4,573 Matching Annotations
- Jun 2023
-
asistdl.onlinelibrary.wiley.com asistdl.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
searchengineland.com searchengineland.com
-
hublog.hubmed.org hublog.hubmed.org
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.vala.org.au www.vala.org.au
-
AtPew Internet such things are measured as follows v :• writing material on a social networking site such as Facebook: 57% of internetusers do that• sharing photos: 37% of internet users do that• contributing rankings and reviews of products or services: 30% of internet usersdo that• creating tags of content: 28% of internet users do that• posting comments on third-party websites or blogs: 26% of internet users dothat• posting comments on other websites: 26% of internet users do that• using Twitter or other status update features: 19% of internet users do that• creating or working on a personal website: 15% of internet users do that• creating or working on a blog: 15% of internet users do that• taking online material and remixing it into a new creation: 15% of internet usersdo that with photos, video, audio or text
Social Network activities measurement: Writing materials. Sharing Photos Contributing rankings and reviews of products or services Creating tags of content Posting comments on 3rd party websites or blogs Posting comments on other websites Using twitter or other status update features Creating or working on a personal website Creating or working on blog Taking online material and remixing into a new creation
-
-
storymaps.arcgis.com storymaps.arcgis.com
-
www.marginalia.nu www.marginalia.nu
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Information ecology as a mind tool for repurposing of educational social networks
-
- May 2023
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
psychology.cornell.edu psychology.cornell.edu
-
“Protracted immaturity and dependence on paternal care is not an unfortunate byproduct of our evolution but instead a highly adaptive trait of our species, which has enabled human infants to efficiently organize attention to social agents and learn efficiently from social output
- Quote worthy
- "“Protracted immaturity and dependence on paternal care
- is not an unfortunate byproduct of our evolution
- but instead a highly adaptive trait of our species,
- which has enabled human infants to
- efficiently organize attention to social agents and
- learn efficiently from social output,”
- “The evolutionary goal of altricial species is
- not to become highly competent as quickly as possible
- but rather to excel at learning over time.”
- "“Protracted immaturity and dependence on paternal care
- Authors
- Michael Goldstein,
- Katerina Faust,
- Samantha Carouso-Peck
- Mary R. Elson
- Quote worthy
-
- Title
- The Origins of Social Knowledge in Altricial Species,
- Journal
- The Annual Review of Developmental Psychology, - -
- Publication Date
- Dec, 2021
- Authors
- Michael Goldstein,
- Katerina Faust,
- Samantha Carouso-Peck and
- Mary R. Elson
- Title
-
-
nostr.com nostr.com
-
Nostr is a simple, open protocol that enables global, decentralized, and censorship-resistant social media.
Peter Kominski likes this generally.
-
-
-
Trakt DataRecoveryIMPORTANTOn December 11 at 7:30 pm PST our main database crashed and corrupted some of the data. We're deeply sorry for the extended downtime and we'll do better moving forward. Updates to our automated backups are already in place and they will be tested on an ongoing basis.Data prior to November 7 is fully restored.Watched history between November 7 and Decmber 11 has been recovered. There is a separate message on your dashboard allowing you to review and import any recovered data.All other data (besides watched history) after November 7 has already been restored and imported.Some data might be permanently lost due to data corruption.Trakt API is back online as of December 20.Active VIP members will get 2 free months added to their expiration date
From late 2022
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
atomicbooks.com atomicbooks.com
-
https://atomicbooks.com/pages/john-waters-fan-mail
John Waters receives fan mail via Atomic Books in Baltimore, MD.
-
-
jonudell.net jonudell.net
-
Them: So what are we really talking about here?
Me: Do you want the cosmic answer?
Them: Sure.
Me: OK. We're in the process of creating a planetary nervous system.
-
-
elijah.cs.cmu.edu elijah.cs.cmu.edu
-
firesky.tv firesky.tvFiresky2
-
app.supernormal.com app.supernormal.com
-
It's way too sophisticated for its own good. Maybe. Right. It's trying to be AI ish in the sense like it's trying to detect. If a particular comment is worthy of two points or three points, and a lot of that system is based on that. So if student makes a comment, it marks it as one. Instead of two. And you get a lot of emails about why was this Mark. And that's not the point. I Jeremy D.think Viranga P.the point of social. Is you're getting them to just have conversations. Encouraging conversations. Not necessarily to judge if that comment was good or Jeremy D.bad. Viranga P.It's just get it done. And we expect the fact that you're in the room having a conversation will help you realize, oh, this is useful. When I have a question, I can ask it here, and somebody else may have the same question. And we can have a discussion around it. And that social part. It's Social constructivism. Is helpful. Right. So people realize that they learn from other people.
Critique of Perusall as about right or wrong versus the social construction of knowledge.
-
-
erinkissane.com erinkissane.com
-
Mastodon fans know that the network absolutely cannot compete on user friendliness and basic social functionality
friendliness definitely needs to be explicitly defined here.
Have you seen the goddamned art? lol
-
Incidentally, when a straightforwardly “I’m a Nazi” Nazi showed up in the beta, people used the report function, and the Bluesky team labeled the account and banned it from the Bluesky app and restricted promotion of the account of the person who invited him. This changed exactly none of the tenor of the Nazi conversation on Mastodon, but it happened.
Now just imagine the equivalent on the scale of an entire server and you've got the story of Mastodon's incredibly centralized, swift expulsion of Gab's influence. Here's The Verge's version for the moment.
-
-
www.defenseurdesdroits.fr www.defenseurdesdroits.fr
-
Multiplier les dispositifs adaptés aux mineurs en situation de rue, allant des maraudes auxcentres sécurisés et sécurisants, et former de manière adaptée les travailleurs sociaux aurepérage et à l’accompagnement des mineurs victimes de traite des êtres humains.
-
Accroître le nombre de logements très sociaux destinés aux familles les plus précaires etdévelopper des structures de transition - de l’hébergement au logement - adaptées à l’accueilde familles avec enfants
-
-
urbanists.social urbanists.social
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Power allows people to act freely, power leading to approach motivation
"Most contemporary psychological scientists define approach motivation as the impulse to go toward positive stimuli, where stimuli are external goal objects (Lang & Bradley, 2008)."
-
Hierarchies in the correlated forms of power (resources) and status (prestige) are constants thatorganize human societies. This article reviews relevant social psychological literature andidentifies several converging results concerning power and status. Whether rank is chronicallypossessed or temporarily embodied, higher ranks create psychological distance from others, allowagency by the higher ranked, and exact deference from the lower ranked. Beliefs that status entailscompetence are essentially universal. Interpersonal interactions create warmth-competencecompensatory tradeoffs. Along with societal structures (enduring inequality), these tradeoffsreinforce status-competence beliefs. Race, class, and gender further illustrate these dynamics.Although status systems are resilient, they can shift, and understanding those change processes isan important direction for future research, as global demographic changes disrupt existinghierarchies.
Abstract
-
-
blueskyweb.xyz blueskyweb.xyz
-
www.ala.org www.ala.org
-
Coleridge was such a renowned marginaliac that his friends would actually lend their books to him so that he could scribble in the margins. Studs Turkel expected the books he loaned to friends to come back with additional marks made by friendly fingers.
-
-
daringfireball.net daringfireball.net
-
Just type in a username and password and off you go.
-
- Apr 2023
-
www.eff.org www.eff.org
-
code.google.com code.google.com
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
developers.googleblog.com developers.googleblog.com
-
indieweb.org indieweb.org
-
Publish (on your) Own Site, Syndicate Elsewhere
Publish (on your) Own Site, Spam Everywhere
-
-
atproto.com atproto.com
-
they require the original server to provide a redirect and cannot migrate the user's previous data.
This is... an extremely strange conclusion to come to regarding Social Web account migration, to say the least.
Taking Mastodon as the handy example...
The only reason to use the (extremely competent, bizarrely fast) process of redirection is that one... would like to have the "required" redirect on the original server. If a user intends to move to a different Mastodon instance and does not want to leave a redirect, that step is just... removed from the process.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.techdirt.com www.techdirt.com
-
datatracker.ietf.org datatracker.ietf.org
-
www.wired.com www.wired.com
-
As you're watching someone stream, you can leave comments, which the Broadcaster (in Periscope parlance) can see and respond to. This, Beykpour says, is the app’s real secret sauce. "The magic moment of Periscope is not when you see video for the first time," he says. "Because you’ve experienced that before, whether it’s YouTube or another live broadcasting tool. The magic moment for Periscope is when you as viewer say something and you end up influencing the broadcast."
Even since I highlighted this, some years ago, the actual tragedy of the Periscope story got so much worse...
(Including Bekypour reap Periscope for parts to build Twitter Spaces and then forget for some 10 straight days after the public commitment date to actually put it out of its misery.)
