175 Matching Annotations
- Jan 2026
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
- Sep 2025
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
They had parties, we got the hangover<br /> by [[Ruth Sunderland]] for The Guardian<br /> accessed on 2025-09-06T12:17:48
-
- Jul 2025
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
In this context, Trump’s Truth Social page is little more than a rapid-response account that illustrates a world that doesn’t actually exist: one in which POTUS looks like a comic-book hero, is universally beloved, and exerts his executive authority to jail or silence anyone who disagrees with him. This sort of revenge fantasy would be sad coming from anyone. That it is coming from the president of the United States, a man obsessed with retribution, who presides over a government that is enthusiastically arresting and jailing immigrants in makeshift camps, is terrifying.
-
- Apr 2025
-
osf.io osf.io
-
framework integrating three therapeutic modes, namely Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), Outdoor Therapy and Group Therapy. We describe the ACT-GRO(ACT-GroupOutdoor) Framework, its components, rationale behind the proposed Framework and explain how each component enhances the other and can be viewed as a system of systems-a term borrowed from engineering –requiring each system to be autonomous, connected, and diverse, with a common purpose and a commitment to a greater outcome. In the second part, we describe how the three therapeutic modes working in an integrative way meet Baldwin’s criteria of a system of systems. Finally, we
This is an interesting example of applying systems of systems concepts to a form of integrated therapy. By maintaining the same rigorous requirements for characterization as a system of systems, a framework emerges which can be applied to other integrated systems.
-
- Mar 2025
-
www.linkedin.com www.linkedin.com
-
Reply to Hajo Bakker on LinkedIn
Hajo Bakker Exam vs. Test -- Een examinering moet veel vanafwegen en niet regulier gebeuren.
Een test (toets) mag vaker gebeuren, en moet weinig vanaf hangen... Geen ouders die straffen voor een laag cijfer (of cijfers afschaffen), geen adviezen die daarvanafhangen, etc.
Het doel van een toets is om je aan te geven wat je krachten en minder sterke punten zijn, dus waar je je op moet focussen met toekomst leren. Dit kan alleen op het moment dat je een toets nabespreekt en op individueel niveau. Klassikaal bespreken heeft vaak weinig nut.
Daarbij komt ook dat een student moet snappen WAAROM het helpt om na te bespreken, de wetenschap erachter. Op het moment dat je de waarom achter het hoe niet goed snapt heeft het hoe minder effect. (dit is waarom in het 4C/ID model ze in een scaffold beginnen met de laatste stap, waarin de informatie van voorgaande stappen is gegeven. Dit zodat als je de vorige stap gaat leren, je een beter idee hebt waar het uiteindelijk voor gebruikt gaat worden en je er dus een betere invulling aan kan geven.)
Semantische verschillen zijn vaak uiterst nuttig om complexe stof te begrijpen. Op het moment dat ze exact hetzelfde waren heeft het weinig nut om meerdere termen te hebben en zouden ze synoniem zijn.
"Exam" is geen synoniem van "test".
Genuanceerde verschillen zijn vaak nuttiger dan "umbrella terms" om goed te communiceren, als uiterst subliem wordt beargumenteerd in "Science of Memory: Concepts" van Roediger III et al.
Daarnaast komt uiteraard bij kijken dat neurocognitieve wetenschap een blauwdruk geeft voor hoe onze brein architectuur in elkaar zit (zie bijvoorbeeld John Sweller, Cognitive Load Theory 2011, en The Forgetting Machine, Rodrigo Quian Quiroga, 2017, Science of Memory: Concepts, Roediger et al., 2007, Ten Steps to Complex Learning, van Merriënboer, 2017).
Dit is universeel toepasbaar, afgezien van mensen met een cognitieve aandoening bijvoorbeeld, dit gaat dus over neurotypische breinen.
Leerstijlen zijn een mythe, wel hebben wij leervoorkeuren, maar door alleen in onze leervoorkeur te leren missen wij bepaalde informatie die cruciaal kan zijn voor beter begrip en meesterschap (mastery).
Beter is het om studietechnieken te gebruiken die overeenkomen met brein-architectuur en die onder te knie te krijgen.
Meer cognitieve belasting te gebruiken (zonder cognitieve overbelasting te veroorzaken). Als leren "makkelijk" voelt is het over het algemeen niet uitdagend genoeg en/of de techniek niet nuttig. Herlezen / samenvatten is simpel maar vrij inefficiënt. Het maken van een GRINDEmap voelt moeilijk maar is vele malen effectiever (zie ook the misinterpreted effort hypothesis).
Zoals Dr. Ahrens al zei: "The one who does the effort, does the learning."
Verder heb ik een heleboel ideëen voor een optimaal onderwijs dat zich aanpast aan het individu in plaats van aan het systeem, maar dit is een te complex en groot onderwerp om zo even hier neer te zetten.
Tags
- Cognitive Load Theory
- Mastery
- Understanding the why behind the how
- Coming to Terms
- 4C/ID
- The Forgetting Machine
- Rodrigo Quian Quiroga
- Study Techniques
- Henry L. Roediger III
- Learning Styles
- Hajo Bakker
- Ten Steps to Complex Learning
- Education
- Schema Formation
- Scaffolding
- Misinterpreted Effort Hypothesis
- Science of Memory: Concepts
- Exams
- Semantics
- Optimal Education
- Reply
- Tests vs. Exams
- Jeroen van Merriënboer
- Studying
- Learning
- Tests
- Sönke Ahrens
- Umbrella Terms
- Learning Techniques
- Educational Myths
- Cognitive Load
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.linkedin.com www.linkedin.com
-
Reply to Gertina Blanket on LinkedIn:
Jij legt in één klap uit datgene wat ik nooit goed heb begrepen uit de literatuur... Het verschil tussen interleaving en varied practice (die vaak als hetzelfde worden gebruikt in de "volksmond").
