There is a value in reading a lot.. But it's not in the number, it is more in the concept of Exploration vs. Specialization. Some form of exploration is highly useful.
- Jun 2024
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
- Mar 2024
-
Local file Local file
-
The development of the card system and itsmore universal adoption within recent years isundoubtedly due in the mail to the development in modernbusiness and factory organisation ; it may be regarded as anoffspring of manufacture in quantities. (Massenfabrikation, Gross-industrie.) The recognised principle in manufacture in quantities ismaximum of output with minimum of labour. The means to attainthis end is specialisation, which in its turn yields greater precisionand accuracy as it^ result. All this is equally applicable to thecard system, and the last factor, greater precision and accuracy,is one of its most conspicuous claims.
Julius Kaiser contemporaneously posits that mass manufacture and maximizing efficiency (greater output for minimum input) are the primary drivers of card index system use in the early 20th century. These also improve both precision and accuracy in handling information which allow for better company or factory operation, which would have been rising concerns for businesses and manufacturing operations at the rise of scientific management during the time period.
-
- Aug 2023
-
-
Imagine the younger generation studying great books andlearning the liberal arts. Imagine an adult population con-tinuing to turn to the same sources of strength, inspiration,and communication. We could talk to one another then. Weshould be even better specialists than we are today because wecould understand the history of our specialty and its relationto all the others. We would be better citizens and better men.We might turn out to be the nucleus of the world community.
Is the cohesive nature of Hutchins and Adler's enterprise for the humanities and the Great Conversation, part of the kernel of the rise of interdisciplinarity seen in the early 2000s onward in academia (and possibly industry).
Certainly large portions are the result of uber-specialization, particularly in spaces which have concatenated and have allowed people to specialize in multiple areas to create new combinatorial creative possibilities.
-
The mathematical specialist, for example, canget further faster into the great mathematicians than a readerwho is without his specialized training. With the help ofgreat books, specialized knowledge can radiate out into agenuine interfiltration of common learning and common life.
Here Hutchins is again prefiguring C.P. Snow's "two cultures". He makes the argument that by having a shared base of knowledge and culture in our society's past history of knowledge (and especially early scientists and mathematicians), everyone, despite their individual interests and specializations, can be an active participant in a broader human conversation.
-
The task is to have a communitynevertheless, and to discover means of using specialties topromote it. This can be done through the Great Conversa-tion.
We need some common culture to bind humanity together. Hutchins makes the argument that the Great Conversation can help to effectuate this binding through shared culture and knowledge.
Perhaps he is even more right in the 2000s than he was in the 1950s?
-
I should like to add that specialization, instead of makingthe Great Conversation irrelevant, makes it more pertinentthan ever. Specialization makes it harder to carry on anykind of conversation; but this calls for greater effort, not theabandonment of the attempt.
The dramatic increase in economic specialization of humanity driven by the Industrial Revolution has many benefits to societies, but it also has detrimental effects when the core knowledge and shared base of the society is lost.
Certainly individuals have a greater reliance on specialists for future outcomes (think about the specialization of areas like climate science which can have destructive outcomes on all of humanity or public health outcomes with respect to vaccines and specialized health care delivery), but they also need to have a common base of knowledge/culture and the ability to think critically for themselves to be able to effect necessary changes, particularly when the pace of those changes is more rapid than humans have generally been evolved to accept them.
-
Do science, technology, industrialization, and specializa-tion render the Great Conversation irrelevant?
Tags
- The Great Conversation
- resurgence of the humanities
- the commons
- trust
- knowledge specialization
- economic specialization
- specialization
- death of the humanities
- Robert Maynard Hutchins
- interdisciplinary research
- education policy
- combinatorial creativity
- industrialization
- eudaimonia
- rapid changes
- human resources
- evolution
- Mortimer J. Adler
- humanities
- Democracy
- shared culture
- interdisciplinary studies
- two cultures
Annotators
-
- Jan 2023
-
laudatortemporisacti.blogspot.com laudatortemporisacti.blogspot.com
-
Basil Lanneau Gildersleeve, "Brief Mention," American Journal of Philology 20.1 (1899) 108-113 (at 108): With all our advance in scientific astronomy, the average modern man is not so familiar with the sky as was his antique brother, and some of the blunders in modern works of fiction that are scored from time to time in scientific journals would hardly have been possible for a ploughman of antiquity, not to say a sailor. The world needs every now and then a reminder that the modern head holds different things from the ancient brain-pan, not necessarily more.
How painfully true this may have been in 1899, it's now much worse in 2023!