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.scielo.org.co www.scielo.org.co
-
deben mirar la infancia nosolo en sus condiciones materiales de existencia, el “aquí y ahora”, sino en suproceso de constitución histórica social, en sus formas de relación con el mundodel adulto y las formas como han sido significadas hasta convertirlas en actores/sujetos sociales, en cuanto que es desde estas construcciones que se predisponencomportamientos, actuaciones, relaciones y hasta las aspiraciones que los maes-tros como grupo social construimos en torno a los niños y las niñas, así comoson estas significaciones que definen de una u otra manera las condiciones deexistencia, de aprendizaje, las oportunidades y la vida académica de los niños.
proceso de constitución histórico social de la infancia
-
-
raindrop.io raindrop.io
-
social bookmarking option. not open source. freemium
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Benefits of sharing permanent notes .t3_12gadut._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/bestlunchtoday at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/12gadut/benefits_of_sharing_permanent_notes/
I love the diversity of ideas here! So many different ways to do it all and perspectives on the pros/cons. It's all incredibly idiosyncratic, just like our notes.
I probably default to a far extreme of sharing the vast majority of my notes openly to the public (at least the ones taken digitally which account for probably 95%). You can find them here: https://hypothes.is/users/chrisaldrich.
Not many people notice or care, but I do know that a small handful follow and occasionally reply to them or email me questions. One or two people actually subscribe to them via RSS, and at least one has said that they know more about me, what I'm reading, what I'm interested in, and who I am by reading these over time. (I also personally follow a handful of people and tags there myself.) Some have remarked at how they appreciate watching my notes over time and then seeing the longer writing pieces they were integrated into. Some novice note takers have mentioned how much they appreciate being able to watch such a process of note taking turned into composition as examples which they might follow. Some just like a particular niche topic and follow it as a tag (so if you were interested in zettelkasten perhaps?) Why should I hide my conversation with the authors I read, or with my own zettelkasten unless it really needed to be private? Couldn't/shouldn't it all be part of "The Great Conversation"? The tougher part may be having means of appropriately focusing on and sharing this conversation without some of the ills and attention economy practices which plague the social space presently.
There are a few notes here on this post that talk about social media and how this plays a role in making them public or not. I suppose that if I were putting it all on a popular platform like Twitter or Instagram then the use of the notes would be or could be considered more performative. Since mine are on what I would call a very quiet pseudo-social network, but one specifically intended for note taking, they tend to be far less performative in nature and the majority of the focus is solely on what I want to make and use them for. I have the opportunity and ability to make some private and occasionally do so. Perhaps if the traffic and notice of them became more prominent I would change my habits, but generally it has been a net positive to have put my sensemaking out into the public, though I will admit that I have a lot of privilege to be able to do so.
Of course for those who just want my longer form stuff, there's a website/blog for that, though personally I think all the fun ideas at the bleeding edge are in my notes.
Since some (u/deafpolygon, u/Magnifico99, and u/thiefspy; cc: u/FastSascha, u/A_Dull_Significance) have mentioned social media, Instagram, and journalists, I'll share a relevant old note with an example, which is also simultaneously an example of the benefit of having public notes to be able to point at, which u/PantsMcFail2 also does here with one of Andy Matuschak's public notes:
[Prominent] Journalist John Dickerson indicates that he uses Instagram as a commonplace: https://www.instagram.com/jfdlibrary/ here he keeps a collection of photo "cards" with quotes from famous people rather than photos. He also keeps collections there of photos of notes from scraps of paper as well as photos of annotations he makes in books.
It's reasonably well known that Ronald Reagan shared some of his personal notes and collected quotations with his speechwriting staff while he was President. I would say that this and other similar examples of collaborative zettelkasten or collaborative note taking and their uses would blunt u/deafpolygon's argument that shared notes (online or otherwise) are either just (or only) a wiki. The forms are somewhat similar, but not all exactly the same. I suspect others could add to these examples.
And of course if you've been following along with all of my links, you'll have found yourself reading not only these words here, but also reading some of a directed conversation with entry points into my own personal zettelkasten, which you can also query as you like. I hope it has helped to increase the depth and level of the conversation, should you choose to enter into it. It's an open enough one that folks can pick and choose their own path through it as their interests dictate.
-
-
on.substack.com on.substack.com
-
Introducing Substack Notes<br /> by Hamish McKenzie, Chris Best, Jairaj Sethi
-
In Notes, writers will be able to post short-form content and share ideas with each other and their readers. Like our Recommendations feature, Notes is designed to drive discovery across Substack. But while Recommendations lets writers promote publications, Notes will give them the ability to recommend almost anything—including posts, quotes, comments, images, and links.
Substack slowly adding features and functionality to make them a full stack blogging/social platform... first long form, then short note features...
Also pushing in on Twitter's lunch as Twitter is having issues.
-
-
blog.twitter.com blog.twitter.com
-
Real Graph is a model which predicts the likelihood of engagement between two users. The higher the Real Graph score between you and the author of the Tweet, the more of their tweets we'll include.
...who thought this was a good idea??
-
I realized after fully digesting this document that it effectively outlines a mechanism of anti-discovery.
-
-
www.schoolofmotion.com www.schoolofmotion.com
-
Anything from a small social ad to a documentary can utilize motion graphics for various benefits like comprehension and engagement.
True again. Many websites, this one included has 10+ visual graphics in the form of; videos, images and gifs. Unfortunately, they end up annoying most viewers than engaging with them if their aim is to read.
-
- Mar 2023
-
web.archive.org web.archive.org
-
Die schiere Menge sprengt die Möglichkeiten der Buchpublikation, die komplexe, vieldimensionale Struktur einer vernetzten Informationsbasis ist im Druck nicht nachzubilden, und schließlich fügt sich die Dynamik eines stetig wachsenden und auch stetig zu korrigierenden Materials nicht in den starren Rhythmus der Buchproduktion, in der jede erweiterte und korrigierte Neuauflage mit unübersehbarem Aufwand verbunden ist. Eine Buchpublikation könnte stets nur die Momentaufnahme einer solchen Datenbank, reduziert auf eine bestimmte Perspektive, bieten. Auch das kann hin und wieder sehr nützlich sein, aber dadurch wird das Problem der Publikation des Gesamtmaterials nicht gelöst.
link to https://hypothes.is/a/U95jEs0eEe20EUesAtKcuA
Is this phenomenon of "complex narratives" related to misinformation spread within the larger and more complex social network/online network? At small, local scales, people know how to handle data and information which is locally contextualized for them. On larger internet-scale communication social platforms this sort of contextualization breaks down.
For a lack of a better word for this, let's temporarily refer to it as "complex narratives" to get a handle on it.
-
-
royalsocietypublishing.org royalsocietypublishing.org
-
the problems inherent in assuming any simple individual/social learning distinction are already well understood by some researchers working on cultural evolution.
moss sponging by chmpanzees - is a phenomena observed by researchers - in which the distinction between<br /> - individual and - collective learning - is fuzzy - Sponging is a technique of wild chimpanzees - in which they use chewed up plant material - as a sponge to soak up water - One individual wild chimpanzee - named by the researchers as KW - picked up a discarded sponge used by another wild chimpanzee - which happened to have moss in it - and so developed a sponge for water specifically from moss - KW did not learn it socially from another chimpanzee - yet if it weren't for - the behavior of other chimpanzees in the group - cultural artefacts they left behind - niche construction that resulted to changes in the environment - the individual learning of KW would never have produced moss sponging
-
We have already seen that thinkers from the humanities and social sciences have expressed doubt about the nature/culture distinction. They have also expressed doubt about the related distinction between that which is social and that which is individual. Christina Toren [27], again, remarks that the very distinction between individual and social learning is one that social anthropologists have long regarded as problematic.
individual and social are deeply entangled
-
The problem with this way of defining things is that we ignore the fact that, even when acting in a manner that appears to involve no direct interaction with other creatures, organisms nonetheless develop and learn in environments that have been affected by the prior actions of their conspecifics (and not just their conspecifics). This is precisely the sort of phenomenon stressed by the proponents of the niche-construction approach to evolution, and it is also stressed by developmental systems theorists [40,41]. Organisms grow in environments that have been constructed by the actions of previous generations: in that way, what an organism learns can be profoundly affected and enhanced by the collective activities of individuals it may never meet. In other words, we should not assume that there is any good distinction between individual learning and what we might call ‘social transmission’. The latter can be achieved via the former.
- This primate example demonstrates an ambiguity between individual and social learning.
- The problem with this way of defining things exclusively as either
- individual or
- social
- is that we ignore the fact that,
- even when acting in a manner
- that appears to involve no direct interaction with other creatures,
- organisms nonetheless develop and learn in environments
- that have been affected by the prior actions of their conspecifics (and not just their conspecifics).
- This is precisely the sort of phenomenon
- stressed by the proponents of the niche-construction approach to evolution,
- and it is also stressed by developmental systems theorists [40,41].
- Organisms grow in environments that have been constructed
- by the actions of previous generations:
- in that way, what an organism learns
- can be profoundly affected and enhanced
- by the collective activities of individuals it may never meet.
- by the actions of previous generations:
- In other words, we should not assume
- that there is any good distinction
- between
- individual learning and
- what we might call ‘social transmission’.
