- Mar 2019
-
www.celt.iastate.edu www.celt.iastate.edu
-
This is one of many pages that describes team based learning. The layout and typeface make this page easy enough to read. The content is rather brief and would suffice for someone who is trying to understand this approach and decide whether it is workable for their own adult learning and training context.
-
- Feb 2019
-
researchguides.uic.edu researchguides.uic.edu
-
Good website explaining PICO including af videotutorial . provided by the University Library of Illinois, Chicago
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Jan 2019
- Nov 2018
-
blogs.wgbh.org blogs.wgbh.org
-
It’s estimated that unneeded or unproven medical procedures cost us billions each year.
-
Significant procedures are sometimes not nearly as effective as you might think. “In 2002, the New England Journal of Medicine published a landmark study where they found that this very common knee operation worked no better than a sham procedure in which a surgeon merely pretended to operate,” Patashnik says.
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
So many medical publications appear worldwide every day that it is no longer possible for an individual medical professional to keep up with the latest state of knowledge. In order to offer support and to encourage new medical research, EBM provides a toolbox of different methods. These tools can be divided into three categories:The first category includes methods that serve to create reliable new knowledge: Someone who would like to compare the advantages and disadvantages of different drugs, for example, will find suitable types of studies here.The second category involves methods that help to summarize the existing knowledge on a subject: They serve to find and select the previously published studies that are best able to answer a particular question. There are now networks of researchers that specialize in looking for the latest research findings and summarizing them to provide easily accessible information.The third category covers methods for presenting information to medical professionals and laypeople in a way that helps them to find, understand and make use of it.The main aim is always to find out what kind of care is most suitable for a particular patient – and how to incorporate their individual preferences and circumstances into the treatment decision.
-
An evidence-based approach also includes informing patients about the pros and cons of medical options so that they can actively be part of the decision.So making a treatment decision in accordance with EBM means basing it on the best available knowledge from clinical research and medical practice. A number of factors play an important role in the decision. As well as the type and severity of the health problem, these include the person's general life situation, personal values and opinions.
-
This is the purpose of evidence-based medicine (EBM): to provide healthcare professionals, patients and those close to them with up-to-date and scientifically proven information on the various medical options that are available to them. It can help to find out what sorts of advantages or disadvantages a treatment or test has, when people might benefit from it and whether it might also be harmful.EBM uses special methods that it has developed to find the highest quality evidence for the benefits of a specific medical intervention. This evidence can be found in conclusive scientific studies. EBM also plays a part in making sure that the research that is done can help patients to answer the most important questions. This means that studies look into both the benefits of a treatment as well as how it affects quality of life, for example.
-
-
catalyst.nejm.org catalyst.nejm.org
-
“It’s about embracing the inscrutable nature of human interactions,” says Chang. Evidence-based medicine was a massive improvement over intuition-based medicine, he says, but it only covers traditionally quantifiable data, or those things that are easy to measure. But we’re now quantifying information that was considered qualitative a generation ago.
Biggest challenges to redesigning the health care system in a way that would work better for patients and improve health
-
-
catalyst.nejm.org catalyst.nejm.org
-
As with other forms of value-based health care, patient-centered care requires a shift in the way provider practices and health systems are designed, managed, and reimbursed. In keeping with the tenets of patient-centeredness, this shift neither happens in a vacuum, it driven by traditional hierarchies in which providers or clinicians are the lone authority. Everyone, from the parking valet and environmental services staff to c-suite members, are engaged in the process, which impacts hiring, training, leadership style, and organizational culture. Patient-centered care also represents a shift in the traditional roles of patients and their families from one of passive “order taker” to one of active “team member.” One of the country’s leading proponents of patient-centered care, Dr. James Rickert, has stated that one of the basic tenets of patient-centered care is that “patients know best how well their health providers are meeting their needs.” To that end, many providers are implementing patient satisfaction surveys, patient and family advisory councils, and focus groups, and using the resulting information to continuously improve the way health care facilities and provider practices are designed, managed, and maintained from both a physical and operational perspective so they become centered more on the individual person than on a checklist of services provided. As the popularity of patient- and family-centered health care increases, it is expected that patients will become more engaged and satisfied with the delivery of their care, and evidence of its clinical efficacy should continue to mount.
