The most prolific Reader in Europe – we might call him a ‘super-contributor’ – was Hartwig Helwich, a professor at the University of Viennawho wrote out the entire Cursor Mundi onto 46,599 slips. His efforts madethe medieval poem the second-most-frequently cited work in the Dictionaryafter the Bible (though in the current OED, it has dropped to eleventh in thetop sources).
This practice of writing out everything onto slips sounds like that used later (double check the timing) by the Thesaurus Linguae Latinae in creating their slip corpus for later work.
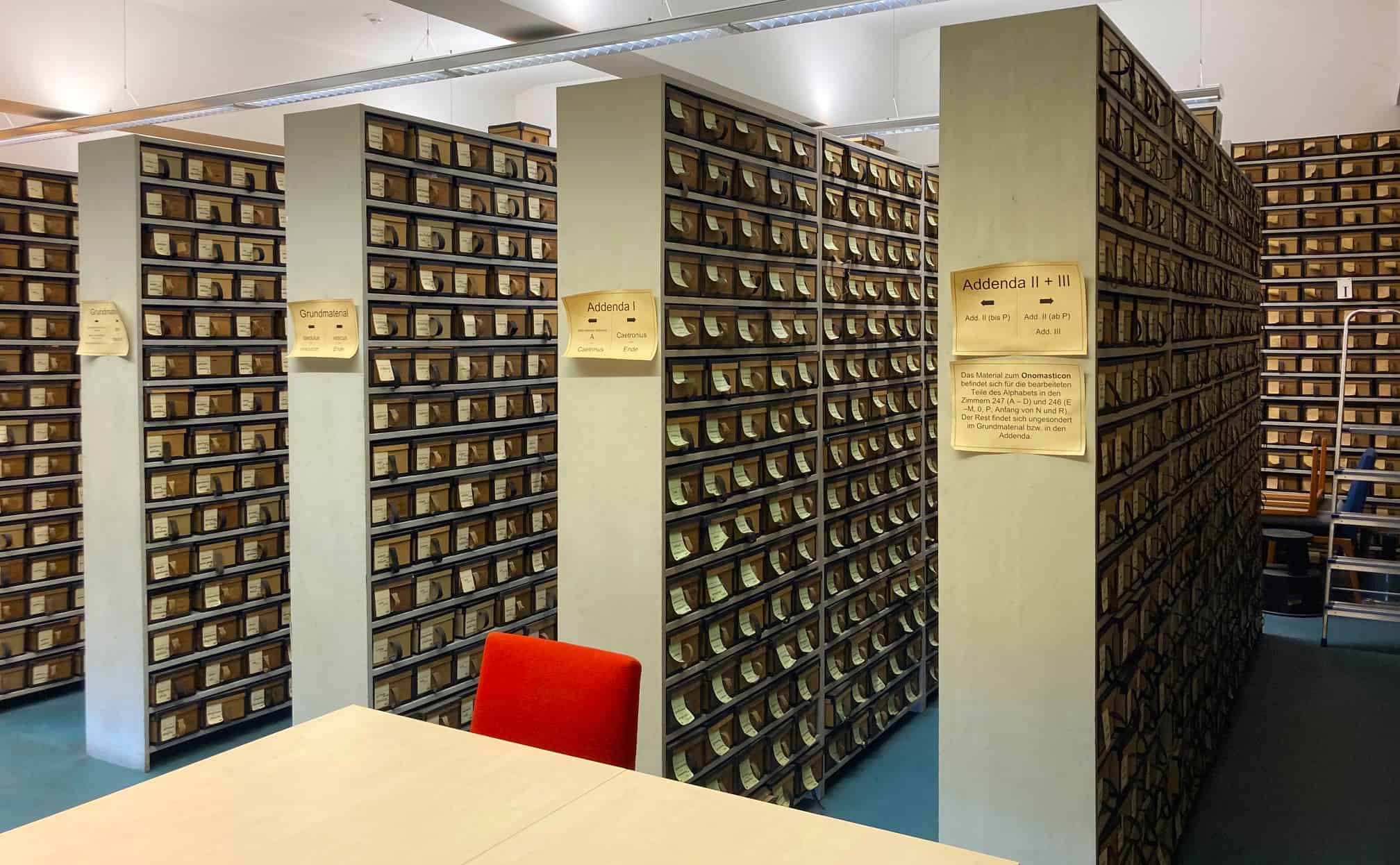








 A slip showing a passage of text from the victory stele of Sesostris III at the Nubian fortress of Semna. The handwriting is that of project leader Adolf Erman, who had "already struggled with the text as a high school student".
A slip showing a passage of text from the victory stele of Sesostris III at the Nubian fortress of Semna. The handwriting is that of project leader Adolf Erman, who had "already struggled with the text as a high school student".