(14:20-19:00)
Dopamine Prediction Error is explained by Andrew Huberman in the following way: When we anticipate something exciting dopamine levels rise and rise, but when we fail it drops below baseline, decreasing motivation and drive immensely, sometimes even causing us to get sad. However, when we succeed, dopamine rises even higher, increasing our drive and motivation significantly... This is the idea that successes build upon each other, and why celebrating the "marginal gains" is a very powerful tool to build momentum and actually make progress. Surprise increases this effect even more: big dopamine hit, when you don't anticipate it.
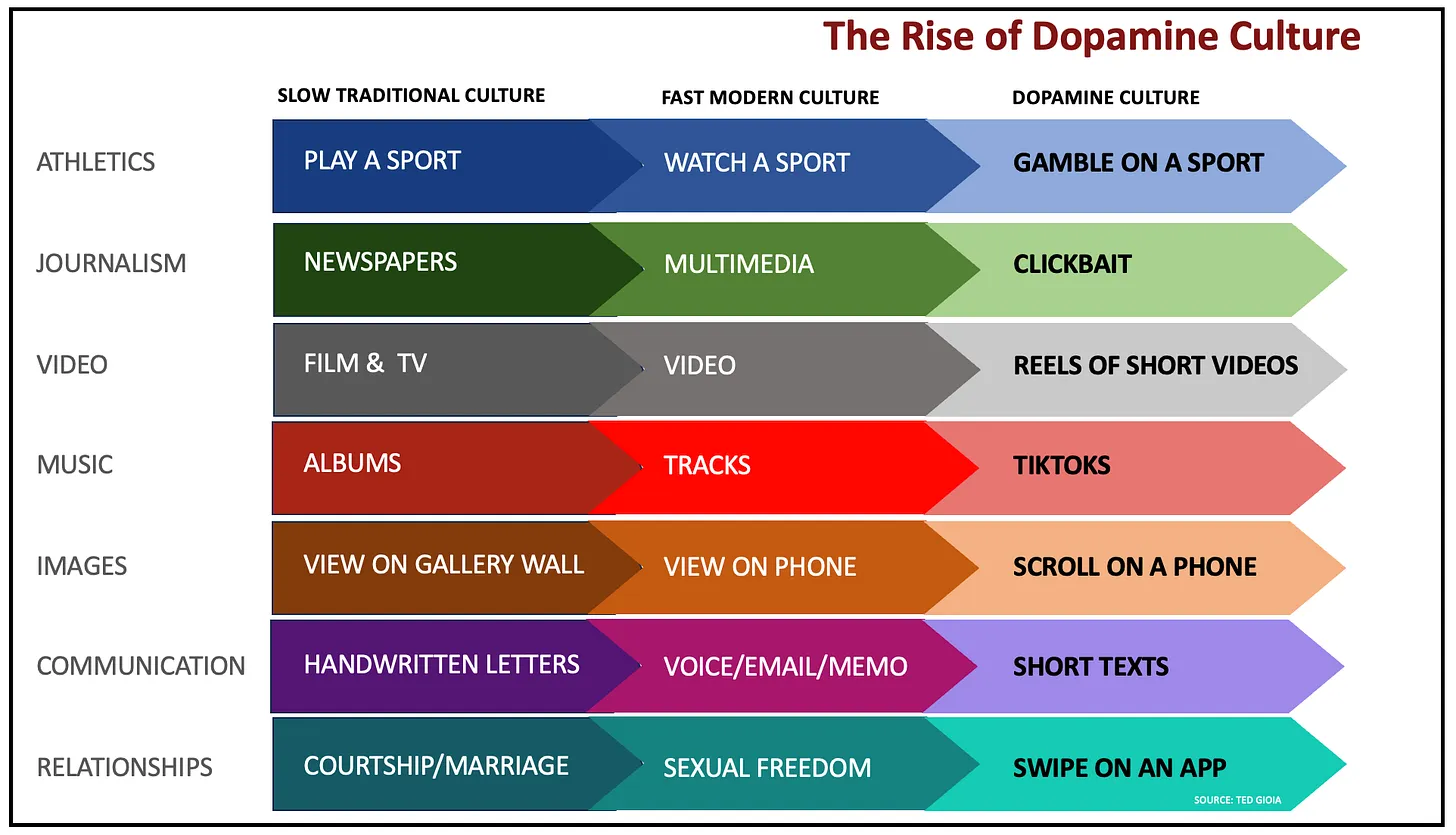
Social Media algorithms make heavy use of this principle, therefore enslaving its user, in particular infinite scrolling platforms such as TikTok... Your dopamine levels rise as you're looking for that one thing you like, but it drops because you don't always have that one golden nugget. Then it rises once in a while when you find it. This contrast creates an illusion of enjoyment and traps the user in an infinite search of great content, especially when it's shortform. It makes you waste time so effectively.
This is related to getting the success mindset of preferring delayed gratification over instant gratification.
It would be useful to reflect and introspect on your dopaminic baseline, and see what actually increases and decreases your dopamine, in addition to whether or not these things help to achieve your ambitions. As a high dopaminic baseline (which means your dopamine circuit is getting used to high hits from things as playing games, watching shortform content, watching porn) decreases your ability to focus for long amounts of time (attention span), and by extent your ability to learn and eventually reach success.
Studying and learning can actually be fun, if your dopamine levels are managed properly, meaning you don't often engage in very high-dopamine emitting activities. You want your brain to be used to the low amounts of dopamine that studying gives. A framework to help with this reflection would be Kolb's.
A short-term dopamine reset is to not use the tool or device for about half an hour to an hour (or do NSDR). However, this is not a long-term solution.