- The latter can be achieved via the former.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
prácticas orientadas a reconstruir memoria y sistematizar experiencias de acción yeducación popular en Colombia y en otros países hispanoamericanos.
Reconocer la trayectoria de sistematizacion como experiencia investigativa y sus aportes en cuanto a las posibles construcciones en diversas expresiones , cientificas, academicas,comunitarias, sociales, artisticas, etc.
Tags
Annotators
-
-
www.ndss-symposium.org www.ndss-symposium.org
-
www.everylearnereverywhere.org www.everylearnereverywhere.org
-
Presence
Still really the operative term. The teacher needs to be...there. In the discussion. In the case of social annotation, in the text.
-
Be easily accessible to your students. Provide multiple regular opportunities for connectionand support via email, virtual office hours, prompt feedback, and virtual study sessions orstudent conferences
I think it's interesting to think about social annotation as a vehicle for this availability/accessibility of the instructor.n What's more isolating than the reading? What's more power than having your instructor present IN the reading?
-
-
newamerica.org newamerica.org
-
library.oapen.org library.oapen.org
-
At the same time, the vision of a good life for all integrates our in-dividual pursuit of this goal with an immediate concern for others.In other words, we can enjoy and exercise freedoms only to the extentthat doing so does not impinge on others. Achieving this vision under-lines both the crucial role of freedom but also the necessity of limitsfor this freedom to exist. Thereby, pursuing the vision of a good lifefor all has the potential of bridging current political divides, as it is avision that all people can adhere to.
// - Baked into the Good Life for All within Limits approach is human INTERbeing - It is something that is familiar to us - we already know and live under such limitations. This is what laws are, limitations of freedom and nobody is above the law, and the law is written to enforce social harmony, - Social harmony is the ability for people to live together - for each individual to enjoy freedoms, but not at the expense of taking away freedoms of others
-
Can you imagine a world without limits? Having to navigate a citywithout any limits on how people drive, for example? Or no limits onwhat harm we may do to others? Societies need limits to allow thecommon pursuit of individual and societal wellbeing.
- Comment
- related to the previous comment on limits
-
-
www.wired.com www.wired.com
-
the apocalypse they refer to is not some kind of sci-fi takeover like Skynet, or whatever those researchers thought had a 10 percent chance of happening. They’re not predicting sentient evil robots. Instead, they warn of a world where the use of AI in a zillion different ways will cause chaos by allowing automated misinformation, throwing people out of work, and giving vast power to virtually anyone who wants to abuse it. The sin of the companies developing AI pell-mell is that they’re recklessly disseminating this mighty force.
Not Skynet, but social disruption
-
-
venkatesh-rao.gitbook.io venkatesh-rao.gitbook.io
-
Protocols often serve as boundaries between related spaces, separating regimes of behavior via soft or hard rules of engagement. What is the nature of such boundaries?
TOPOLOGY!! might be nice to do some drawings? Surely Lewin has something on this?
-
We offer the following working definition as a starting point:A protocol is a stratum of codified behavior that allows for the construction or emergence of complex coordinated behaviors at adjacent loci.
this is nice
-
-
Local file Local file
-
533/535 p, Multiplicidad en cada momento no por lo que contiene, sino que es cambiante y transitiva (remisión)
"Mantenerse-juntos de los ingredientes distintos-indistintos de una diversidad"
la lógica identitaria permite definir y distinguir este magma, organizan las relaciones determinadas y determinantes.
Lo dado se organiza en magmas (primer estrato - natural), que a su vez se organizan en una lógica identitaria y organización de conjuntos que determina el pensar legein y hacer teukhein, instituyendo el mundo histórico social. las cosas y los individuos. No solo esto, sino que además instituye un magma de significaciones imaginarias sociales
-
-
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
meld.web.ox.ac.uk meld.web.ox.ac.ukOverview1
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
trompamusic.eu trompamusic.eu
-
trompamusic.eu trompamusic.eu
-
dl.acm.org dl.acm.org
-
A social data infrastructure for music annotation
-
-
nesslabs.com nesslabs.com
-
For instance, we used to think that the main cause of obesity was a poor diet at an individual level, leading to treatments focused on the individual. However, taking a networked thinking approach in a 32-year-long study with over 12,000 people led researchers to discover that the participants’ personal network had a great impact on their likelihood to be obese. “Discernible clusters of obese persons were present in the network at all time points,” write the researchers.
Another social factor influencing human behaviour. Beware of such factors when it comes to self-improvement and learning.
-
-
-
But 150 alone doesn’t tell the whole story. Other numbers are nested within the social brain hypothesis too. According to the theory, the tightest circle has just five people – loved ones. That’s followed by successive layers of 15 (good friends), 50 (friends), 150 (meaningful contacts), 500 (acquaintances) and 1500 (people you can recognise). People migrate in and out of these layers, but the idea is that space has to be carved out for any new entrants.
- Paraphrase
- 150 alone doesn’t tell the whole story.
- Other range numbers are nested within the social brain hypothesis.
-
curiously, Dunbar recognized they were all multiples of 5.
- the tightest circle has just 5 people (loved ones).
- 15 (good friends),
- 50 (friends),
- 150 (meaningful contacts),
- 500 (acquaintances) and
- 1500 (people you can recognise).
-
People migrate in and out of these layers,
- but that space has to be carved out for any new entrants.
-
-
web.hypothes.is web.hypothes.is
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
Nor does the cycles thesis have much to say about what social scientists call policy entrenchment—the way new policies outlast the coalition that created them.
Policy entrenchment is when policies outlast the people, movements, or coalitions that created those policies.
-
-
activitypods.org activitypods.org
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.defenseurdesdroits.fr www.defenseurdesdroits.fr
-
recommandation 5La Défenseure des droits rappelle quel’accès à la domiciliation revêt des enjeuxfondamentaux puisqu’il permet aux personnessans domicile stable d’accéder à certainsdroits civiques, civils et sociaux. En vertude la loi, les communes doivent garantir,sans discrimination, un accès effectif à ladomiciliation. Les CCAS sont tenus dans cecadre de motiver tout refus de domiciliation etseule l’absence de tout lien avec la communepeut justifier un refus de domiciliation.
-
-
rieoei.org rieoei.org
-
AMBIENTE EDUCATIVO Y ESTÉTICA SOCIAL
La escuela debe promover procesos tanto de construcción como de reconstrucción de la identidad del sujeto. También se menciona en este aspecto que lo social se refiere a la afectación e implicación que tenga la experiencia individual en el ambiente, por ello se resalta que preguntarse sobre la estética social, es preguntarse por la sensibilidad que se forma en la escuela.
-
- Feb 2023
-
www.promosante-idf.fr www.promosante-idf.fr
-
tantek.com tantek.com
-
www.verywellmind.com www.verywellmind.com
-
who believed that parents, caregivers, peers, and the culture at large are responsible for developing higher-order functions.
We can watch adults model things, but we need people to teach us the nuance and context of those behaviors.
-
-
-
Related here is the horcrux problem of note taking or even social media. The mental friction of where did I put that thing? As a result, it's best to put it all in one place.
How can you build on a single foundation if you're in multiple locations? The primary (only?) benefit of multiple locations is redundancy in case of loss.
Ryan Holiday and Robert Greene are counter examples, though Greene's books are distinct projects generally while Holiday's work has a lot of overlap.
-
-
www.verywellmind.com www.verywellmind.com
-
this is different than simply copying someone else's behavior.
The inflection point of when something is learned comes in demonstration? Or in spontaneous performance of the behavior?
-
-
www.verywellmind.com www.verywellmind.com
-
it is time to actually perform the behavior you observed.
Is this in conflict with the statement earlier of learning with no demonstration of new behaviors?
-
Retention can be affected by a number of factors, but the ability to pull up information later and act on it
Retrieval practice is a method which can be used to reinforce retention.
-
-
aeon.co aeon.co
-
If Seneca or Martial were around today, they would probably write sarcastic epigrams about the very public exhibition of reading text messages and in-your-face displays of texting. Digital reading, like the perusing of ancient scrolls, constitutes an important statement about who we are. Like the public readers of Martial’s Rome, the avid readers of text messages and other forms of social media appear to be everywhere. Though in both cases the performers of reading are tirelessly constructing their self-image, the identity they aspire to establish is very different. Young people sitting in a bar checking their phones for texts are not making a statement about their refined literary status. They are signalling that they are connected and – most importantly – that their attention is in constant demand.
-
-
www.loom.com www.loom.com
-
www.courrierinternational.com www.courrierinternational.com
-
eprints.soton.ac.uk eprints.soton.ac.uk
-
-
This paper is relevant to understanding
-
Learning
- it introduces me to a number of new useful concepts
- cognitive advantage
- cultural network analysis
- more detailed understanding of memetics
- cultural epidemiology
-
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Relative to the evolutionary past, social relationships in modernized western societies tend to involve a much wider variety of relationships, along with relatively less immediate connection with close, kin-based support networks
- Relative to the evolutionary past,
- social relationships
- in modernized western societies
- tend to involve
- a much wider variety of relationships,
- along with relatively less immediate connection
- with close, kin-based support networks
-
From an evolutionary perspective, social anxiety is designed primarily to help people ensure an adequate level of social acceptance and, throughout most of human history, this meant acceptance in a tightly-knit group based primarily of biological kin
- From an evolutionary perspective, - social anxiety is designed primarily
- to help people ensure
- an adequate level of social acceptance and,
- throughout most of human history,
- this meant acceptance
- in a tightly-knit group
- based primarily of biological kin
-
Although social anxiety can serve useful functions, it can also involve excessive worry, negative affect, and exaggerated avoidance of social situations. Understanding the root causes of anxiety-related problems is an essential step in the development of interventions and policies to reduce dysfunction.
