Adler's levels of reading?
Adler, Mortimer J., and Charles Van Doren. How to Read a Book: The Classical Guide to Intelligent Reading. Revised and Updated edition. 1940. Reprint, Touchstone, 2011.
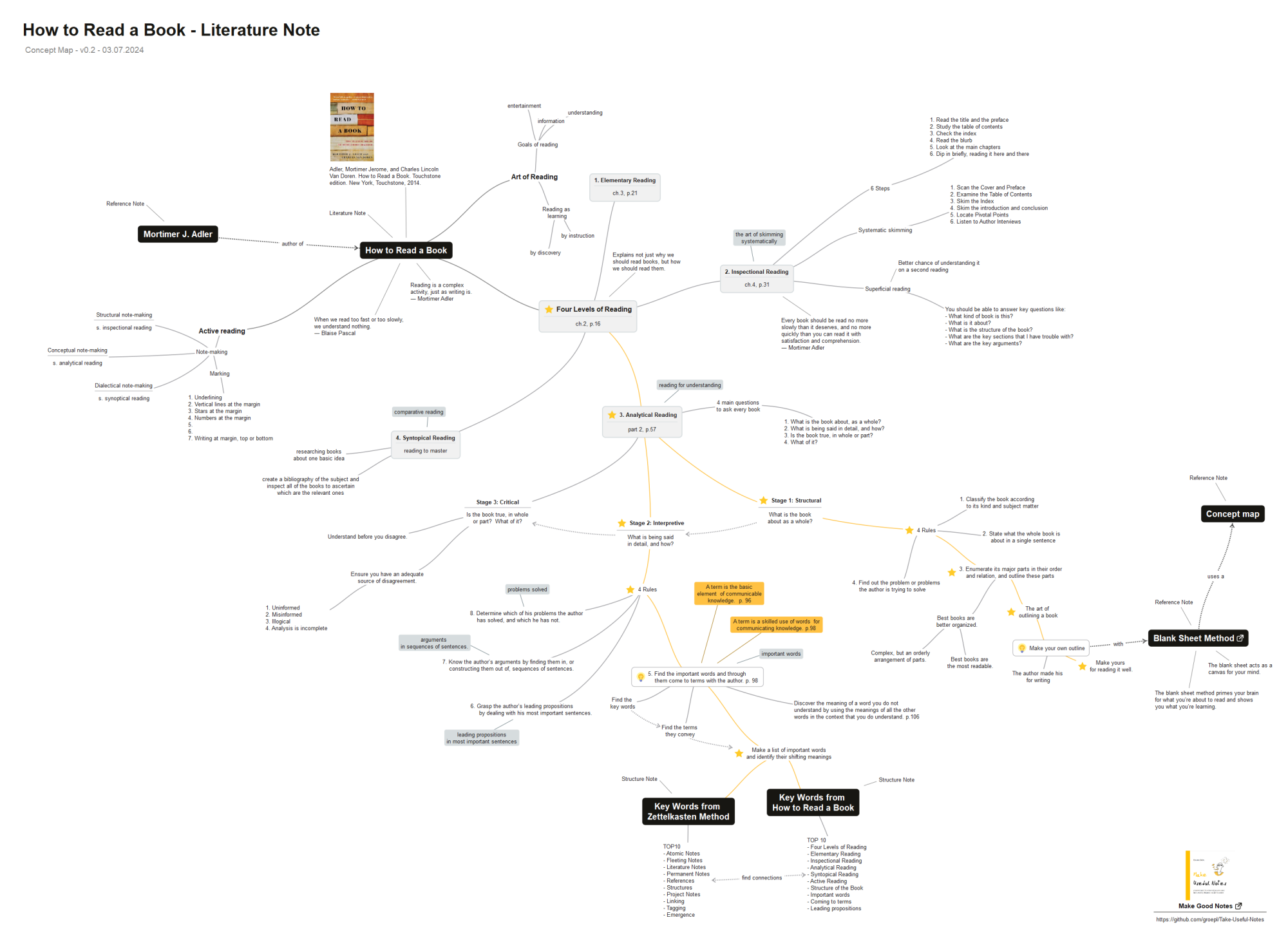
Edmund Gröpl's concept map of Adler & Van Doren's How to Read a Book via https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/comment/20668#Comment_20668:
Dr. Harry McNeill’s June 1940 assessment in Interracial Review
Interesting commentary here on conversion of African-Americans to Catholicism as well as self-help nature of reading for improvement. Analogizes African-Americans without Catholicism to Mortimer J. Adler as a Jew.
Possible tone of colonialism to assimilate African-Americans into Western Culture here? Though still somehow some space for movement and growth.
acques Barzun, “Review of How to Read a Book, by Mortimer Adler,”Saturday Review (March 9, 1940): 6–7; Adler, Philosopher at Large, 67.
available at: https://www.unz.com/print/SaturdayRev-1940mar09-00006/
Barzun, Jacques. "Read, Do Not Run" Review of How to Read a Book, by Mortimer J. Adler. The Saturday Review, March 9, 1940.
