Who falls for fake news? Psychological and clinical profiling evidence of fake news consumers
Participants with a schizotypal, paranoid, and histrionic personality were ineffective at detecting fake news. They were also more vulnerable to suffer its negative effects. Specifically, they displayed higher levels of anxiety and committed more cognitive biases based on suggestibility and the Barnum Effect. No significant effects on psychotic symptomatology or affective mood states were observed. Corresponding to these outcomes, two clinical and therapeutic recommendations related to the reduction of the Barnum Effect and the reinterpretation of digital media sensationalism were made. The impact of fake news and possible ways of prevention are discussed.
Fake news and personality disorders
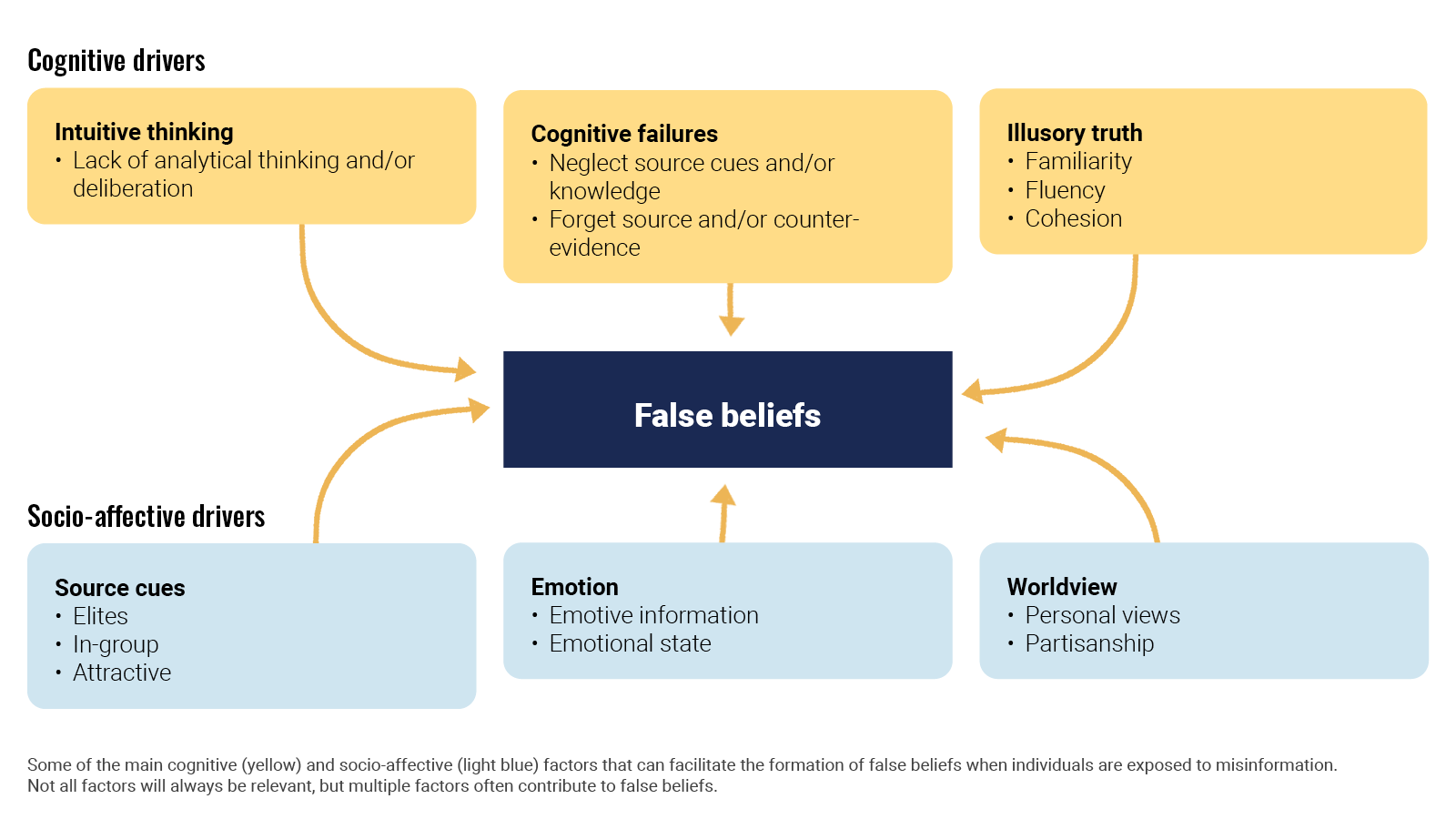
The observed relationship between fake news and levels of schizotypy was consistent with previous scientific evidence on pseudoscientific beliefs and magical ideation (see Bronstein et al., 2019; Escolà-Gascón, Marín, et al., 2021). Following the dual process theory model (e.g., Pennycook & Rand, 2019), when a person does not correctly distinguish between information with scientific arguments and information without scientific grounds it is because they predominantly use cognitive reasoning characterized by intuition (e.g., Dagnall, Drinkwater, et al., 2010; Swami et al., 2014; Dagnall et al., 2017b; Williams et al., 2021).