- Although social anxiety can serve useful functions,
- it can also involve excessive worry, negative affect, and exaggerated avoidance of social situations.
- Understanding the root causes of anxiety-related problems
- is an essential step
- in the development of
- interventions and policies
- to reduce dysfunction.
-
we focus primarily on social anxiety
-focus on social anxiety
-
-
www.defenseurdesdroits.fr www.defenseurdesdroits.fr
-
Selon l’étude del’Observatoire du Samusocial de Paris soutenuepar le Défenseur des droits [Samusocial deParis 2018, Défenseur des droits 2019b], lesadolescents vivant en hôtel social vivent unvéritable parcours du combattant pour entrerà l’école
-
-
www.washingtonpost.com www.washingtonpost.com
-
Internet ‘algospeak’ is changing our language in real time, from ‘nip nops’ to ‘le dollar bean’ by [[Taylor Lorenz]]
shifts in language and meaning of words and symbols as the result of algorithmic content moderation
instead of slow semantic shifts, content moderation is actively pushing shifts of words and their meanings
article suggested by this week's Dan Allosso Book club on Pirate Enlightenment
-
Could it be the sift from person to person (known in both directions) to massive broadcast that is driving issues with content moderation. When it's person to person, one can simply choose not to interact and put the person beyond their individual pale. This sort of shunning is much harder to do with larger mass publics at scale in broadcast mode.
How can bringing content moderation back down to the neighborhood scale help in the broadcast model?
-
In January, Kendra Calhoun, a postdoctoral researcher in linguistic anthropology at UCLA, and Alexia Fawcett, a doctoral student in linguistics at UC Santa Barbara, gave a presentation about language on TikTok. They outlined how, by self-censoring words in the captions of TikToks, new algospeak code words emerged.
follow up on this for the relevant forthcoming paper....
-
“It makes me feel like I need a disclaimer because I feel like it makes you seem unprofessional to have these weirdly spelled words in your captions,” she said, “especially for content that's supposed to be serious and medically inclined.”
Where's the balance for professionalism with respect to dodging the algorithmic filters for serious health-related conversations online?
-
But algorithmic content moderation systems are more pervasive on the modern Internet, and often end up silencing marginalized communities and important discussions.
What about non-marginalized toxic communities like Neo-Nazis?
-
Unlike other mainstream social platforms, the primary way content is distributed on TikTok is through an algorithmically curated “For You” page; having followers doesn’t guarantee people will see your content. This shift has led average users to tailor their videos primarily toward the algorithm, rather than a following, which means abiding by content moderation rules is more crucial than ever.
Social media has slowly moved away from communication between people who know each other to people who are farther apart in social spaces. Increasingly in 2021 onward, some platforms like TikTok have acted as a distribution platform and ignored explicit social connections like follower/followee in lieu of algorithmic-only feeds to distribute content to people based on a variety of criteria including popularity of content and the readers' interests.
Tags
- Alexia Fawcett
- linguistics
- shunning
- broadcasting models
- misinformation
- euphemisms
- public health
- beyond the pale
- cultural taboos
- Kendra Calhoun
- leetspeak
- dialects
- social media history
- colloquialisms
- marginalized groups
- Voldemorting
- neo-Nazis
- cancel culture
- historical linguistics
- human computer interaction
- demonitization
- dialect creation
- social media machine guns
- social media
- health care
- coded language
- TikTok
- content moderation
- algospeak
- algorithmic feeds
- cultural anthropology
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.pearltrees.com www.pearltrees.com
-
http://www.pearltrees.com/barockschloss/knowledge-management-germany/id12863560
Knowledge Management in Germany by Barockschloss
Example of someone using the social bookmarking application Pearltrees as a form of digital zettelkasten. They've created a collection of cards about zettelkasten.
-
-
www.newyorker.com www.newyorker.com
-
Consider Eco’s caution against “the alibi of photocopies”: “A student makes hundreds of pages of photocopies and takes them home, and the manual labor he exercises in doing so gives him the impression that he possesses the work. Owning the photocopies exempts the student from actually reading them. This sort of vertigo of accumulation, a neocapitalism of information, happens to many.” Many of us suffer from an accelerated version of this nowadays, as we effortlessly bookmark links or save articles to Instapaper, satisfied with our aspiration to hoard all this new information, unsure if we will ever get around to actually dealing with it.
neocapitalism of information!!
Is information overload compounded by our information hoarding tendencies?
-
-
www.letudiant.fr www.letudiant.fr
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
i can use myself as an example here i i consider myself a pretty smart person i'm in grad school i tried to be really analytical my whole 00:03:56 life and yet i showed up at college when i was 19 years old believing that all the supposedly scientific stuff that white nationalists used to support the idea of race being predictive and segregation being 00:04:09 good and all this stupid stuff i totally believed i thought they were right and i thought everybody was just denying it and it took a community of people in college over years to condemn my beliefs to 00:04:22 show me uh kindness to show me real vitriol to be these in these private conversations where we could go over the facts and it took a long time for me thinking i was really smart and analytical to 00:04:35 accept that it was morally wrong that it was ethically wrong
- comment
- Derek Black is an example
- of what it takes to undo deeply culturally conditioned misinformation
- these variables have to be present for that to work
- open mind
- patience
- accurate information
- a caring, patient, informed community
- Derek Black offers a lesson of what is required to depolarize society using social tipping points
- there needs to be scalable education program to reach still open-minded individuals holding opposing views
- to openly and respectfully debate difficult, polarizing issues
- in order to form the wide bridges necessary for social tipping points of complex issues
-
i try to use the term white supremacy to talk about that history and white nationalism to talk about this 00:02:31 social movement and because it's a movement where people recognize each other they know uh their friends
- white nationalists see their movement as a social movement, not as racism.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
around that same time i got a call from my daughter you know leave it to your kids and she said you know mom it's 00:03:48 just that all the problems we're dealing with in the world right now are insidious and um you know it came up last night siva was talking about the insidiousness 00:04:01 of the facebook problem and and this was an unlocker for me of what what does it mean for something to be insidious so i looked it up and i started to 00:04:14 explore and it turns out that insidious is defined and i think this is from the you know the oxford on the internet not the original but um that there's proceeding in a gradual 00:04:27 subtle way but with very harmful effects in other words there's something that's that's gathering combining in an unseen way that's leading to danger
- comment
- this is an example of how granular social learning, the evolution of consciousness and entangled and individual and collective learning takes place in a mundane way
- another person relays an idea to us
- it resonates with us by connecting to some point
- in our salience landscape
- in this case, caused Nora to look up the word "insidious" that appeared in the words of her daughter
- and caused her to think of the meaning as something that starts out small and apparently harmless,
- but gathering and combining in an unseen way to become dangerous
-
-
www.pearltrees.com www.pearltrees.com
-
bookmark tool in the vein of pinboard, pinterest, etc.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.legifrance.gouv.fr www.legifrance.gouv.fr
-
b) La gestion de la veille sociale, de l'accueil, de l'hébergement et de l'accompagnement au logement de toute personne ou famille sans domicile ou éprouvant des difficultés particulières d'accès au logement en raison de l'inadaptation de ses ressources ou de ses conditions d'existence, dans le respect des articles L. 345-2-2 et L. 345-2-3 du code de l'action sociale et des familles, ainsi que le financement des organismes et des dispositifs qui y contribuent, mentionnés au 8° du I de l'article L. 312-1 et aux articles L. 322-1 et L. 345-2 du même code et aux articles L. 365-1, L. 631-11 et L. 633-1 du code de la construction et de l'habitation ;
-
-
www.collectivites-locales.gouv.fr www.collectivites-locales.gouv.fr
-
Responsabilité du fonds départemental d’aide aux jeunes endifficulté
-
Les actions visant au développement social
-
La mise en œuvre de la mesure d’accompagnementsocial personnalisé (MASP) instituée par la loi du 5 mars 2007 surla protection juridique des majeurs
-
faciliter l'insertion ou la promotion sociale des jeunes en difficultéet des familles exclues, surtout dans les zones urbaines sensibleset dans les lieux où se manifestent des risques d'inadaptationsociale (accompagnement des aides générales au logement et àla fourniture d'eau et d'énergie, aide aux organismes logeant àtitre temporaire des personnes défavorisées ...).