Het een gaat over verschillende hoeken kijken naar hetzelfde idee (varied practice) terwijl het ander gaat over verschillende maar soortgelijke ideëen (interleaving), bijvoorbeeld meerdere soorten wiskunde (algebra, trigonometrie, etc.).
Hierbij wil ik uiteraard wel zeggen dat blocked practice niet per se direct toegepast moet worden als het over automatisering gaat -- de cognitieve schemata moeten eerst goed gevormd zijn. Zie ook 4C/ID (Ten Steps to Complex Learning). Ofwel, eerst goede encoding + retrieval (Spaced Interleaved Retrieval, mindmapping, etc.) en dan focus op "drilling" / knowledge fluency.
Het sneller maken / automatiseren heeft geen enkel nut als het begrip er nog niet goed in zit. Dit moet geverifiëerd worden.
Kennis is natuurlijk ook erg interdisciplinair. Ik wordt er extreem blij van als ik een link leg tussen een boek over filosofie en efficiënt leren/onderwijs bijvoorbeeld.
Zo las ik ooit een boek over romeinse oratoren met een misleidende titel "How to Win an Argument" van Marcus Tullius Cicero, vertaald door James M. May, en hierin kwam ik tegen dat de oude Romeinen al door hadden dat LOGICA is wat het brein doet onthouden, en dit hoeft dus geen objective logica te zijn maar meer een correcte reflectie van hoe je eigen geest werkt en verbanden legt.
Dit is direct in lijn met wat ik weet van cognitieve leerpsychologie en mijn klein beetje kennis van neurowetenschap (waar ik dit jaar dieper in wil duiken).
Informatie in isolatie is nooit stevig, het moet zich vastklampen aan ankers en andere kennis (voorkennis eventueel), en de lerende (niet de onderwijzende) moet actief bezig zijn om deze verbanden te leggen.
Zoals ik wel vaker quote van Dr. Sönke Ahrens: "The one who does the effort does the learning."
Als ik een boek lees denk ik automatisch aan hoe ik dit kan relateren aan wat al in mijn second mind (Zettelkasten) zit. Ik denk niet meer linear, alleen maar non-linear. Standaard in verbanden.
Hier wat bronnen (impliciet) genoemd: - Cicero, M. T. (2016). How to win an argument: An ancient guide to the art of persuasion (J. M. May, Trans.). Princeton University Press. - Ahrens, S. (2017). How to take smart notes: One simple technique to boost writing, learning and thinking: for students, academics and nonfiction book writers. CreateSpace. - fast, sascha. (100 C.E., 45:02). English Translation of All Notes on Zettelkasten by Luhmann. Zettelkasten Method. https://zettelkasten.de/posts/luhmanns-zettel-translated/ - Luhmann, N. (1981a). Communicating with Slip Boxes (M. Kuehn, Trans.). 11. - Luhmann, N. (1981b). Kommunikation mit Zettelkästen. In H. Baier, H. M. Kepplinger, & K. Reumann (Eds.), Öffentliche Meinung und sozialer Wandel / Public Opinion and Social Change (pp. 222–228). VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-322-87749-9_19 - Moeller, H.-G. (2012). The radical Luhmann. Columbia University Press. - Scheper, S. (2022). Antinet Zettelkasten: A Knowledge System That Will Turn You Into a Prolific Reader, Researcher and Writer. Greenlamp, LLC.
- Schmidt, J. F. K. (2016). Niklas Luhmann’s Card Index: Thinking Tool, Communication Partner, Publication Machine. In Forgetting Machines: Knowledge Management Evolution in Early Modern Europe (pp. 287–311). Brill. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004325258_014
- Schmidt, J. F. K. (2018). Niklas Luhmann’s Card Index: The Fabrication of Serendipity. Sociologica, 12(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.6092/issn.1971-8853/8350
Tags
- Niklas Luhmann
- Marcus Tullius Cicero
- Encoding
- Education
- Spaced Interleaved Retrieval
- Intellectualism
- Varied Practice vs. Interleaving
- Varied Practice
- James M. May
- Interleaving
- Schema Automation
- Reply
- Interdisciplinary Knowledge
- Learning
- Retrieval
- Antinet
- 4C/ID
- Knowledge Work
- Zettelkasten
- Schema Formation
- Teaching
- Gertina Blanket
- Ten Steps to Complex Learning
Annotators
URL
-
- Dec 2024
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
for - adjacency - curiosity of the other - polarization - Common Human Denominator - the sacred - TED Talk - Can curiosity heal division? - Scott Shigeoka - 2024 Dec - othering - self and other - adjacency - deep curiosity - Deep Humanity Common Human Denominators (CHD) - awakening to the sacred - a good transition - social tipping points for complex contagion - wide bridges
- Summary / adjacency
- between
- deep curiosity
- Deep Humanity Common Human Denominators (CHD)
- social tipping points for complex contagion
- new adjacency relationships
- Scott Shigeoka is a researcher on social divisions.