Cultural shift to patient-centered care
-
-
www.joe.org www.joe.org
-
Thinking in Multimedia: Research-Based Tips on Designing and Using Interactive Multimedia Curricula.
This article examines various methods of delivery: multimedia integration, possibly including audio, video, slides, and animation. The recommendation is to carefully consider which online delivery mode matches with the learner, and to be cognizant that not everyone learns in the same manner. Certain topics may be best presented in live videos and not in power-point slides show as meaning may be lost or not delivered correctly. It’s important to follow-up with immediate assessment and feedback to continue to develop effective training.
RATING: 5/5 (rating based upon a score system 1 to 5, 1= lowest 5=highest in terms of content, veracity, easiness of use etc.)
-
-
www.ncolr.org www.ncolr.org
-
The Importance of Interaction in Web-Based Education: A Program-level Case Study of Online MBA Courses
This case study explores perceptions of instructors vs. end-users with web-based training. It examines various technologies and techniques.
RATING: 4/5 (rating based upon a score system 1 to 5, 1= lowest 5=highest in terms of content, veracity, easiness of use etc.)
-
-
content.ebscohost.com content.ebscohost.com
-
Transformation for adults in an Internet-based learningenvironment—is it necessary to be self-directed?
REDIRECT to this URL Tranformation for adults
This study explores transformative learning theory (TLT) for adults in the Internet-base learning environment and questions the need for students to be self-directed. The study also includes the Constructivist Internet-based Learning Environment Scale (CILES). The Self-directed Learning Readiness Scale(SDLRS) as modified by Chang (2006) was used to meet the cultural needs of the participants. In conclusion, the results have a high reliability factor and add quantitative research to previous qualitative studies.<br> Further discussion is suggested regarding the technical and emancipatory learning interests on adult online learners.
RATING: 8/10
-
-
www.hindawi.com www.hindawi.com
-
Mobile Based User-Centered Learning Environment for Adult Absolute Illiterates
This study reviewed the education of absolute illiterates globally. It was based on the creation of game-based learning (GBL) which provides a user-friendly learning platform with little cost and little intimidation for the learner. The research also identified 60% of the world's illiterate population residing in rural areas with little access to computers and educational centers. The GBL environments created real world environments that allow learners to practice real-life scenarios in familiar surroundings using 3-D technology. The study also adapted a English language program to meet the needs of various languages. The context of the game is a farmer and a wife then acquire items and count them in their native language. The numbers used in counting are spoken and the game produces the correlating number so the learner becomes familiar with the written form of the letter. In conclusion, the participants identified that the mobile learning was more beneficial than PC applications due to unreliable electrical service at home. The mobile system was also available on demand.and applied to participants real-life usage.
RATING: 10/10
-
-
www.iste.org www.iste.org
-
Using Model Strategies forIntegrating Technology into Teaching
In this pdf, there are many helpful tips and techniques in creating a foundation for technology. The introduction of model strategies are laid out with lots of supporting detail and examples and weblinks. It includes nearly 400 pages of peer-reviewed lessons, models and various strategies.
RATING: 5/5 (rating based upon a score system 1 to 5, 1= lowest 5=highest in terms of content, veracity, easiness of use etc.)
-
- Oct 2018
- Jul 2018
-
www.orca.uconn.edu www.orca.uconn.edu
-
TICA Checklist: Used for Project Based Learning (Check list for stages one, two, and three)
-
-
www.bie.org www.bie.org
-
Tiny House Project
Great video to demonstrate PBL
-
-
www.bie.org www.bie.org
-
Students work on a project over an extended period of time – from a week up to a semester – that engages them in solving a real-world problem or answering a complex question. They demonstrate their knowledge and skills by developing a public product or presentation for a real audience.