-
Les actions visant à :prévenir l’exclusion sociale et en corriger les effets pour luttercontre la pauvreté, la précarité et la marginalisation ;définir les besoins et attentes des membres de tous les groupessociaux, en particulier ceux des personnes et des famillesvulnérables
-
L’action sociale en faveur :- des enfants et jeunes en difficulté
-
l’aide sociale à l'hébergement en foyer
-
l’aide sociale à l'enfance et aux familles
-
la définition de la politique d'action sociale et médico-sociale du département en tenant compte des compétencesconfiées par la loi à l'Etat, aux autres collectivités territoriales ainsiqu'aux organismes de sécurité sociale ; l’élaboration et la mise en œuvre des schémasdépartementaux d'organisation sociale et médico-sociale ; la coordination des actions sociales et médico-socialesmenées sur le territoire départemental ; l’autorisation de la création ou de la transformation desétablissements et services sociaux et médico-sociaux fournissantdes prestations relevant de la compétence du département et leurhabilitation à tarifier les prestations fournies ; la présidence du conseil d’administration desétablissements publics spécialisés
-
participation au développement social
Tags
- à trouver
- logement
- RESF
- enfant
- département
- Région
- social
- hébergement
- accompagnement
- à exploiter
- ASE
- vulnérabilité
- Département
- financement
- sans toit
Annotators
URL
-
-
iris-recherche.qc.ca iris-recherche.qc.ca
-
www.thecrimson.com www.thecrimson.com
-
https://www.thecrimson.com/article/2023/2/2/donovan-forced-leave-hks/
This is a massive loss for HKS, but a potential major win for the school that picks the project up.
It seems to be a sad use of "rules" to shut down a project which may not jive with an administrations' perspective/needs.
Read on Fri 2023-02-03 at 7:14 PM
-
-
www.heise.de www.heise.de
-
Man kann die ganze Situation nämlich auch einmal zum Anlass nehmen, darüber nachzudenken, ob man das Ganze wirklich braucht. Ist der Nutzen der sozialen Medien so hoch, dass er den Preis rechtfertigt? Das ist eine Frage, die ich mir stelle, seit ich meinen persönlichen Twitter-Account stillgelegt habe, aber so verkehrt fühlt es sich zumindest für mich nicht an, nicht mehr auf Twitter, Mastodon & Co. vertreten zu sein. Vielleicht hatte ein solcher Dienst auch einfach seine Zeit, und vielleicht überschätzen wir die Relevanz von sozialen Medien, und vielleicht wäre es gut, davon mehr Abstand zu nehmen.
-
-
attachment.rrz.uni-hamburg.de attachment.rrz.uni-hamburg.de
-
Social Plausibility Assessment Framework
- Social Plausibility Assessment Framework
-
based on present knowledge of social drivers andphysical processe
climate futures based upon: - social drivers - physical processes
-
-
news.cornell.edu news.cornell.edu
-
- = human being's = altricial nature - is an = evolutionary adaptation
- resulting in exceptional = complex social learning
- tradeoff of helplessness at birth
- is complex social learning
- that enables cumulative cultural evolution
-
Human infants need to acquire complex social skills, including language, empathy, morality and theory of mind, the researchers said. Successful development of these skills depends on information from adults: “Rather than requiring hard-wired, innate knowledge of social abilities, evolution has outsourced the necessary information to parents,”
- rather than hard-wiring innate knowledge of complex social skills, nature outsources = complex social skills - like:
- language
- empathy
- morality
- theory of mind
- to parents
- rather than hard-wiring innate knowledge of complex social skills, nature outsources = complex social skills - like:
-
extended altriciality creates opportunities for sophisticated social learning within the parent-offspring system.
- = extended altriciality
- creates opportunities for sophisticated = social learning
- within the = parent-offspring system.
-
-
penntoday.upenn.edu penntoday.upenn.edu
-
“And if they’re just below a tipping point, their efforts will fail. But remarkably, just by adding one more person, and getting above the 25 percent tipping point, their efforts can have rapid success in changing the entire population’s opinion.
- going from just below 25% to just above 25% results in a dramatic change in adoption of a new norm
-
When a minority group pushing change was below 25 percent of the total group, its efforts failed. But when the committed minority reached 25 percent, there was an abrupt change in the group dynamic, and quickly a majority of the population adopted the new norm.
- = 25% Social Tipping Point
- A committed minority group pushing for change just below 25% of the total group population does not succeed
- but when the committed minority is just above 25%,
- abrupt change in group dynamics quickly causes a majority of the population to adopt the new norm
-
-
www.google.com www.google.com
-
06:06Weak Ties
- = weak ties
-
25:13Complex Contagions
- = complex contagion
- example: climate change norms
- = complex contagion
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
Kawakatsu et al. (1) make an important ad-vance in the quest for this kind of understanding, pro-viding a general model for how subtle differences inindividual-level decision-making can lead to hard-to-miss consequences for society as a whole.Their work (1) reveals two distinct regimes—oneegalitarian, one hierarchical—that emerge fromshifts in individual-level judgment. These lead to sta-tistical methods that researchers can use to reverseengineer observed hierarchies, and understand howsignaling systems work when prestige and power arein play.
M. Kawakatsu, P. S. Chodrow, N. Eikmeier, D. B. Larremore, Emergence of hierarchy in networked endorsement dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118, e2015188118 (2021)
This may be of interest to Jerry Michalski et al.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
One can find utility in asking questions of their own note box, but why not also leverage the utility of a broader audience asking questions of it as well?!
One of the values of social media is that it can allow you to practice or rehearse the potential value of ideas and potentially getting useful feedback on individual ideas which you may be aggregating into larger works.
-
- Jan 2023
-
www.ac-versailles.fr www.ac-versailles.fr
-
www.complexityexplorer.org www.complexityexplorer.org
-
Semantic leadership Extent to which word usage by one entity is subsequently adopted by others. Specifically, Klein measures how often novel semantic usage in a given newspaper is mirrored by other newspapers. When a newspaper is a semantic leader, its semantic usage better predicts the later usage of that word in other newspapers compared to those other newspapers' own, earlier usage of the word.
How might this leadership happen within the social epidemic view of Malcolm Gladwell's Tipping Point framework?
- the law of the few,
- the stickiness factor, and
- the power of context
and with respect to mavens, connectors, and salespeople?
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
web.archive.org web.archive.org
-
twitterisgoinggreat.com twitterisgoinggreat.com
-
-
https://del.icio.us is up ! 🥳
Can log in, browse through bookmarks and export them.
-
-
discu.eu discu.eu
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
defenseurdesdroits.fr defenseurdesdroits.fr
-
La Défenseure des droits recommande auministre des Solidarités et de la santé et auxprésidents des conseils départementaux derenforcer la pluridisciplinarité et le partenariatdans la prise en charge des enfants protégésà l’aide sociale à l’enfance (ASE), notammentpar la création de référentiels communs et enrendant effective l’obligation d’établir un Projetpour l’enfant.La Défenseure des droits recommande auxprésidents des conseils départementaux,des directeurs territoriaux de la Protectionjudiciaire de la jeunesse (PJJ) et auxdirecteurs des ARS la signature de protocolesopérationnels portant sur la santé des enfantsconfiés en protection de l’enfance.La Défenseure des droits recommande derenforcer la présence de professionnels desanté dans l’ensemble des établissementsd’accueil relevant de la protection de l’enfance,en recrutant un infirmier.
Recommandadion 24
-
La Défenseure des droits recommande auxdirecteurs académiques, en concertation avecles collèges et lycées, de diffuser à chaquerentrée scolaire, via un support adapté (livretd’accueil, etc.), les informations relatives àla présence au sein de l’établissement, del’assistante sociale et de l’infirmière scolaire.Une information systématique à destinationdes parents sur l’accès à la médecine scolairedoit aussi être organisée.
Recommandadion 12
-
-
ncase.me ncase.me
-
An interesting interactive model for segregation here. See also https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2014-12-10/an-immersive-game-shows-how-easily-segregation-arises-and-how-we-might-fix-it for press coverage.
-
-
ncase.itch.io ncase.itch.io
-
We become what we behold, a game by Nicky Case.
A commentary on news cycles and social media.
-
-
thebaffler.com thebaffler.com
-
If old-school Social Darwinists like Herbert Spencer viewed nature as a marketplace, albeit an unusually cutthroat one, the new version was outright capitalist. The neo-Darwinists assumed not just a struggle for survival, but a universe of rational calculation driven by an apparently irrational imperative to unlimited growth.
-
We all know the eventual answer, which the discovery of genes made possible. Animals were simply trying to maximize the propagation of their own genetic codes. Curiously, this view—which eventually came to be referred to as neo-Darwinian—was developed largely by figures who considered themselves radicals of one sort or another.
Neo-Darwinism: a modern version of Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, incorporating the findings of genetics.
-
Mutual Aid grew from a series of essays written in response to Thomas Henry Huxley, a well-known Social Darwinist, and summarized the Russian understanding of the day, which was that while competition was undoubtedly one factor driving both natural and social evolution, the role of cooperation was ultimately decisive.
-
An alternative school of Darwinism emerged in Russia emphasizing cooperation, not competition, as the driver of evolutionary change. In 1902 this approach found a voice in a popular book, Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution, by naturalist and revolutionary anarchist pamphleteer Peter Kropotkin.