After publication in February 1940, How to Read a Book propelledAdler to the forefront of the Great Books Movement and into a posi-tion now referred to as a “public intellectual.”
How to Read a Book providedrules for reading. The rules constituted the book’s heart: (1) readingfrom the whole to the parts, designated as the “structural or analyticreading”; (2) reading from parts to the whole, or an “interpretive orsynthetic” reading; and (3) deciding to agree or disagree, the “criticalor evaluative” reading.
An interesting synopsis of the rules of reading from Adler's text.
Theindexer will want a feel, before they begin, for the concepts that willneed to be flagged, or taxonomized with subheadings. They mightskim the book – reading it in full but at a canter – before tackling itproperly with the software open. Or they may spend a while, as apreliminary, with the book’s introduction, paying attention to itschapter outline – if it has one – to gain a sense of what to look outfor. Often, having reached the end of the book, the indexer will returnto the first few chapters, going over them again now that they havegained a conceptual mapping of the work as a whole.
It's no wonder that Mortimer J. Adler was able to write such a deep analysis of reading in How to Read a Book after having spent so much time indexing the ideas behind The Great Books of the Western World.
Indexing requires a solid inspectional read at minimum, but will often go deeper into contexts which require at least some analytical reading. To produce the Syntopicon, one must go even further into analytical reading to provide the proper indexing of ideas so that they may be sub-categorized and used for deeper analysis for things such as comparison and contrast of those ideas.
How to Read a Book. Los Angeles: KCET Los Angeles, 1975. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y_rizr8bb0c.
13 part series including:<br /> - 01:33:02 Part 8: How to read Stories - 01:46:13 Part 9: What Makes a Story Good - 01:59:24 Part 10 How to Read a Poem - Shakespeare sonnet 116, "admit" definition - Wordsworth poem about London and nature - 02:12:49 Part 11: Activating Poetry and Plays - 02:26:09 Part 12: How to Read Two Books at the Same Time - 02:39:29 Part 13: The Pyramid of Books
2023-11-29: Since the original video was removed, one can also view the series at: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLPajsb520dyzNw9mHsZnrzi5w9N_amS7E
How to Read a Book, Chapter 4 by Dan Allosso<br /> https://danallosso.substack.com/p/how-to-read-a-book-chapter-4
Annotations at: https://docdrop.org/video/Y_rizr8bb0c/
Adler, Mortimer J., and Charles Van Doren. How to Read a Book. Revised and Updated edition. 1940. Reprint, New York: Simon & Schuster, 1972.
Annotation URL: urn:x-pdf:47749dd5c860ea4a9b8749ab77a009da<br /> Annotation search
Zhao briefly describes Cal Newport's Questions, Evidence, Conclusions (QEC) framework which she uses as a framework for quickly annotating books and then making notes from those annotations later.
How does QEC differ from strategies in Adler/Van Doren?
How to Write a Thesis (Umberto Eco) - my reading notes<br /> by Raul Pacheco-Vega
perfunctory positive review; no great insight
Schiller, Melanie. “Ahrens, S. (2017). How to Take Smart Notes: One Simple Technique to Boost Writing, Learning and Thinking for Students, Academics and Nonfiction Book Writers.” Journal of Writing Research 9, no. 2 (October 15, 2017): 227–31. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2017.09.02.05.
Manfred Kuehn in Umberto Eco on How to Write a Thesis at 2015-01-30<br /> (accessed:: 2023-02-23 11:29:34)
Kuehn felt Luhmann's writing on note taking was more exciting that Umberto Eco's.
For her online book clubs, Maggie Delano defines four broad types of notes as a template for users to have a common language: - terms - propositions (arguments, claims) - questions - sources (references which support the above three types)
I'm fairly sure in a separate context, I've heard that these were broadly lifted from her reading of Mortimer J. Adler's How to Read a book. (reference? an early session of Dan Allosso's Obsidian Book club?)
These become the backbone of breaking down a book and using them to have a conversation with the author.
I am going to add some optional 'reading and doing' directions to my posts. Might be helpful.
https://howaboutthis.substack.com/p/the-knowledge-that-wont-fit-inside
Reasonable overview article with some nice pros/cons.
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Learning Commons </span> in Annotating a text - The Lion, The Witch and The Wardrobe - LibGuides at Mater Christi College (<time class='dt-published'>02/24/2022 13:46:42</time>)</cite></small>
How many times have you heard the cliché, for example, read between the lines? It turns out, the key to reading between the lines is actually to write between the lines. Once you start, you'll discover a whole new reading experience, elevated from that of a one-sided lecture to a two-sided conversation.
reading as a conversation between myself and the text.
The idea of the hermeneutic circle is to envision a whole in terms how the parts interact with each other, and how they interact with the whole. That may sound a little bit out there, so let’s have a look at a concrete example.
This is a general concept, the rest of the article extrapolates the idea to the act of reading. This may be a stretch, since it implies that whatever can be broken into parts will belong to the hermeneutic circle, while this only applies to interpreting (text)
Zimmer, C. (2020, June 1). How You Should Read Coronavirus Studies, or Any Science Paper. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/article/how-to-read-a-science-study-coronavirus.html