- He is also queer and embarked on an adventurous, embedded, courageous and personal research project to venture into Trump country
- to apply his academic training and curiosity to see if he could
- find a way to form authentic relationships with people he had always considered 'the other'
- What the one year experiment taught him was that deep and authentic curiosity is a valuable tool for learning the ubiquitous othering now prevalent in our modern world
- Out of this experience, he wrote a best selling book called
- Seek: How curiosity can transform your life and change the world
- to apply his academic training and curiosity to see if he could
- Curiosity is a powerful technique to mitigate othering and is aligned with Deep Humanity Common Human Denominators, which are fundamental qualities all humans share which are.
- important for navigating the rapid transition our species of going through
- whose appreciation remind each of us that we are sacred
- Social TIpping Points of complex contagion requires building wide bridges to diverse groups early on
- Scott's experiement illustrates building wide bridges
- Indyweb information infrastructure is open source and supports diversity as it increases the efficacy of collaboration
Tags
- adjacency - curiosity of the other - polarization - Common Human Denominator - the sacred - from TED Talk - Can curiosity heal division? - Scott Shigeoka - 2024 Dec
- TED Talk - Can curiosity heal division? - Scott Shigeoka - 2024 Dec
- adjacency - deep curiosity - Deep Humanity Common Human Denominators (CHD) - awakening to the sacred - a good transition - social tipping points for complex contagion - wide bridges
- othering - self and other
Annotators
URL
-
- Nov 2024
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
mankind isn't getting all that much more effective at collectively dealing with complex problems maybe that's what i could concentrate on so that's what i committed to
for - Douglas Engelbart - life purpose - improve our ability to collectively deal with complex problems
-
- Oct 2024
-
ageoftransformation.org ageoftransformation.org
-
for - rapid whole system change - Nafeez Ahmed - planetary phase shift - Nafeez Ahmed - planetary adaptive cycle - Nafeez Ahmed - essay - The End of Scarcity? From ‘Polycrisis’ to Planetary Phase Shift - Nafeez Ahmed - 2024 Oct 16 - to - book - The Ascent of Humanity - chapter 8 Self and Cosmos: The Gaian Birthing - stillborn and the perilous journey through the womb - Charles Eisenstein
summary - This is a good article that makes sense of the inflection point that humanity now faces as it contends with multiple existential crisis - It summarizes the complexity of our polycrisis and its precarity and lays the theory for looking at the polycrisis from a different perspective: - as a planetary phase shift towards the potential end of scarcity and the next stage of our species evolution - Through the lens of ecologist Crawford Stanley Holling's lens of the adaptive cycle of ecological population dynamics, - and especially his 2004 paper "From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds" - Nafeez extends Holling's argument that we are undergoing a planetary adaptive cycle in which the back-loop is the dying industrial era. - In this sense, it is reminiscent of the writings of Charles Eisenstein in his book "The Ascent of Humanity", chapter 8: Self and Cosmos:, The Gaian Birth. - Eisenstein uses the the perilous journey of birth through the womb door as a metaphor of the transition we are currently undergoing.
to - paper - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004 - https://hyp.is/KYCm2pFrEe-_PEu84xshXw/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol9/iss1/art11/main.html?ref=ageoftransformation.org - book - The Ascent of Humanity - Chapter 8 - The Gaian Birthing - Charles Eisenstein - https://hyp.is/r8scTpG_Ee-gLTujlli5hQ/charleseisenstein.org/books/the-ascent-of-humanity/eng/the-gaian-birthing/
-
major transitions “brought about on a global scale by the Internet and by climate, economic, and geopolitical changes” suggest that industrial civilisation is moving into the “back-loop” of a planetary-scale adaptive cycle
for - planetary adaptive cycle - 2004 paper - Crawford Stanley Holling - to - paper - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004
to - paper - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004 - https://hyp.is/KYCm2pFrEe-_PEu84xshXw/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol9/iss1/art11/main.html?ref=ageoftransformation.org
-
the emergence of greater vulnerability because of the increasing number of interconnections that link that wealth, and those who control it, in efforts to sustain it
for - quote / insight - decreased resiliency due to tight network of elites - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004 - creative alternatives - liminal spaces - rapid whole system change
quote / insight - decreased resiliency due to tight network of elites - (see quote below) - The front-loop phase is more predictable, - with higher degrees of certainty. - In both the natural and social worlds, - it maximizes production and accumulation. - We have been in that mode since World War II. - The consequence of this is not only an accumulation and concentration of wealth, - but also the emergence of greater vulnerability because of - the increasing number of interconnections that link that wealth, and - those who control it, - in efforts to sustain it. - Little time and few resources are available for alternatives that explore different visions or opportunities. - Emergence and novelty is inhibited. - This growing connectedness leads to increasing rigidity in its goal to retain control, - and the system becomes ever more tightly bound together. - This reduces resilience and the capacity of the system to absorb change, - thus increasing the threat of abrupt change. - We can recognize the need for change but become politically stifled in our capacity to act effectively.