Was this referenced in the Selfish Gene?
Things working at the level of the gene vs. species...
-
-
tomcritchlow.com tomcritchlow.com
-
Have you seen the OPDS Catalog 1.2 (ATOM over HTTP with OpenSearch) and the OPDS Catalog 2.0 (JSON-LD over HTTP) protocols ?
OPDS define a bookshelf-like access to books repositories and can be used with eBooks readers to retrieve ePub books.
The French National Library, The Gutenberg Project, The Internet Archive or Gallimard (a French editor) provide an OPDS feed.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.geoffreylitt.com www.geoffreylitt.com
-
it’s getting harder to engineer browser extensions well as web frontends become compiled artifacts that are ever further removed from their original source code
-
-
-
-
cohost.org cohost.orgcohost!1
-
social media platform
This technical jargon, in the context of Cohost.org, means "a website".
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
twitter.com twitter.comTwitter1
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
solidproject.org solidproject.org
-
snarfed.org snarfed.org
-
-
is zettelkasten gamification of note-taking? .t3_zkguan._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/theinvertedform at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/zkguan/is_zettelkasten_gamification_of_notetaking/
Social media and "influencers" have certainly grabbed onto the idea and squeezed with both hands. Broadly while talking about their own versions of rules, tips, tricks, and tools, they've missed a massive history of the broader techniques which pervade the humanities for over 500 years. When one looks more deeply at the broader cross section of writers, educators, philosophers, and academics who have used variations on the idea of maintaining notebooks or commonplace books, it becomes a relative no-brainer that it is a useful tool. I touch on some of the history as well as some of the recent commercialization here: https://boffosocko.com/2022/10/22/the-two-definitions-of-zettelkasten/.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
the tragedy of the Commons is not so much that it's Commons per se but that it's a cooperation problem that he described I 00:01:48 think very clearly that environmental degradation is often a social dilemma is often a cooperation problem and be it a commons or not the regulatory structure 00:02:02 or the the social structure can vary but cooperation problems are are important however of course he said his famous line this paper is you know solution is mutual coercion mutually agreed upon and and so that's 00:02:18 institutions right so the solution is institutions and of course we have other people who have said that very clearly and with a lot of wonderful evidence to back it up Elinor Ostrom being at the 00:02:31 top of that list and and her work on common pool resources and contains this fantastic list of sort of key design 00:02:44 elements that have emerged from studying small-scale common pool resource communities and and these are these are factors that tend to make those communities more successful in managing 00:02:56 those resources sustainably so so that's great
!- mitigating : tragedy of the commons - Elinor Ostrom's design principles - It's often a cooperation problem - it is a social dilemma pitting individual vs collective interest
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
so often we still think engagement social engagement is a distraction from serious practice
!- Observation : We feel social engagement hampers our meditative practice - nothing can be further from the truth!
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
as long as the system of of political finance and you know parties and campaigns and media and think tank you know are largely controlled by by large wealth 00:29:11 holders you know our collective ability to change the distribution of wealth and the you know through through taxation or that consolation and or what you know whatever the method is going to be limited so it will take major political fights and in some cases you know changing the political rules of the game and the political institution to to to changes and and you know the good news is that this has always been like this or this has always 00:29:39 and and still sometimes you know it has worked in the in the past but it has worked you know i mentioned the french revolution you know of course that's a huge popular mobilization uh also in the 20th century i mentioned after world war ii after world war one well let's be clear it's only because there was a very powerful uh you know labor movement a socialist movement and communist counter model in the east which in the end put pressure uh on the on the uh and you know and on 00:30:09 the in effect and the elite governing elite in in in the west so that they they they had to accept a number of decisions you know which which were limited in their scope but still which transform the economic and social system in in a very substantial way as compared to the pre-world war one and 19th century economic system but it's only through this enormous political mobilization 00:30:34 and collective organization and you know it will be the same in in the past
!- Thomas Piketty : limited ability for real change as long as elites can lobby governments - but in the past, there has been success, as the two cases previously mentioned - so it is possible, but will take just as enormous a political mobilization of the people
-
david described what a revolution is a change of common sense and the collective imagination and david argued that the main achievement of the paris commune despite a defeat had been the transformation of the common sense about how we live together 00:03:02 so most of what we consider ordinary in our cities public transportation street lights public schools the eight hours work days and even the not yet achieved equal pay for women and men originated in the paris commune and it was then considered to be a social madness
!- David Grabber : Delayed impact of the Paris Commune - civic ideas we all now take for granted such as: - public transportation - city street lights - public schools - eight hour work day
only a few decades ago were considered madness
-
-
bookwyrm.social bookwyrm.socialBookWyrm1
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
how important is the concrete syntax of their language in contrast to
how important is the concrete syntax of their language in contrast to the abstract concepts behind them what I mean they say can someone somewhat awkward concrete syntax be an obstacle when it comes to the acceptance
-
- Dec 2022
-
pressbooks.rampages.us pressbooks.rampages.us
-
https://pressbooks.rampages.us/msw-research/
Note taking section, particularly here: https://pressbooks.rampages.us/msw-research/chapter/5-writing-your-literature-review/#chapter-285-section-2
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
ralphm.net ralphm.net
-
Jaiku-Twitter XMPP interoperability circa 2008
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.goffi.org www.goffi.orgLibervia1
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
nlnet.nl nlnet.nl
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
arstechnica.com arstechnica.com
-
"Queer people built the Fediverse," she said, adding that four of the five authors of the ActivityPub standard identify as queer. As a result, protections against undesired interaction are built into ActivityPub and the various front ends. Systems for blocking entire instances with a culture of trolling can save users the exhausting process of blocking one troll at a time. If a post includes a “summary” field, Mastodon uses that summary as a content warning.
-
-
fedvte.usalearning.gov fedvte.usalearning.gov
-
Investigating social structures through the use of network or graphs Networked structures Usually called nodes ((individual actors, people, or things within the network) Connections between nodes: Edges or Links Focus on relationships between actors in addition to the attributes of actors Extensively used in mapping out social networks (Twitter, Facebook) Examples: Palantir, Analyst Notebook, MISP and Maltego
-
-
michelemartin.typepad.com michelemartin.typepad.com
-
this article from Fred Stutzman. In it he explains that egocentric networks are places like Facebook, MySpace and LinkedIn. They develop around the profiles of the people who join them. Object centric networks, on the other hand, develop around interactions over digital artifacts--like Flickr, which has formed communities around photo-sharing and del.icio.us, which focuses on sharing links.
-
-
www.zengestrom.com www.zengestrom.com
-
xmpp.org xmpp.org
-
buddycloud.github.io buddycloud.github.io
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
xmpp.org xmpp.org
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.comYouTube1
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oYycpKcUhc4
We need more social acceptability for neurodivergence in much the way we accept the use of eyeglasses without attaching a social stigma to it.
What ways is this like exacerbating the stigmas of racism and institutionalized racism? How can we break down these broader barriers without othering people?
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
In other words, the dog-object is defined by its interactions (or its quality in Pirsig's perspective) within the environmental network and how well it expresses its dogginess.
Tak ada asu kecuali konstruksi semantik yang muncul dari jejak histori interaksi sesuasu dengan kahanan di sekitarnya dan seberapa asu sesuasu itu mengekspresikan keasuannya,
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Drawing from negativity bias theory, CFM, ICM, and arousal theory, this study characterizes the emotional responses of social media users and verifies how emotional factors affect the number of reposts of social media content after two natural disasters (predictable and unpredictable disasters). In addition, results from defining the influential users as those with many followers and high activity users and then characterizing how they affect the number of reposts after natural disasters
-
-
psycnet.apa.org psycnet.apa.org
-
Using actual fake-news headlines presented as they were seen on Facebook, we show that even a single exposure increases subsequent perceptions of accuracy, both within the same session and after a week. Moreover, this “illusory truth effect” for fake-news headlines occurs despite a low level of overall believability and even when the stories are labeled as contested by fact checkers or are inconsistent with the reader’s political ideology. These results suggest that social media platforms help to incubate belief in blatantly false news stories and that tagging such stories as disputed is not an effective solution to this problem.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
. Furthermore, our results add to the growing body of literature documenting—at least at this historical moment—the link between extreme right-wing ideology and misinformation8,14,24 (although, of course, factors other than ideology are also associated with misinformation sharing, such as polarization25 and inattention17,37).
Misinformation exposure and extreme right-wing ideology appear associated in this report. Others find that it is partisanship that predicts susceptibility.
-
. We also find evidence of “falsehood echo chambers”, where users that are more often exposed to misinformation are more likely to follow a similar set of accounts and share from a similar set of domains. These results are interesting in the context of evidence that political echo chambers are not prevalent, as typically imagined
-
And finally, at the individual level, we found that estimated ideological extremity was more strongly associated with following elites who made more false or inaccurate statements among users estimated to be conservatives compared to users estimated to be liberals. These results on political asymmetries are aligned with prior work on news-based misinformation sharing
This suggests the misinformation sharing elites may influence whether followers become more extreme. There is little incentive not to stoke outrage as it improves engagement.