Good source to further look into PBL
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.bie.org www.bie.org
-
PBL is entrenched in the concept of the elements being “ongoing.” Building a PBL culture in the classroom isn’t just about doing a project every quarter. It’s about using the Design Elements as often as possible. It’s about offering Choice in different assignments, rubrics, deadlines, or partnerships on an everyday basis. It’s about training students to ask great questions not just when creating a Need to Know list, but when using Google, when asking for feedback, or to even develop their own peer-to-peer assessments. The need to teach literacy is also ongoing.
great descriptor of PBL
-
- Apr 2018
-
liftingbridges.weebly.com liftingbridges.weebly.comMy Site1
-
Community-base Learning
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
hypothes.is hypothes.is
-
The fraught United States presidential election cycle of 2016 has revealed a country divided along geographical and ideological lines. It has also bolstered a narrative of haves and have-nots, pitting the so-called coastal elites against “heartland” America.
-
- Feb 2018
-
mattheneus-healthcare.com mattheneus-healthcare.com
-
First, the industry is demanding it. Those who are paying for healthcare—the government, employers, patients, commercial health plans—want more value for their healthcare dollar. The transaction-driven, fee-for-service model has helped contribute to a fragmented healthcare system that has led to major challenges in healthcare. This fee-for-service model is simply not sustainable.
Those who are paying for healthcare—the government, employers, patients, commercial health plans—want more value for their healthcare dollar. The transaction-driven, fee-for-service model has helped contribute to a fragmented healthcare system that has led to major challenges in healthcare. This fee-for-service model is simply not sustainable.
-
- Jan 2018
-
www.insidehighered.com www.insidehighered.com
-
it also required elusive buy-in from administrators and a new approach to thinking about the classroom experience.
There are benefits and drawbacks to such modern learning spaces. On one hand, the space(s) being used for technological advancement need to be designated, built/remodeled and shown to be used regularly by students, this process takes a long time and a lot of funding to perfect, which is what administration do not want to hear. Such spaces do not have to be used only for online courses and studying, which is a point made later in this article, it can be versatile and useful for all students if designed right. As technology improves, educators with more training in technology are becoming more widespread and students utilize online resources and technology more, the necessity of having these spaces increases.
-
-
mattheneus-healthcare.com mattheneus-healthcare.com
-
reliability and accessibility of big data will help facilitate increased reliance upon outcomes-based contracting and alternative payment models.
reliability and accessibility of big data will help facilitate increased reliance upon outcomes-based contracting and alternative payment models.
-
- Dec 2017
-
mattheneus-healthcare.com mattheneus-healthcare.com
-
fee-for-service payment models to value-based care
-
- Nov 2017
-
www.educause.edu www.educause.edu
-
Courses are severely limited in the ability to access other courses even within the institution (so much for "connecting silos"), and when courses end, students are typically cast out, unable to refer to past activity in their ongoing studies or in their lives (so much for "promoting lifelong learning").
Which is where a different type of unbundling can happen. “Courses” may limit our thinking.
-
-
mfeldstein.com mfeldstein.com
-
Let's imagine a world in which universities, not vendors, designed and built our online learning environments.
-
In an ideal world, every class would have its own unique mix of these capabilities based on what's appropriate for the students, teacher, and subject.
How about systems with a different granularity from the class/course/cohort models?
-
-
halfanhour.blogspot.com halfanhour.blogspot.com
-
they depended mostly on pre-recorded videos for content (following the Khan Academy) model. This was content that was intended to be 'learned' by students.
-
-
wrapping.marthaburtis.net wrapping.marthaburtis.net
-
The College of Education faculty and administrators needed an ePortfolio because of increasing demands from the Commonwealth of Virginia to demonstrate students’ and graduates’ competencies.