to - quote - we are now in a back-loop of a planetary adaptive cycle - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004 - https://hyp.is/FTRDoJFuEe-rsvdKeYjr0g/www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol9/iss1/art11/main.html?ref=ageoftransformation.org
comment - These ideas are quite important for those change actors working to emerge creative alternatives - liminal spaces - rapid whole system change
Tags
- planetary phase shift - Nafeez Ahmed
- quote / insight - decreased resiliency due to tight network of elites - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004
- to - quote - we are now in a back-loop of a planetary adaptive cycle - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004
- creative alternatives - liminal spaces - rapid whole system change
- to - paper - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004
- planetary adaptive cycle - Crawford Stanley Holling
- to - paper - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004
- to - book - The Ascent of Humanity - chapter 8 Self and Cosmos: The Gaian Birthing - stillborn and the perilous journey through the womb - Charles Eisenstein
- planetary adaptive cycle - 2004 paper - Crawford Stanley Holling
- essay - The End of Scarcity? From ‘Polycrisis’ to Planetary Phase Shift - Nafeez Ahmed - 2024 Oct 16
- rapid whole system change - Nafeez Ahmed
- planetary adaptive cycle - Nafeez Ahmed
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.ecologyandsociety.org www.ecologyandsociety.org
-
The front-loop phase is more predictable, with higher degrees of certainty. In both the natural and social worlds, it maximizes production and accumulation. We have been in that mode since World War II. The consequence of this is not only an accumulation and concentration of wealth, but also the emergence of greater vulnerability because of the increasing number of interconnections that link that wealth, and those who control it, in efforts to sustain it. Little time and few resources are available for alternatives that explore different visions or opportunities. Emergence and novelty is inhibited. This growing connectedness leads to increasing rigidity in its goal to retain control, and the system becomes ever more tightly bound together. This reduces resilience and the capacity of the system to absorb change, thus increasing the threat of abrupt change. We can recognize the need for change but become politically stifled in our capacity to act effectively.
for - quote - we are in a back-loop phase - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004 - creative alternatives - liminal spaces - rapid whole system change
comment - This is important for discussion for change actors working in liminal spaces attempting to give birth to creative alternatives
-
for - planetary adaptive cycle - entering back-loop phase - paper - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004 - from - essay - The End of Scarcity? From ‘Polycrisis’ to Planetary Phase Shift - Nafeez Ahmed - 2024
from - essay - The End of Scarcity? From ‘Polycrisis’ to Planetary Phase Shift - Nafeez Ahmed - 2024 - https://hyp.is/okOeDJFqEe-9ZsMEsKWR9w/ageoftransformation.org/the-end-of-scarcity-from-polycrisis-to-planetary-phase-shift/
Tags
- from - essay - The End of Scarcity? From ‘Polycrisis’ to Planetary Phase Shift - Nafeez Ahmed - 2024
- planetary adaptive cycle - entering back-loop phase - paper - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004
- quote - we are in a back-loop phase - From Complex Regions to Complex Worlds - Crawford Stanley Holling - 2004
- creative alternatives - liminal spaces - rapid whole system change
Annotators
URL
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Engagingwith the slip box should feel exciting, not anxiety-producing.
I often find that people who discuss "workflows" and the idea of "processing" their notes are the ones who are falling trap to the anxiety-producing side of the work.
BD should have found more exciting words for "processing" which he uses two more times in the next paragraph.
This relates to Luhmann's quote about only doing what is easy/fun/flow:<br /> - https://hypothes.is/a/TQyC1q1HEe2J9fOtlKPXmA<br /> - https://hypothes.is/a/EyKrfK1WEe2RpEuwUuFA7A
Compare: - being trapped in the box: https://hypothes.is/a/AY7ABO0qEeympasqOZHoMQ - idea of drudgery in the phrase "word processing"
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Rhythm, Grammar, Vocab-ulary, Punctuation, etc. It was hard to break thefaggots when they were in a bundle, but it was easyto break them when they were taken one by one.
Notice that again he's emphasizing breaking down the problem into steps, and he's using a little analogy to do so, just like he had described previously.
-
- Aug 2024
-
www.aljazeera.com www.aljazeera.com
-
Costs of War
-
military-industrial comple
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Military%E2%80%93industrial_complex
-
- Jul 2024
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
( ~ 6:25-end )
Steps for designing a reading plan/list: 1. Pick a topic/goal (or question you want to answer) & how long you want to take to achieve this. 2. Do research into the books necessary to achieve this goal. Meta-learning, scope out the subject. The number of books is relative to the goal and length of the goal. 3. Find the books using different tools such as Google & GoodReads & YouTube Recommendations (ChatGPT & Gemini are also useful). 4. Refine the book list (go through reviews, etc., in Adlerian steps, do an Inspectional Read of everything... Find out if it's truly useful). Also order them into a useful sequence for the syntopical reading project. Highlight the topics covered, how difficult they are, relevancy, etc. 5. Order the books (or download them)
Reminds me a bit of Scott Young's Metalearning step, and doing a skill decomposition in van Merriënboer et al.'s 10 Steps to Complex Learning
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Good video. Funnily enough, I related it to Mazlow's hierarchy of competence a minute before you mentioned it. (Mr. Hoorn here, btw.) Another connection I made was to van Merriënboer et al. their "Ten Steps to Complex Learning" or "4 Component Instructional Design". Particularly with regards to doing a skill decomposition (by analyzing experts, the theory, etc.) in order to build a map for how best to learn a complex skill, reducing complexity as much as possible while still remaining true to the authentic learning task; i.e., don't learn certain skills in isolation (drill) unless the easiest version of a task still causes cognitive overload. Because if you learn in isolation too much, your brain misses on the nuances of application in harmony (element interactivity). Related to the concept of "the whole is greater than the sum of its parts". You can master each skill composite individually but still fail epically at combining them into one activity, which is often required.