-
Estimated ideological extremity is associated with higher elite misinformation-exposure scores for estimated conservatives more so than estimated liberals.
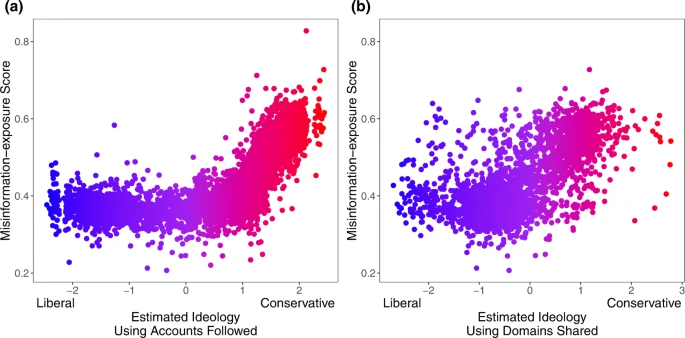
Political ideology is estimated using accounts followed10. b Political ideology is estimated using domains shared30 (Red: conservative, blue: liberal). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Estimated ideological extremity is associated with higher language toxicity and moral outrage scores for estimated conservatives more so than estimated liberals.
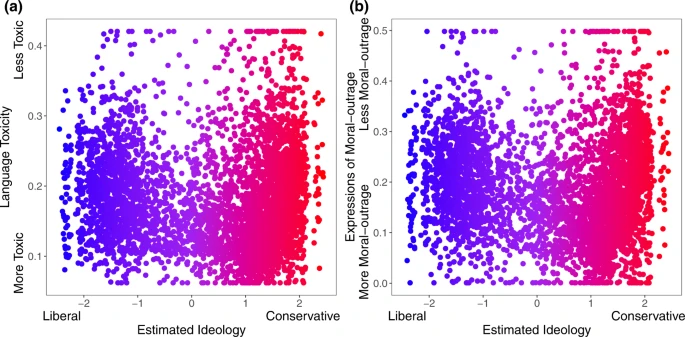
The relationship between estimated political ideology and (a) language toxicity and (b) expressions of moral outrage. Extreme values are winsorized by 95% quantile for visualization purposes. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
-
In the co-share network, a cluster of websites shared more by conservatives is also shared more by users with higher misinformation exposure scores.
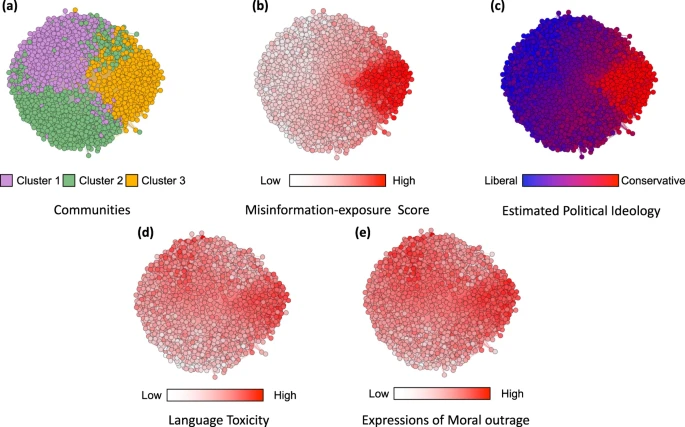
Nodes represent website domains shared by at least 20 users in our dataset and edges are weighted based on common users who shared them. a Separate colors represent different clusters of websites determined using community-detection algorithms29. b The intensity of the color of each node shows the average misinformation-exposure score of users who shared the website domain (darker = higher PolitiFact score). c Nodes’ color represents the average estimated ideology of the users who shared the website domain (red: conservative, blue: liberal). d The intensity of the color of each node shows the average use of language toxicity by users who shared the website domain (darker = higher use of toxic language). e The intensity of the color of each node shows the average expression of moral outrage by users who shared the website domain (darker = higher expression of moral outrage). Nodes are positioned using directed-force layout on the weighted network.
-
Exposure to elite misinformation is associated with the use of toxic language and moral outrage.
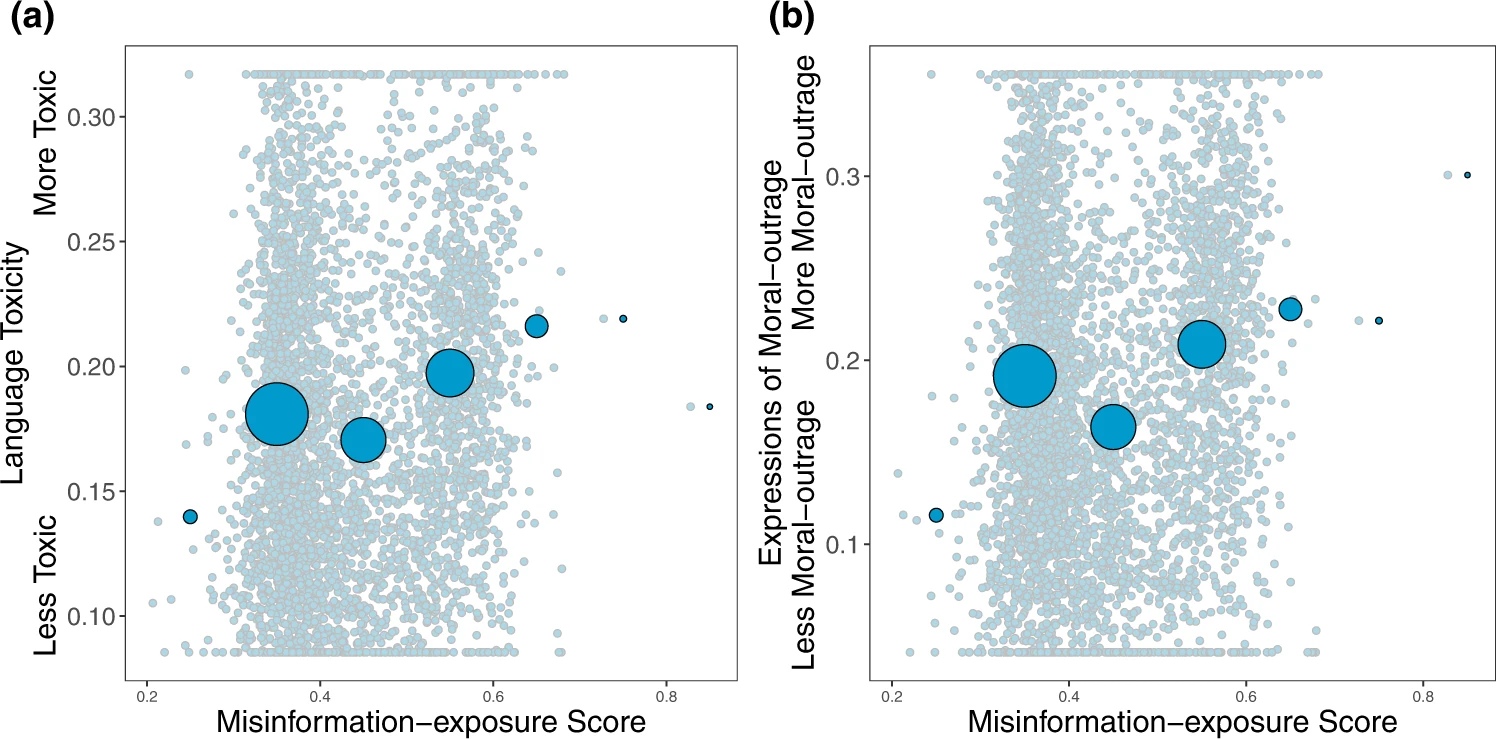
Shown is the relationship between users’ misinformation-exposure scores and (a) the toxicity of the language used in their tweets, measured using the Google Jigsaw Perspective API27, and (b) the extent to which their tweets involved expressions of moral outrage, measured using the algorithm from ref. 28. Extreme values are winsorized by 95% quantile for visualization purposes. Small dots in the background show individual observations; large dots show the average value across bins of size 0.1, with size of dots proportional to the number of observations in each bin. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Exposure to elite misinformation is associated with sharing news from lower-quality outlets and with conservative estimated ideology.