-
-
www.imsglobal.org www.imsglobal.org
-
An institution has implemented a learning management system (LMS). The LMS contains a learning object repository (LOR) that in some aspects is populated by all users across the world who use the same LMS. Each user is able to align his/her learning objects to the academic standards appropriate to that jurisdiction. Using CASE 1.0, the LMS is able to present the same learning objects to users in other jurisdictions while displaying the academic standards alignment for the other jurisdictions (associations).
Sounds like part of the problem Vitrine technologie-éducation has been tackling with Ceres, a Learning Object Repository with a Semantic core.
-
-
events.educause.edu events.educause.edu
-
Moving to a Web of Linked Data for Credential Ecosystems
Oh? Credentials going Semantic? CBE going TBL?
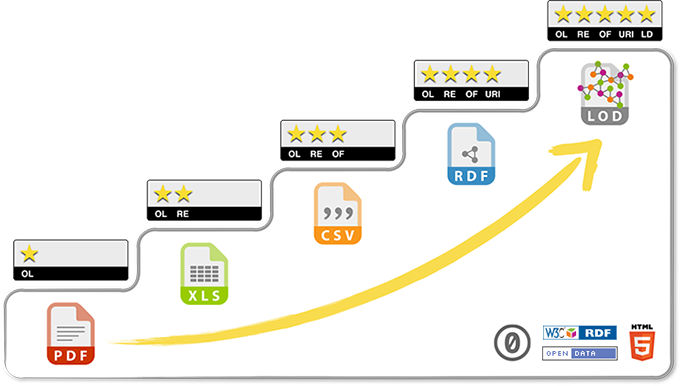
Might be worth a deeper discussion with @jeffgrann, at some point.
-
-
www.imsglobal.org www.imsglobal.org
-
The IMS Global Competencies and Academic Standards Exchange™ specification (CASE)™ is used to exchange information about learning and education competencies. CASE also transmits information about rubrics, criteria for performance tasks, which may or may not be aligned to competencies.
Interesting that they explicitly talk about tasks which may not be aligned to competencies. Leaves room for co-curricular activities and microcredentials.
-
Thanks to @jeffgrann for the heads-up! Clearly, people have been waiting for this. We’ll have to wait for the concrete results (not all IMS Global activities make as big of a splash as the others). But it’s very interesting. And needed. For instance, Quebec uses a competencies model all the way to higher education (its Cégeps are post-secondary institutions for vocational training and pre-university education). Thing is, they lack consistent frameworks. CASE won’t make these magically appear, but at least it gives them room for impact.
-
- Oct 2017
-
www.homelandsecuritynewswire.com www.homelandsecuritynewswire.com
-
A computer simulation of refugees’ journeys as they flee major conflicts can correctly predict more than 75 percent of their destinations, and may become a vital tool for governments and NGOs to help better allocate humanitarian resources.
-
-
knowledge.kaltura.com knowledge.kaltura.com
-
CreatingaRuleBasedPlaylist
-
- Sep 2017
-
rampages.us rampages.us
-
knowledge-based economy
What do we mean by knowledge based economy?
-
- Aug 2017
-
www.edutopia.org www.edutopia.org
-
Project-based learning typically is grounded in the following elements: Role-playing Real-world scenarios Blended writing genres Multiple reading genres Authentic assessments Authentic audiences Real-world expertise brought into the classroom Units that assess multiple skills Units that require research and comprehension of multiple subjects Student choice Collaboration Multiple methods of communication (writing, oral speaking, visual presentations, publishing, etc.)
A good overview of the elements of PBL.
-
- Mar 2017
-
scalar.usc.edu scalar.usc.edu
-
Acknowledging prior learning
"Students come to the classroom with preconceptions about how the world works. If their initial understanding is not engaged, they may fail to grasp the new concepts and information that are taught, or they may learn them for purposes of a test but revert to their preconceptions outside the classroom". How People Learn
Examples: Harvard graduates talk about: seasons electricity mass of trees 3:50
"A critical feature of effective teaching is that it elicits from students their preexisting understanding of the subject matter to be taught and provides opportunities to build on—or challenge—the initial understanding."