-
( ~ 5:00 )
The first stage of learning a complex skill is creating relevance, not in the sense of making knowledge relevant to your life; but rather in seeing what is relevant to learn at this point in the learning career.
Building a map...
The actions are exploration and challenge. Exploration = getting diverse opinions from others and learning the theory & variables. Challenge = open-mindedness for other beliefs and assumptions.
Reminds me of 10 Steps to Complex Learning for curriculum design, where doing a skill decomposition is one of the first steps in designing the curriculum, and either being an expert or having access to experts is paramount.
-
-
egusphere.copernicus.org egusphere.copernicus.org
-
for - social tipping point - 2023 paper - paper details
paper details - title: The Pareto effect in tipping social networks: from minority to majority - author - Jordan Everall - Jonathan. F Donges - Ilona. M. Otto - Preprint date - 20 Nov 2023 - Publication - EGUsphere Preprint Repository
summary - This is a recent 2023 paper that summarizes social tipping point research for fields of interest to me, such as climate change. - I'm reading, looking for any real world experimental validation of social tipping point in climate change - I didn't find any but still interesting
from - search - google - research on complex contagion refutes the 25% social tipping point threshold - https://www.google.com/search?q=research+on+complex+contagion+refutes+the+25%25+social+tipping+point+threshold&oq=research+on+complex+contagion+refutes+the+25%25+social+tipping+point+threshold&gs_lcrp=EgZjaHJvbWUyBggAEEUYOTIGCAEQRRhA0gEJMjAyOTRqMGo3qAIAsAIA&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 - search results returned of interest - The Pareto effect in tipping social networks: from minority to ... - https://egusphere.copernicus.org/preprints/2023/egusphere-2023-2241/
-
- Jun 2024
-
-
how do we sort of cultivate an 00:40:56 intuition for complex systems right for those second third nth order effects
for - question - Entangled Worlds podcast - How do we cultivate intuition for complex systems - to access those higher order effects? - answer - Nora Bateson - practice everywhere
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
The main idea, able to be generalized, I get from this video is that in order to develop any skill, whether it is learning or something else, you need to break it down into its constituents, much like the 4 Component Instruction Design model argues, and figure out where your weak links are.
The more accurately you know the system of your skill, the better you know what to potentially improve on. This requires research, and sometimes asking experts.
Another benefit of networking.
-
-
www.linkedin.com www.linkedin.com
-
Wonderful article by the philosopher Jared Henderson, who I regularly watch on YouTube.
-
- May 2024
-
-
the real answer doesn't lie there because all they can do is to go on associating groups of gene expression with particular proteins or particular diseases or whatever and with 00:28:39 the tiniest associations and um that creates all sorts of problems and biomedical sense it creates all sorts of ethical problems
for - problem with gene therapy - Very little association between genes and disease - very complex associations
-
- Apr 2024
-
philpapers.org philpapers.org
-
from - Big Think article - Dan Carlin on humanity’s uncontrollable “Prometheus complex” - https://hyp.is/go?url=https%3A%2F%2Fbigthink.com%2Fthinking%2Fdan-carlin-on-humanitys-uncontrollable-prometheus-complex%2F&group=world
-
-
-
humanity's seemingly unstoppable instinct toward creation. The psychoanalyst Gaston Bachelard coined a term that encapsulates this drive: the "Prometheus complex."
for - progress trap - Prometheus complex - adjacency - progress trap - Prometheus complex - Gaston Bachelard - Gaston Bachelard - French philosopher
adjacency - between - progress trap - Prometheus complex - Gaston Bachelard - adjacency statement - Prometheus complex and progress traps have much in common: - both look at the shadow side of innovation - The mythology of Icarus geting too close the sun is one common to both - Bachelard wrote a pith work on the analysis of the element of fire, in which he introduced the concept of the Prometheus complex - https://philpapers.org/rec/OSEPCA
-
Our hands and our brains will, perhaps unconsciously, drift toward the very thing we’re debating if we should do.
for - quote - Prometheus complex - progress trap
quote - Prometheus complex - progress trap - (see below)
- Our hands and our brains will,
- perhaps unconsciously
- drift towad the very thing we're debating if we should do
- author - Jenny Thomson
- Our hands and our brains will,
-
as the rational, intellectual part of ourselves wrestles with the decision, a deeper, Promethean part of ourselves has pressed it already.
for - quote - Prometheus complex - progress trap
quote - Prometheus complex - progress trap - (see below)
- As the rational, intellectual part of ourselves wrestles with the decision,
- a deeper Promethean part of ourselves has pressed it (the red button) already
- author - Jenny Thomson
- As the rational, intellectual part of ourselves wrestles with the decision,
-
for - progress trap - Prometheus complex - Dan Carlin - Gaston Bachelard - philosopher
summary - This short article brings up an interesting connection between - the Prometheus complex, - a term coined by the French philosopher Gaston Bachelard and - progress traps, - the unintended consequences of progress - The key insight is that human beings may have an Achilles Heel - the desire to know, even at the cost of harm - could be such a powerful impulsive urge - that we throw caution to the wind and - Icarus mythology may be a self-fulfilling prophecy - This also echos the views of my colleague Gyuri Lajos, - that invention for invention sake possesses this very dark side. - This is an important adjacency - as it questions the ethics of knowledge for knowledge sake - As we know from - the history of - progress and its shadowy counterpart, - the progress trap - our impulsive urge to invent has harmful impacts on everyone, - and these continually compound with time
-
At the core, it seems the deeper drive is to invent anything that we’re capable of inventing.