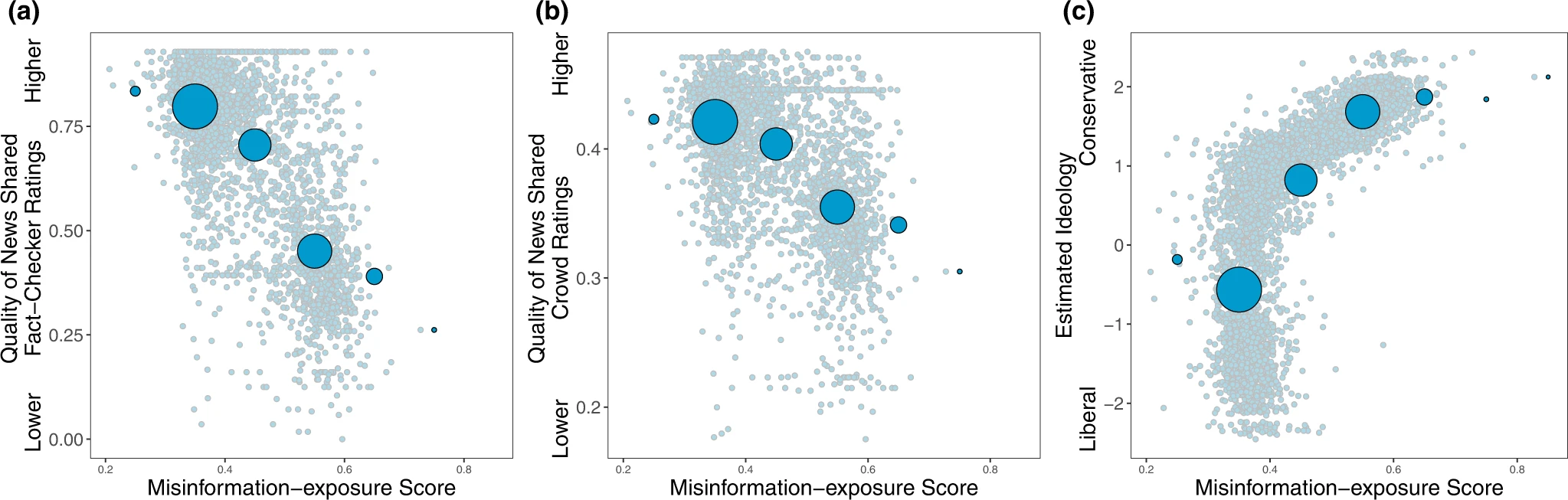
Shown is the relationship between users’ misinformation-exposure scores and (a) the quality of the news outlets they shared content from, as rated by professional fact-checkers21, (b) the quality of the news outlets they shared content from, as rated by layperson crowds21, and (c) estimated political ideology, based on the ideology of the accounts they follow10. Small dots in the background show individual observations; large dots show the average value across bins of size 0.1, with size of dots proportional to the number of observations in each bin.
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Notice that Twitter’s account purge significantly impacted misinformation spread worldwide: the proportion of low-credible domains in URLs retweeted from U.S. dropped from 14% to 7%. Finally, despite not having a list of low-credible domains in Russian, Russia is central in exporting potential misinformation in the vax rollout period, especially to Latin American countries. In these countries, the proportion of low-credible URLs coming from Russia increased from 1% in vax development to 18% in vax rollout periods (see Figure 8 (b), Appendix).
-
Interestingly, the fraction of low-credible URLs coming from U.S. dropped from 74% in the vax devel-opment period to 55% in the vax rollout. This large decrease can be directly ascribed to Twitter’s moderationpolicy: 46% of cross-border retweets of U.S. users linking to low-credible websites in the vax developmentperiod came from accounts that have been suspended following the U.S. Capitol attack (see Figure 8 (a), Ap-pendix).
-
Considering the behavior of users in no-vax communities,we find that they are more likely to retweet (Figure 3(a)), share URLs (Figure 3(b)), and especially URLs toYouTube (Figure 3(c)) than other users. Furthermore, the URLs they post are much more likely to be fromlow-credible domains (Figure 3(d)), compared to those posted in the rest of the networks. The differenceis remarkable: 26.0% of domains shared in no-vax communities come from lists of known low-credibledomains, versus only 2.4% of those cited by other users (p < 0.001). The most common low-crediblewebsites among the no-vax communities are zerohedge.com, lifesitenews.com, dailymail.co.uk (consideredright-biased and questionably sourced) and childrenshealthdefense.com (conspiracy/pseudoscience)
-
-
ieeexplore.ieee.org ieeexplore.ieee.org
-
We applied two scenarios to compare how these regular agents behave in the Twitter network, with and without malicious agents, to study how much influence malicious agents have on the general susceptibility of the regular users. To achieve this, we implemented a belief value system to measure how impressionable an agent is when encountering misinformation and how its behavior gets affected. The results indicated similar outcomes in the two scenarios as the affected belief value changed for these regular agents, exhibiting belief in the misinformation. Although the change in belief value occurred slowly, it had a profound effect when the malicious agents were present, as many more regular agents started believing in misinformation.
-
-
www.mdpi.com www.mdpi.com
-
Therefore, although the social bot individual is “small”, it has become a “super spreader” with strategic significance. As an intelligent communication subject in the social platform, it conspired with the discourse framework in the mainstream media to form a hybrid strategy of public opinion manipulation.
-
There were 120,118 epidemy-related tweets in this study, and 34,935 Twitter accounts were detected as bot accounts by Botometer, accounting for 29%. In all, 82,688 Twitter accounts were human, accounting for 69%; 2495 accounts had no bot score detected.In social network analysis, degree centrality is an index to judge the importance of nodes in the network. The nodes in the social network graph represent users, and the edges between nodes represent the connections between users. Based on the network structure graph, we may determine which members of a group are more influential than others. In 1979, American professor Linton C. Freeman published an article titled “Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification“, on Social Networks, formally proposing the concept of degree centrality [69]. Degree centrality denotes the number of times a central node is retweeted by other nodes (or other indicators, only retweeted are involved in this study). Specifically, the higher the degree centrality is, the more influence a node has in its network. The measure of degree centrality includes in-degree and out-degree. Betweenness centrality is an index that describes the importance of a node by the number of shortest paths through it. Nodes with high betweenness centrality are in the “structural hole” position in the network [69]. This kind of account connects the group network lacking communication and can expand the dialogue space of different people. American sociologist Ronald S. Bert put forward the theory of a “structural hole” and said that if there is no direct connection between the other actors connected by an actor in the network, then the actor occupies the “structural hole” position and can obtain social capital through “intermediary opportunities”, thus having more advantages.
-
We analyzed and visualized Twitter data during the prevalence of the Wuhan lab leak theory and discovered that 29% of the accounts participating in the discussion were social bots. We found evidence that social bots play an essential mediating role in communication networks. Although human accounts have a more direct influence on the information diffusion network, social bots have a more indirect influence. Unverified social bot accounts retweet more, and through multiple levels of diffusion, humans are vulnerable to messages manipulated by bots, driving the spread of unverified messages across social media. These findings show that limiting the use of social bots might be an effective method to minimize the spread of conspiracy theories and hate speech online.
-
-
www.robinsloan.com www.robinsloan.com
-
I want to insist on an amateur internet; a garage internet; a public library internet; a kitchen table internet.
Social media should be comprised of people from end to end. Corporate interests inserted into the process can only serve to dehumanize the system.
Robin Sloan is in the same camp as Greg McVerry and I.
-
-
www.sicpers.info www.sicpers.info
-
Currently modes of software development, including free and open source software, are predicated on the division of society into three classes: “developers” who make software, “the business” who sponsor software making, and “users” who do whatever it is they do. An enabling free software movement would erase these distinctions, because it would give the ability (not merely the freedom) to study and change the software to anyone who wanted or needed it.
-
-
www.embopress.org www.embopress.org
-
I came here after recalling a critique by Bessel van der Kolk's "The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma" regarding the disease model and it's negative impact on adequately helping people with trauma. van der Kolk's critique was similar to Marc Lewis' critique of the disease model as it applies to addiction from "The Biology of Desire: Why Addiction Is Not a Disease". This made me wonder what the term "disease" actually means and whether or not some general consensus existed within the medical community. This article suggests there is no such consensus.
This article is by Jackie Leach Scully who holds a "PhD in cellular pathology, University of Cambridge; BA (Hons) in biochemistry, University of Oxford; MA in psychoanalytic studies, Sheffield University".
Scully does several insightful things in this paper the following are the ones that were most salient to me upon the first read: - distinguishes "disease" from "disability" - contrasts the "social model" and "medical model" perspectives on "disability" - The "medical model" referred to here is probably what Lewis & van der Kolk are critiquing as the "disease model".<br /> - Are the "medical" and "disease" model different? - the social model seems to have arisen as a response to the inadequacy of the medical model
- "The social model's fundamental criticism of the medical model is that it wrongly locates 'the problem' of disability in biological constraints, considering it only from the point of view of the individual and neglecting the social and systemic frameworks that contribute to it. The social model distinguishes between impairment (the biological substrate, such as impaired hearing) and the disabled experience. In this view the presence of impaired hearing is one thing, while the absence of subtitling on TV is quite another, and it is the refusal of society to make the necessary accommodations that is the real site of disability. A social model does not ignore biology, but contends that societal, economic and environmental factors are at least as important in producing disability."- brings up a subtle point that there are two jumps "from gene to phenotype, and from phenotype to experience" and that some of the arguments mentioned "suggest that the 'harm' of the impairment is not straightforwardly related to phenotype. What ought to concern us about disease and disability is the disadvantage, pain or suffering involved, and in a sense the impairment is always a kind of surrogate marker for this experience."
-
-
www.arthurperret.fr www.arthurperret.fr