-
Metacognition activities in support of metacognitive practices
This is a basic principle from the researh presented in How People Learn
-
Formative Assessment
Another Basic Principle from learning research.
-
Community Centered
-
- Jan 2017
-
www.edutopia.org www.edutopia.org
-
PBL is the ongoing act of learning about different subjects simultaneously. This is achieved by guiding students to identify, through research, a real-world problem (local to global) developing its solution using evidence to support the claim, and presenting the solution through a multimedia approach based in a set of 21st-century tools.
Interesting look at PBL and 21st century learning
-
PBL is the ongoing act of learning about different subjects simultaneously. This is achieved by guiding students to identify, through research, a real-world problem (local to global) developing its solution using evidence to support the claim, and presenting the solution through a multimedia approach based in a set of 21st-century tools
Interesting look at PBL AND 21st century learning.
-
- Dec 2016
-
www.knightfoundation.org www.knightfoundation.org
-
Fact-based journalism now competes with false information for our attention while our cities and citizens become both more connected by technology and more divided by ideology and income. The values reflected in lines of code, whether it be at the ATM, when we search on internet or drive a car, are already affecting what we think, what we do and what information we share with those around us.
-
-
www.propublica.org www.propublica.org
-
The ubiquitous social network not only allows advertisers to target users by their interests or background, it also gives advertisers the ability to exclude specific groups it calls “Ethnic Affinities.”
why aren't we seeing more about this in the news?? How is this not ILLEGAL???
-
- Aug 2016
-
www.elearnspace.org www.elearnspace.org
-
Content is the least stable and least valuable part of education.
-
- Jun 2016
-
www.atlantamagazine.com www.atlantamagazine.com
-
Title: What is it? An oral history of Izzy, the mascot marketing snafu of Olympic proportions - Atlanta Magazine
Keywords: fantastic mascot—cobi, public appearances—, bob cohn, atlanta-based artist, york city, billy wanted, spanish art, children thought, vice president, senior director, blue blob, acog spokesperson, billy looked, easy character, olympic city, olympic games, olympic bid, question billy
Summary: <br>Bob Cohn, cofounder of public relations agency Cohn & Wolfe, member of Payne’s mascot committee: In Barcelona in 1992, they had a fantastic mascot—Cobi, who was typical of Spanish art and filled with creativity.<br>Some of them wrote us back letters [that essentially said] “The nerve!” or “We’re not doing anything for nothing.”<br>So it couldn’t be characters that existed in Georgia lore.<br>Somebody sent us a deer.<br>John Ryan, then senior director at DESIGNefx, the animation division of Crawford Communications: The basic job was to design something that would appeal to children and broadly on a world stage.<br>Photograph by Rich Mahan/Atlanta Journal-Constitution via AP<br>It wore five Olympic rings—two on its eyes and three on its tail—and oversized sneakers nearly half the size of its body.<br>Bob Brennan, then ACOG spokesperson: Billy Payne wanted to do something modern, reflective of the technological world we lived in.<br>You had movies like Jurassic Park, Total Recall.<br>Shuman: I received Hi-Rez right at the deadline, a Friday.<br>When Billy looked at that [proposal], he said, “Gee whiz, wow.<br>Payne: As CEO of the Olympic Games, I felt it was both our responsibility and within my authority to make whatever decisions needed to be made.<br>Shuman: By the time I got back on Monday afternoon, Ginger told me Billy had made his decision.<br>Were we raising enough money?<br>Shuman: You didn’t question Billy.<br>Payne: The logical question that you would ask on seeing it is “What is it?” I guess we just said, “Well, we should just put it into one word.”<br>Shuman: The name, Whatizit, was almost worse than the character itself.