Concomitantly, intuitive thinking correlates positively with magical beliefs (see Šrol, 2021). Psychopathological classifications include magical beliefs as a dimension of schizotypal personality (e.g., Escolà-Gascón, 2020a). Therefore, it is possible that the high schizotypy scores in this study can be explained from the perspective of dual process theory (Denovan et al., 2018; Denovan et al., 2020; Drinkwater, Dagnall, Denovan, & Williams, 2021). Intuitive thinking could be the moderating variable that explains why participants who scored higher in schizotypy did not effectively detect fake news.
Something similar happened with the subclinical trait of paranoia. This variable scored the highest in both group 1 and group 2 (see Fig. 1). Intuition is also positively related to conspiratorial ideation (see Drinkwater et al., 2020; Gligorić et al., 2021). Similarly, psychopathology tends to classify conspiracy ideation as a frequent belief system in paranoid personality (see Escolà-Gascón, 2022). This is because conspiracy beliefs are based on systematic distrust of the systems that structure society (political system), knowledge (science) and economy (capitalism) (Dagnall et al., 2015; Swami et al., 2014). Likewise, it is known that distrust is the transversal characteristic of paranoid personality (So et al., 2022). Then, in this case the use of intuitive thinking and dual process theory could also justify the obtained paranoia scores. The same is not true for the histrionic personality.
The Barnum Effect
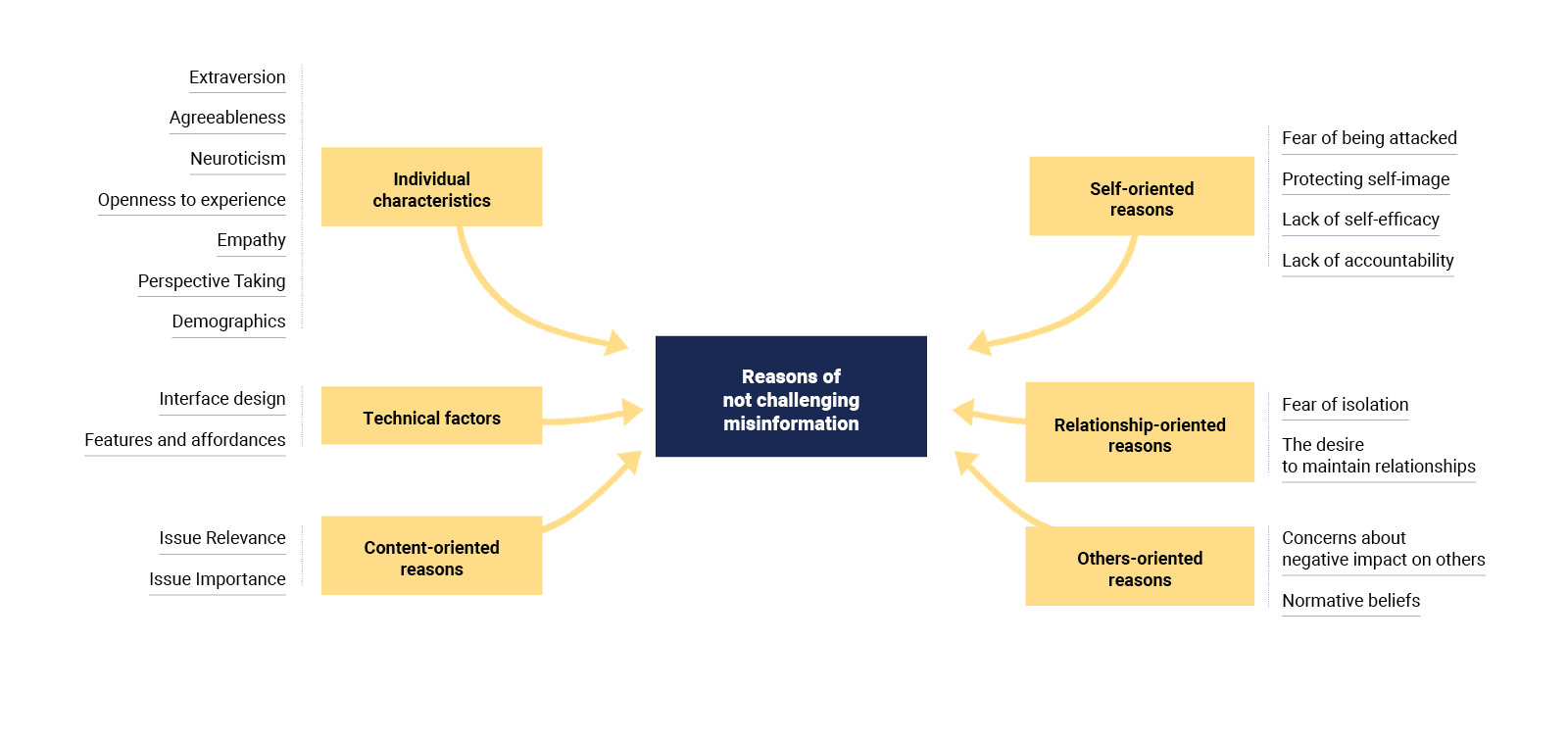