Specialization of knowledge tends to fit the lifeways of the people who hold and maintain it. Changing lifeways means one must lose one or more domains and begin using or curating different domains of knowledge.
In a global world of specialization, humans who specialize are forced to rely more heavily on the experience and veracity of those around them who have also specialized. One may be able to have a Ph.D. in astrophysics, but their knowledge of the state of the art in anthropology or economic policy may be therefore utterly undeveloped. As a result they will need to rely on the knowledge and help of others in maintaining those domains.
This knowledge specialization means that politicians will need to be more open about what they think and say, yet instead politicians seem to be some of the least knowledge about almost anything.
This is just the start of a somewhat well-formed thesis I've developed elsewhere, but not previously written out... more to come...
-
- Nov 2022
-
developer.mozilla.org developer.mozilla.org
-
A File object is a specific kind of Blob, and can be used in any context that a Blob can.
-
- Oct 2022
-
stephanango.com stephanango.com
-
By becoming a hybrid you can choose how you want to be unique. Countless unique combinations are available to you.
-
Being U-shaped requires bravery, because it’s so unusual. U-shaped people tend to be subjected to greater skepticism, because no one else really understands what they alone can see.
Advantage of U-shaped hybrid
-
T-shaped. They tend to be natural leaders because they understand how different responsibilities overlap, and how to construct effective teams and processes.
Advantage of T-shaped hybrid
-
The U-shaped path means developing skills that are not often found together. Like engineering and dancing, or singing and design.
U-shaped hybrid type of specialization
-
The T-shaped hybrid path is one that many curious people follow. You grow your skillset and experience in areas that are adjacent to your dominant expertise. For example engineering and design, or singing and dancing.
T-shaped hybrid type of specialization
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Aug 2022
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Livan, G., Pappalardo, G., & Mantegna, R. N. (2021). Quantifying the relationship between specialisation and reputation in an online platform. ArXiv:2111.07144 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2111.07144
-
- Jun 2022
-
davidepstein.com davidepstein.com
-
WHY GENERALISTS TRIUMPH IN A SPECIALIZED WORLD “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes ‹›
Many university presidents site the value of basic research to fuel the more specialized research spaces.
Example: we didn't have any application for x-rays when their basic science was researched, but now they're integral to a number of areas of engineering, physics, and health care.
What causes this effect? Is it the increased number of potential building blocks that provide increased flexibility and complexity to accelerate the later specializations?
Link this to: https://hyp.is/-oEI3OF5EeybM_POWlI9WQ/www.maggiedelano.com/garden/helpful-books
-
- Oct 2021
-
-
The Bauhaus began with the metaphor of a church and the Lyonel Feininger depiction of a modern cathedral as a symbol for a new faith in the synthesis of art and technology.
The fusion of art, technology, and spirituality has been the foundation of my thinking as a designer as I have explored design practice, design education, and design philosophy.
We mistakenly focused on physical artifacts without fully realizing—and questioning—the values that were being embodied in architecture, built to reinforce our habits and behaviours into social, economic, and political systems. Technology has enabled us to scale, accelerate, and amplify these systems to envelope the globe.
We have been engaged in social architecture, a form of metaphysical design. It has been a form of colonization that has been built on individualism, specialization, and authoritarianism.
-
-
bauhouse.medium.com bauhouse.medium.com
-
Social: learned helplessness (individuality)Economic: trained incapacities (specialization)Political: bureaucratic intransigence (authoritarianism)
The neoliberal world order is designed to serve a colonial system of capitalist extraction that only benefits the 1%.
- Social: learned helplessness (individuality)
- Economic: trained incapacities (specialization)
- Political: bureaucratic intransigence (authoritarianism)
-
accountability, reparations, and radical social change
The mechanisms of our compliance with the dominant system are designed into the system:
- Social: learned helplessness (individuality)
- Economic: trained incapacities (specialization)
- Political: bureaucratic intransigence (authoritarianism)
-
-
www.cbc.ca www.cbc.ca
-
Academia: All the Lies: What Went Wrong in the University Model and What Will Come in its Place
“Students are graduating into a brutal job market.”
The entreprecariat is designed for learned helplessness (social: individualism), trained incapacities (economic: specialization), and bureaucratic intransigence (political: authoritarianism).
The Design Problem
Three diagrams will explain the lack of social engagement in design. If (in Figure 1) we equate the triangle with a design problem, we readily see that industry and its designers are concerned only with the tiny top portion, without addressing themselves to real needs.