<br>Does it all run together?<br>Ryan: We had to have [final] designs submitted by March [1992], knowing it’d be debuted in August at the Barcelona Games.<br>It really looked funky.<br>In a huge stadium it can’t be little.<br>Shuman: To generate interest about the mascot, we did these billboards all over town saying, “Whatizit?” We built up this huge anticipation.<br>Ryan: It was made very clear that if secrecy was violated, Crawford could lose future contracts.<br>Photograph courtesy of Harry Shurman<br>Meanwhile an amorphous animated character filled the stadium’s video monitors.<br>Evans: I took the field with Gregg Burge, the famous New York [tap] dancer.<br>Joel Babbit, CEO of the Narrative Content Group, veteran ad exec who worked with Payne to promote the Olympic bid, and City Hall’s first-ever chief marketing and communications officer under Jackson: If Maynard had an opinion, he kept it to himself.<br>“How do you say ‘Whatizit’ in Mandarin?”<br>Like, this is it?<br>Completely and totally horrified.<br>They’re complaining: This is terrible.<br>But [ACOG] had a lot riding on the mascot financially from license sales.<br>Robert Hollander, then ACOG’s vice president of licensing: My heart dropped into my stomach.<br>Hula: It’s something that’s supposed to evoke an image of Atlanta, the host city, and it really didn’t do that at all.<br>We didn’t even think we were compelled to do something that would make somebody in Australia say, “That mascot must be from Atlanta, Georgia.” It never crossed our minds.<br>It was sort of like a bigger Charlotte.<br>Photograph courtesy of R. Land<br>Ronnie Land, an Atlanta-based artist, better known as R. Land, who has made Izzy-inspired art: This was our “Hey, world, we’re Atlanta” moment.<br>LaTara Smith (née Bullock), ACOG’s “project coordinator for Izzy appearances” during the Olympics: I’ve heard everything from toothpaste to blue blob.<br>Hiskey: People were going to focus on the crazy blue thing because there wasn’t a lot of other cool stuff here.<br>Bob Hope, president of Atlanta-based public relations firm Hope-Beckham Inc.: I thought [Billy] briefly lost his mind.<br>Kevin Sack, a New York Times reporter based in Atlanta, wrote in a 1996 story that “[i]t is precisely Izzy’s nothingness that has unwittingly made him an apt symbol for this Olympic city.<br>Whatizit’s costume made Mike Luckovich’s punchline.<br>People were embarrassed [by Whatizit].<br>You wish people would look at the good stuff instead of focusing on the minutiae and losing the big picture.<br>Campbell: I suspect I hurt some people’s feelings.<br>Photograph by Raymond McCrea Jones<br>ACOG officially retired Whatizit in October 1993.<br>It worked.<br>Babbit: I liked the name Izzy.<br>Jacqueline Blum, senior vice president of Film Roman, the animation studio behind The Simpsons, King of the Hill, and Garfield and Friends, which produced an Izzy cartoon for TV: Izzy was a character created by committee.<br>Ryan: You got into a scenario where you have multiple art directors and bosses.<br>Hope: [Izzy was] like New Coke.<br>Smith: Izzy developed a nose.<br>Shuman: We had these stars coming out of his tail at one point.<br>I raised my hand and said, “Maybe not?” They left the shoes the way they are.<br>The costume had to get softer.<br>Evans: Children loved the mascot.<br>I’d guess probably close to 15 percent.<br>Watkins: I’m guessing [the bestselling item] would be the doll that was 12 inches that could be carried under a kid’s arm.<br>Lounge chair pillows.<br>Shuman: Billy wanted to market the shoes.<br>Blum: It’s not a particularly easy character to animate.<br>Hollander: Our broadcast partner, NBC, had gotten out of the children’s program business.<br>Watkins: They created an Izzy balloon that flew in New York City in the Macy’s Thanksgiving Day Parade.<br>Photograph by Caroline C. Kilgore<br>Evans helped create a mascot program that recruited volunteers through auditions.<br>Smith: By the time the Olympics came around, we had upwards of 20 Izzys that could be in different places at one time.