for - impulsive urge - invention - adjacency - progress trap - impulsive urge to invent - Prometheus complex - Gyuri Lajos perspective
Adjacency - between - progress trap - impulsive urge - Gyuri Lajos perspective - Prometheus complex - adjacency statement - It would seem that the the Prometheus complex - is an apt description of that which Gyuri objects to in innovation, namely - innovation for innovation sake - in other words, the impulsive urge merely to know - even if it brings a terrible price
-
under the name of the Prometheus complex
for - definition - Prometheus complex
definition - Prometheus complex - All those tendencies which impel us to know - as much as our fathers, more than our fathers - as much as our teachers, more than our teachers - author - Gaston Bachelard
-
[I wonder] whether or not human society actually has the agency that we think we have to not invent something if we think it might be bad.
for - quote - Dan Carlin - quote - progress trap - Prometheus complex - Dan Carlin
quote - progress trap - Prometheus complex - (see below)
- [I wonder] whether or not human society actually has the agency that we think we have
- to not invent something if we think it might be bad.
- If you look down the technological road in the distance and see something horrible, could humankind go,
- ‘Oh, you know what? We’re just not going to go there.’
- I’m not sure we have that agency.
comment - Deep Humanity praxis proposes that a new discipline of Progress traps is what is needed to do exactly this - Give us a meta perspective so that we can assess future harm and damage as - AN ACTIONABLE FORESIGHT, not a - TREATABLE HINDSIGHT
- [I wonder] whether or not human society actually has the agency that we think we have
Tags
- adjacency - progress trap - impulsive urge to invent - Prometheus complex - Gyuri Lajos perspective
- Icarus mythology - progress trap
- quote - Prometheus complex - progress trap
- quote - progress trap - Prometheus complex
- progress trap - Prometheus complex
- dark side of invention
- definition - Prometheus complex
- Prometheus complex - philosopher - Gaston Bachelard
- quote - Dan Carlin
- adjacency - Prometheus complex - progress trap
- Prometheus complex
- Dan Carlin - podcast - Hardcore History
Annotators
URL
-
- Mar 2024
-
jods.mitpress.mit.edu jods.mitpress.mit.edu
- Feb 2024
-
hypothes.is hypothes.is
-
One of my inquiries was for anecdotes regarding mistakes made between the twins by their near relatives. The replies are numerous, but not very varied in character. When the twins are children, they are usually distinguished by ribbons tied round the wrist or neck; nevertheless the one is sometimes fed, physicked, and whipped by mistake for the other, and the description of these little domestic catastrophes was usually given by the mother, in a phraseology that is some- [p. 158] what touching by reason of its seriousness.
Tags
- The parental mistake highlights that even when twins are in the same house or even siblings in the same house can develop diffrent traits through parental mistakes. For instance
- We can see that mistaken one twin for another by spanking the wrong one could create a god complex in the twin that got away with bad behavior. while the twin who was unjustly spanked could feel inferior to the other twin even other people. Therefore nuture developing different traits based on parent's upbringing.
Annotators
URL
-
-
rwu.brightspace.com rwu.brightspace.com
-
Other people are the mirror in witch we see ourselves. Individual judge himself in the light of what he percives to be the way in wich others judge him in comparison to thenselves.
-
-
inthesetimes.com inthesetimes.com
-
“We’re seeing people turn right for a number of different reasons,” argues journalist Eoin Higgins
for left-to-right sliders - complex reasons
“We’re seeing people turn right for a number of different reasons,” - argues journalist Eoin Higgins, - author of a forthcoming book on formerly left-wing journalists - who’ve aligned with reactionary tech billionaires.
- “There are
- financial incentives, there are
- attention incentives, there are
- culture war differences as people are becoming more conservative on culture; there’s
- a sense of being betrayed by progressives and the Left.
- There are so many different reasons that
- reducing this to people
- going too far [left] and
- going to the Right
- is an oversimplification.
- “There are
-
- Dec 2023
-
-
many people are complex systems thinkers even though they don't know it
-
for: example - systems thinking, quote -: many people are complex systems thinkers
-
quote:
- many people are complex systems thinkers even though they don't know it
- Thomas Homer-Dixon
-
date: 2023
-
examples: complex systems clichés
- the whole of greater than the sum of its parts
- nonlinearities
- the straw that broke the camels back
- emergence
- the whole of greater than the sum of its parts
-
comment
- the first one could be that systems are not the same as just all the parts
- the second one could also represent Tipping points and nonlinearities of complex systems
-
-
- Sep 2023
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
08:00 his sword technique was adaptable, mendable, consistent with the complex nature of reality, that changes constantly, not resisting change but adapting self to it
- see zk on how a more dynamic approach to productivity and systems can help us reflect reality more closely, ever changing
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
mywiki.wooledge.org mywiki.wooledge.org
-
If IFS is unset, or its value is exactly <space><tab><newline>, the default, then any sequence of IFS characters serves to delimit words. If IFS has a value other than the default, then sequences of the whitespace characters space and tab are ignored at the beginning and end of the word, as long as the whitespace character is in the value of IFS (an IFS whitespace character). Any character in IFS that is not IFS whitespace, along with any adjacent IFS whitespace characters, delimits a field. A sequence of IFS whitespace characters is also treated as a delimiter. If the value of IFS is null, no word splitting occurs.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
juliandavid.co.uk juliandavid.co.uk
-
It was a radically different idea of nature and a radically different idea of the Unconscious—which were for Jung, the same thing. The Unconscious was no more than the inwardness of nature. For Freud it was the reject-matter of civilization, and the whole purpose of his psychology was to enable men to reject it more firmly. For Jung, the Unconscious was Mother; and the Oedipus myth was concerned with man’s troubled relationship (for he has to leave her) to that great, unconscious source.
