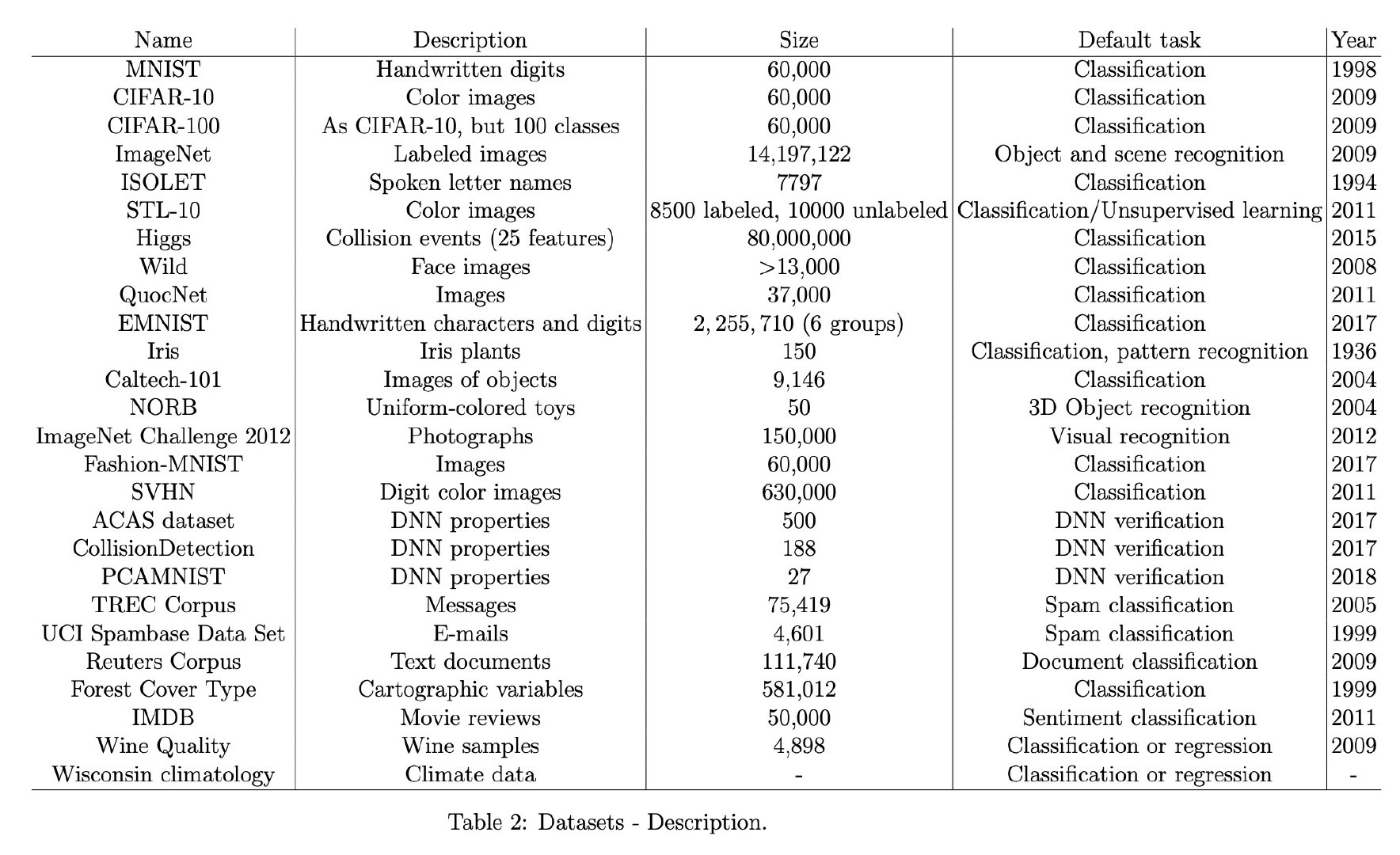
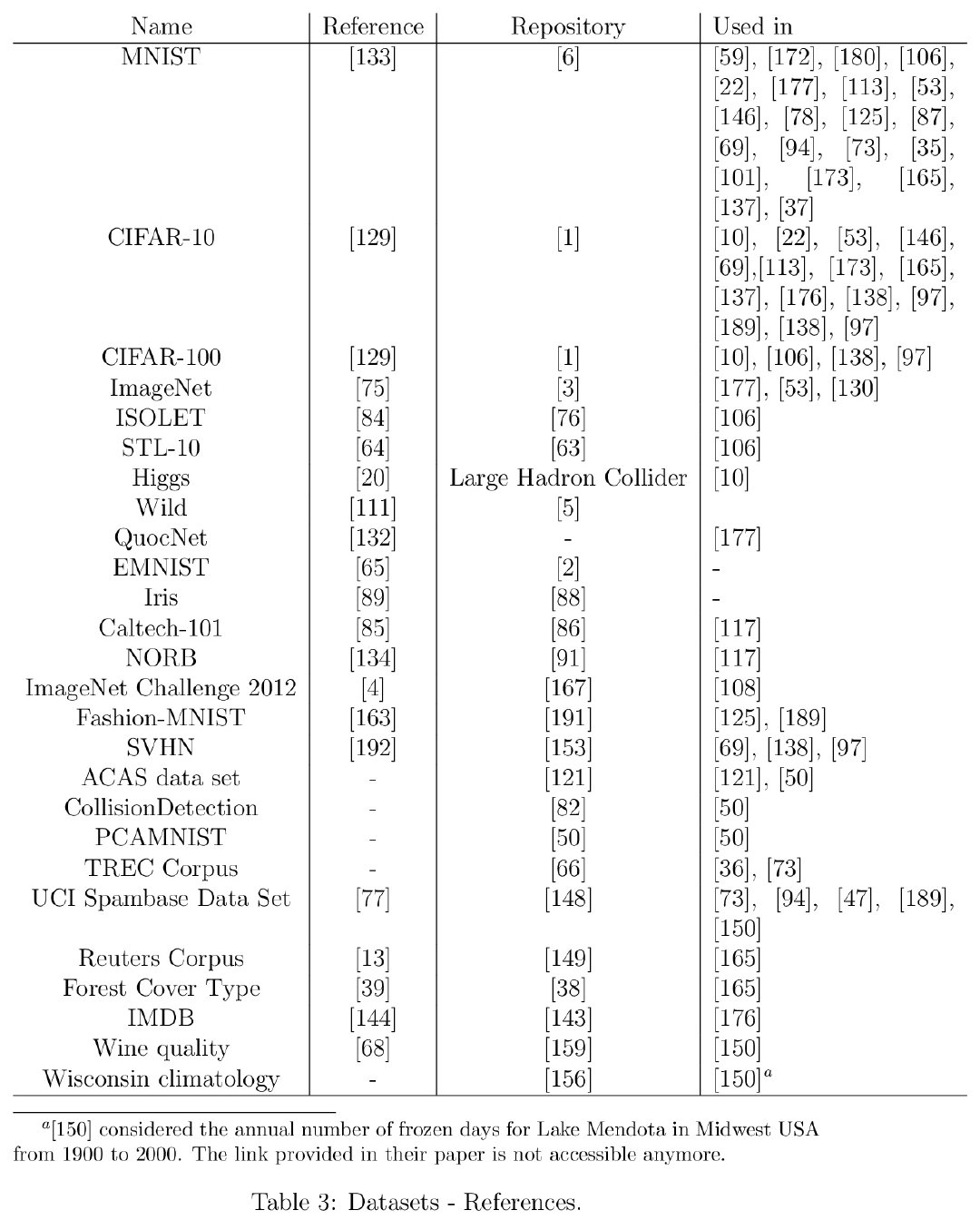
for example our standard english language model is trained with something like maybe 100 gigabytes or so of text um that gives it a strength as if you would throw bird at it with the google corpus so the other thing is of course uh a small corpus like that is computed in two hours or three hours on a on a laptop yeah so that's the other thing uh by the way i didn't mention our fingerprints are actually a boolean so when we when we train as i said we are not using floating points
for - comparison - cortical io vs normal AI - training dataset size and time