<br>I asked [Izzy], “How does one become the mascot?” They were having tryouts the next weekend.<br>Don’t exclude children.<br>For example, Izzy loved everyone, so whether it was a critic or a fan, you didn’t show any negative emotion.<br>Izzy had a size 22 sneaker, so you had to fit your shoe inside Izzy’s shoe, inside another little pocket, and be able to walk around in his big feet.<br>Jay: You entered through the top of his mouth.<br>Smith: A lot of children thought it would be fun to swing on the tail.<br>Evans: The lighting bolt eyebrows and rings on the tail were prime targets for being pulled, punched, or ripped off for a souvenir.<br>Smith: Handlers began watching the perimeter.<br>Photograph courtesy of Harry Shuman<br>Is he still waiting for a shuttle bus?<br>Smith: We took over one of the Olympic headquarters offices.<br>Other times it would be outside as a crowd-pleaser.<br>Jay: We were instructed to wear the Izzy costume 30 minutes on, 30 minutes off, because you would sweat.<br>Wilsterman: There were two fans at the top of Izzy’s head [inside the costume].<br>I was able to whisper into a little microphone that went into the escort’s ear.<br>Smith: Izzy didn’t talk.<br>Izzy didn’t do public appearances—only [ones for] ticketed sponsors.<br>Brennan: I don’t think Izzy showed up at the closing ceremony.<br>Jay: When the flame went out, so did Izzy.<br>The question came up: Can someone dress up in the Izzy costume to greet visitors in the Atlanta History Center?<br>Photograph courtesy of LaTara Smith<br>Smith: I still have one of the Izzy costumes.<br>Payne: People didn’t like it.<br>I never lost my enthusiasm for Izzy.<br>Was it the greatest experience of my life?<br>Evans: I do appreciate the originality and willingness to do something different.<br>Land: Atlanta tries so hard to be what we think the world wants to view us as.<br>Shuman: Izzy was kind of like Colony Square—a little bit before his time.<br>Smith: It would’ve been easier to have a phoenix.<br>It didn’t say anything.<br>Babbit: It doesn’t matter what it was.<br>It was bizarre.<br>An image of Izzy?<br>Shuman: Usually everything Billy touched turned to gold.<br>This article originally appeared in our July 2016 issue.<br>Tags: 1996 Atlanta Olympics, 1996 Olympics, Atlanta Olympics, Billy Payne, Izzy, John Ryan, Olympics, R. Land, Whatizit<br>
-
- May 2016
-
www.isetl.org www.isetl.org
-
Wenzler and Cartier (1999) make an effective case for the use of games in organizational learning by asserting that “Games and simulations help organizations develop symbolic thinking and gestalt understanding; help them create memories of the future; enable shared experiences and the building of shared intelligence; and, possibly most important, develop their members' motivation and confidence to act,” (p. 375). A number of books and manuals (e.g., Pike & Busse, 1995; Stolovich & Keeps, 2002; Thiagarajan, 2003) advocate this kind of learner or trainee involvement
Really nice quote and several sources on the utility of games in corporate training. I don't see why these same principles couldn't be applied in higher ed setting.
-
Cruickshank, D. R., & Telfer, R. (2001). Classroom games and simulations. Theory into Practice, 19(1), 75-80.
I should get a copy of this
-
Games promote transfer because they require student participation and active involvement with the material within a rich context (Cruickshank & Telfer, 2001).
Games promote transfer is an assertion rather than evidence based argument. I hope Cruickshank and Telfer provide the evidence.
-
In the second part of the study, five faculty members were mentored to change traditional lectures to interactive games. A review of their perceptions of success and difficulty in using such activities in the college classroom, their students’ perceptions of the exercise, and student performance identified both benefits and costs. Suggestions are made for strategies to successfully implement games in the college classroom, based on consideration of these benefits and costs and the survey results.