Unconscious as nature (“mother”) for Jung — awfulness of humanity, repressed, for Freud
-
- Aug 2023
-
-
Can policy promote beneficial norm change? The model suggests that effective interventions lower the tipping threshold.
- for: social tipping point, STP, TPF, social norms, complex contagion, lowering threshold
- policy changes can lower tipping point thresholds
-
Two factors consistently helped hasten beneficial change in our study.
- for: social tipping point, STP, tipping point, social norm, complex contagion
- study findings
- Two factors can help hasten beneficial change
- common understanding of the benefits from change due to:
- events that attract attention
- opinion polls that aggregate information
- finding an angle on an issue that appeals to a broad demographics
- perserverence
- leaders who persevere even at great cost
- common understanding of the benefits from change due to:
- Two factors can help hasten beneficial change
-
- Jul 2023
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
- for: social tipping point, STP
- title
- Creating Change: How to Make Big Things Happen
- guest
- Damon Centola
- description
- a very clear exposition of how complex contagion works and what must be done to spread complex behavior change
- comment
- this is particularly important for rapid whole system change and mobilizing a bottom-up movement to deal with our current polycrisis
-
- Jun 2023
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
persecution complex
- Persecution complex
- One of the most widely and deeply spread memes, and corresponding behavior within Evangelical Christians is a persecution complex
- This is a attitude of righteousness and feeling attacked for holding their righteous views
- This meme and accompanying behavior appeals to base emotion of fear to shut down intelligent conversation
- It makes them impervious to constructive criticism
- Persecution complex
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
persecution complex
- Persecution complex
- One of the most widely and deeply spread memes, and corresponding behavior within Evangelical Christians is a persecution complex
- This is a attitude of righteousness and feeling attacked for holding their righteous views
- This meme and accompanying behavior appeals to base emotion of fear to shut down intelligent conversation
- It makes them impervious to constructive criticism
- Persecution complex
-
- Apr 2023
-
beiner.substack.com beiner.substack.com
-
Daniel Schmachtenberger has spoken at length about the ‘generator functions’ of existential risk, in essence the deeper driving causes.
Definition - generator function of existential risk - the deeper driving cause of existential risk - two examples of deep causes - rivalrous dynamics - complicated systems consuming their complex substrate
Claim - Alexander Beiner claims that - the generator function of these generator functions is physicalism
-
- Mar 2023
-
web.archive.org web.archive.org
-
Structures and Transformations of the Vocabulary of the Egyptian Language: Text and Knowledge Culture in Ancient Egypt. “Altägyptisches Wörterbuch: Berlin-Brandenburgische Akademie der Wissenschaften 1999,” 2007. https://web.archive.org/web/20180627163317/https://aaew.bbaw.de/wbhome/Broschuere/index.html.
-
Die schiere Menge sprengt die Möglichkeiten der Buchpublikation, die komplexe, vieldimensionale Struktur einer vernetzten Informationsbasis ist im Druck nicht nachzubilden, und schließlich fügt sich die Dynamik eines stetig wachsenden und auch stetig zu korrigierenden Materials nicht in den starren Rhythmus der Buchproduktion, in der jede erweiterte und korrigierte Neuauflage mit unübersehbarem Aufwand verbunden ist. Eine Buchpublikation könnte stets nur die Momentaufnahme einer solchen Datenbank, reduziert auf eine bestimmte Perspektive, bieten. Auch das kann hin und wieder sehr nützlich sein, aber dadurch wird das Problem der Publikation des Gesamtmaterials nicht gelöst.
Google translation:
The sheer quantity exceeds the possibilities of book publication, the complex, multidimensional structure of a networked information base cannot be reproduced in print, and finally the dynamic of a constantly growing and constantly correcting material does not fit into the rigid rhythm of book production, in which each expanded and corrected new edition is associated with an incalculable amount of effort. A book publication could only offer a snapshot of such a database, reduced to a specific perspective. This too can be very useful from time to time, but it does not solve the problem of publishing the entire material.
While the writing criticism of "dumping out one's zettelkasten" into a paper, journal article, chapter, book, etc. has been reasonably frequent in the 20th century, often as a means of attempting to create a linear book-bound context in a local neighborhood of ideas, are there other more complex networks of ideas which we're not communicating because they don't neatly fit into linear narrative forms? Is it possible that there is a non-linear form(s) based on network theory in which more complex ideas ought to better be embedded for understanding?