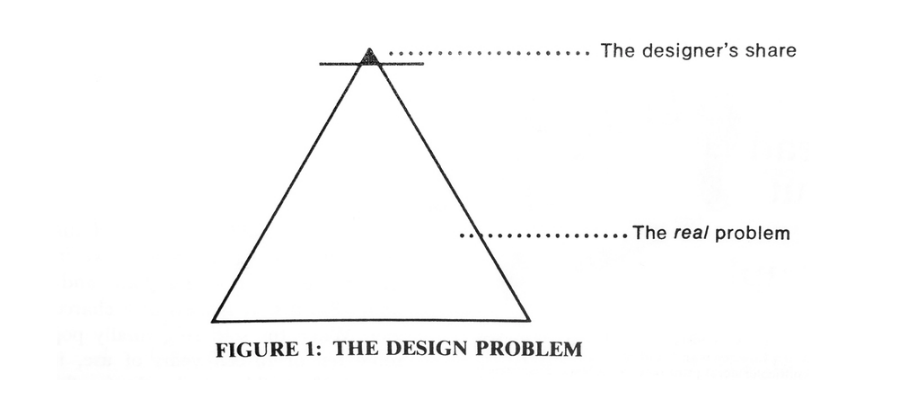
(Design for the Real World, 2019. Page 57.)
The other two figures merely change the caption for the figure.
- Figure 1: The Design Problem
- Figure 2: A Country
- Figure 3: The World
-
- Sep 2021
-
sakai.duke.edu sakai.duke.edu
-
mill dam, attending a Baptist association and a public hanging.56 This general irregularity must be placed within the irregular cycle of the working week (and indeed of the working year) which provoked so much lament from moralists and mercantilists in the seventeenth and eighteenth centu
The irregularity of the work day of the common people in the 17th and 18th centuries ran counter to the desires of both moralists and mercantilists.
What might this tension tell us about both power structures both then and today?
While specialization since that time has increased the value of goods we produce, does it help in the value of our lives and happiness?
-
- Feb 2021
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Atkisson, C., & Finn, K. (2020). Redundant relationships in multiplex food sharing networks increase food security in a nutritionally precarious environment. ArXiv:2011.12817 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2011.12817
-
- Jan 2021
-
-
This syntax easily provides all the features of components, like let: bind: and on:. <svelte:fragment /> is just a component with a special name.
-
- Dec 2020
-
www.whatech.com www.whatech.com
-
And then it will help you choose a specialization in the field that you like.
-
Find Your Passion, Then Monetize It The
-
Try a little of everything, and then choose a specialization. Money is not the most important thing. You need to LOVE your activity! But you don't know what you like until you try it.
-
- Nov 2020
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
There is a growing mountain of research. But there is increased evidence that we are being bogged down today as specialization extends. The investigator is staggered by the findings and conclusions of thousands of other workers—conclusions which he cannot find time to grasp, much less to remember, as they appear. Yet specialization becomes increasingly necessary for progress, and the effort to bridge between disciplines is correspondingly superficial.
As scientific progress extends into increased specializations, efforts at integrating across disciplines are increasingly superficial.
-
Professionally our methods of transmitting and reviewing the results of research are generations old and by now are totally inadequate for their purpose. If the aggregate time spent in writing scholarly works and in reading them could be evaluated, the ratio between these amounts of time might well be startling. Those who conscientiously attempt to keep abreast of current thought, even in restricted fields, by close and continuous reading might well shy away from an examination calculated to show how much of the previous month's efforts could be produced on call. Mendel's concept of the laws of genetics was lost to the world for a generation because his publication did not reach the few who were capable of grasping and extending it; and this sort of catastrophe is undoubtedly being repeated all about us, as truly significant attainments become lost in the mass of the inconsequential.
Specialization, although necessary, has rendered it impossible to stay up to date with the advances of a field.
-
- Sep 2020
-
github.com github.com
-
The same as the mixed() schema required, except that empty strings are also considered 'missing' values.
-
- May 2020
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Holcombe, A. (2019). Farewell authors, hello contributors. Nature, 571(7764), 147–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-02084-8
-
- Nov 2018
-
-
edical specialization dates back at least to the time of Galen. For most of medicine’s history, however, the boundaries of medical fields have been based on factors such as patient age (pediatrics and geriatrics), ana-tomical and physiological systems (ophthalmology and gastroenter-ology), and the physician’s tool-set (radiology and surgery). Hos-pital medicine, by contrast, is defined by the location in which care is delivered. Whether such delineation is a good or bad sign for physicians, patients, hospitals, and society hinges on how we understand the interests and as-pirations of each of these groups
-
- Oct 2017
-
www.paulgraham.com www.paulgraham.com
-
The most valuable insights are both general and surprising. F = ma for example.
Why is this surprising? It is a definition. A force is what causes an acceleration.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-