It sounds like there was some PD on game based teaching and then an evaluation of how well the faculty applied games in their classrooms.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
elearningwiki.com elearningwiki.com
-
Competency-based learning
-
- Mar 2016
-
www.edsurge.com www.edsurge.com
-
Team-based, contextualized learning underlies the instruction for each track;
-
- Sep 2015
- Feb 2014
-
s3.amazonaws.com s3.amazonaws.com
-
The innate qualities of intellectual pr operty, however, in combination with INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY: POLICY FOR INNOVATION 15 strong economic motivations have led U.S. intellectual property policy to operate according to rights - based, non - utilitarian theory, possibly as a result of lobbying (capture theory).
Lobbying has led to a rights-based non-utilitarian theory copyright policy in the US at the present time (2014).
-
The “romantic conception of authorship” mentioned earlier as a formative trend of the rights - based theory of intellectual property is evident in the first pe rspective: t he notion that ideas are individual achievements and of indeterminate origin (not reliant on a process of building) (Fisher, 1999, Sect. II. B).
-
-
euro.ecom.cmu.edu euro.ecom.cmu.edu
-
Ho w to R ead a Judicia l Opin ion: A G uid e for N ew L aw Stu den ts Professor Orin S. Kerr George Washington University Law School Washington, DC Version 2.0 (August 2005) This essay is desig ned to help entering law students understand ho w to read cas es for class. It explains what judicial opinions are, how they are structured, and what you should look for when you read them. Part I explains the various ingredients found in a typical judicial opinion, and is the most essential section of the essay . Par t II discusses what you should look for when you re ad an opinion for class. Part II I con clu des with a brief discussion of why law schools use the case method.
I need a way to add tags to a document that will apply to all annotations in a particular document (except where explicitly canceled).
The problem is that I often want to query all annotations related to a specific document, collection of documents, or type of activity.
Type of activity requires further explanation: Given a document or collection of documents I may annotate the document for different reasons at different times.
For example, while annotating the reading materials, video transcripts, and related documents for the CopyrightX course there are certain types of annotations that may be "bundled together" so that when I search for those things later I can easily narrow my searches to just that subset of annotations; but at the same time I need a way to globally group things together.
While reading judicial opinions the first activity/mode of interaction with a particular document may be to identify the structure of the judicial opinion (the document attached to this annotation describes the parts of the judicial opinion I might want to identify: *caption, case citation, author, facts of the case, law of the case, disposition, concurring and/or dissenting opinions, etc).
The above-described mode I may use for multiple documents in one session related to the course syllabus for the week.
To connect each of these documents together I might add the tags: copyx (my shorthand for the name of the course, CopyrightX), week 1 (how far into the course syllabus), foundations (the subject matter in the syllabus which may span week 1, week 2, etc), judicial opinions (the specific topic I am focused on learning at the moment (may or may not be related to the syllabus).
Later on another day I might update my existing annotations or add new ones when I am preparing to study for an exam. I might add tags like to study, on midterm, on final to mark areas I need to review.
After the exam I might add more tags based on my test score, especially focusing on areas that received a poor score so I can study that section more or, if I missed some sections so didn't study and it resulted in a poor score in that area, add tags to study for later if necessary.
I have many more examples and modes of interaction in mind that I can explain more later, but it all hinges on a rich and flexible tagging system that:
- allows tagging a document once in a way that applies to all annotations in a document
- allows tagging a session once in a way that applies to all annotations in all documents connected to a particular session
- allows tagging a session and/or a document that bundles together new tags added to an annotation (e.g. tags for grammar/spelling, tags for rhetological fallacy classification, etc)
- fast keyboard-based selection of content
- batch selection of annotation areas with incremental filling-- I may want to simply select all the parts of a document to annotate first and then increment through each of those placeholders to fill in tags and commentary
- Mark multiple sections of the document at once to combine into a single annotation
- Excerpting only parts of a text selection, but still carry the surrounding textual context with the excerpt to easily expose the surrounding context when necessary
- A summary view of a document that is the result of remixing parts of the original document with both clarifications or self-containing summary re-writes and/or commentary from the reader
- structural tagging vs content tagging
-