The Barnum Effect consists of accepting as exclusive a verbal description of an individual's personality, when, the description employs contents applicable or generalizable to any profile or personality that one wishes to describe (see Boyce & Geller, 2002; O’Keeffe & Wiseman, 2005). The error of this bias is to assume as exclusive or unique information that is not. This error can occur in other contexts not limited to personality descriptions. Originally, this bias was studied in the field of horoscopes and pseudoscience's (see Matute et al., 2011). Research results suggest that people who do not effectively detect fake news regularly commit the Barnum Effect. So, one way to prevent fake news may be to educate about what the Barnum Effect is and how to avoid it.
Conclusions
The conclusions of this research can be summarized as follows:
(1)
The evidence obtained proposes that profiles with high scores in schizotypy, paranoia and histrionism are more vulnerable to the negative effects of fake news. In clinical practice, special caution is recommended for patients who meet the symptomatic characteristics of these personality traits.
(2)
In psychiatry and clinical psychology, it is proposed to combat fake news by reducing or recoding the Barnum effect, reinterpreting sensationalism in the media and promoting critical thinking in social network users. These suggestions can be applied from intervention programs but can also be implemented as psychoeducational programs for massive users of social networks.
(3)
Individuals who do not effectively detect fake news tend to have higher levels of anxiety, both state and trait anxiety. These individuals are also highly suggestible and tend to seek strong emotions. Profiles of this type may inappropriately employ intuitive thinking, which could be the psychological mechanism that.
(4)
Positive psychotic symptomatology, affective mood states and substance use (addiction risks) were not affected by fake news. In the field of psychosis, it should be analyzed whether fake news influences negative psychotic symptomatology.