Some of Niklas Luhmann's writing may show some of this complexity and local or even regional circularity, but perhaps it's a necessary means of communication to get these ideas across as they can't be placed into linear forms.
One can analogize this to Lie groups and algebras in which our reading and thinking experiences are limited only to local regions which appear on smaller scales to be Euclidean, when, in fact, looking at larger portions of the region become dramatically non-Euclidean. How are we to appropriately relate these more complex ideas?
What are the second and third order effects of this phenomenon?
An example of this sort of non-linear examination can be seen in attempting to translate the complexity inherent in the Wb (Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache) into a simple, linear dictionary of the Egyptian language. While the simplicity can be handy on one level, the complexity of transforming the entirety of the complexity of the network of potential meanings is tremendously difficult.
-
Die schiere Menge sprengt die Möglichkeiten der Buchpublikation, die komplexe, vieldimensionale Struktur einer vernetzten Informationsbasis ist im Druck nicht nachzubilden, und schließlich fügt sich die Dynamik eines stetig wachsenden und auch stetig zu korrigierenden Materials nicht in den starren Rhythmus der Buchproduktion, in der jede erweiterte und korrigierte Neuauflage mit unübersehbarem Aufwand verbunden ist. Eine Buchpublikation könnte stets nur die Momentaufnahme einer solchen Datenbank, reduziert auf eine bestimmte Perspektive, bieten. Auch das kann hin und wieder sehr nützlich sein, aber dadurch wird das Problem der Publikation des Gesamtmaterials nicht gelöst.
link to https://hypothes.is/a/U95jEs0eEe20EUesAtKcuA
Is this phenomenon of "complex narratives" related to misinformation spread within the larger and more complex social network/online network? At small, local scales, people know how to handle data and information which is locally contextualized for them. On larger internet-scale communication social platforms this sort of contextualization breaks down.
For a lack of a better word for this, let's temporarily refer to it as "complex narratives" to get a handle on it.
Tags
- Lie theory
- complex narratives
- digitized note collections
- thinking inside of the box
- Lie groups
- social media
- dumping out one's zettelkasten
- references
- insight
- network theory
- small local wastes in exchange for greater global efficiencies
- XX
- zettelkasten complexity
- zettelkasten examples
- Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache
- misinformation
- experimental nonfiction
- card index as autobiography
- read
- non-linear narratives
- linear narratives
- rhetoric
- local vs. global
- thinking outside of the box
- open questions
- media studies
- context collapse
- digital humanities
Annotators
URL
-
- Feb 2023
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
i can use myself as an example here i i consider myself a pretty smart person i'm in grad school i tried to be really analytical my whole 00:03:56 life and yet i showed up at college when i was 19 years old believing that all the supposedly scientific stuff that white nationalists used to support the idea of race being predictive and segregation being 00:04:09 good and all this stupid stuff i totally believed i thought they were right and i thought everybody was just denying it and it took a community of people in college over years to condemn my beliefs to 00:04:22 show me uh kindness to show me real vitriol to be these in these private conversations where we could go over the facts and it took a long time for me thinking i was really smart and analytical to 00:04:35 accept that it was morally wrong that it was ethically wrong
- comment
- Derek Black is an example
- of what it takes to undo deeply culturally conditioned misinformation
- these variables have to be present for that to work
- open mind
- patience
- accurate information
- a caring, patient, informed community
- Derek Black offers a lesson of what is required to depolarize society using social tipping points
- there needs to be scalable education program to reach still open-minded individuals holding opposing views
- to openly and respectfully debate difficult, polarizing issues
- in order to form the wide bridges necessary for social tipping points of complex issues
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
| physics/mathematics | Classical Physics | Quantum Mechanics |<br /> |---|---|---|<br /> | State Space | fields satisfying equations of laws<br>- the state is given by a point in the space | vector in a complex vector space with a Hermitian inner product (wavefunctions) |<br /> | Observables | functions of fields<br>- usually differential equations with real-valued solutions | self-adjoint linear operators on the state space<br>- some confusion may result when operators don't commute; there are usually no simple (real-valued) numerical solutions |
-
-
news.cornell.edu news.cornell.edu
-
Human infants need to acquire complex social skills, including language, empathy, morality and theory of mind, the researchers said. Successful development of these skills depends on information from adults: “Rather than requiring hard-wired, innate knowledge of social abilities, evolution has outsourced the necessary information to parents,”
- rather than hard-wiring innate knowledge of complex social skills, nature outsources = complex social skills - like:
- language
- empathy
- morality
- theory of mind
- to parents
- rather than hard-wiring innate knowledge of complex social skills, nature outsources = complex social skills - like:
-
-
penntoday.upenn.edu penntoday.upenn.edu
-
real-life situations can be much more complicated, the authors’ model allows for the exact 25 percent tipping point number to change based on circumstances. Memory length is a key variable, and relates to how entrenched a belief or behavior is.
- 25% social tipping point threshold is adjustable
- depending on the variables of the context
- = question - how do we apply this adjustability for complex contagion such as climate change norms?
-
-
www.google.com www.google.com
-
25:13Complex Contagions
- = complex contagion
- example: climate change norms
- = complex contagion
-
- Jan 2023
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
A term recommended by Eve regarding an interdisciplinary approach that accounts for multiple feedback loops within complex systems. Need to confer complex systems science to see if ADHD is already addressed in that domain.
-
- Dec 2022
-
link.springer.com link.springer.com
-
complex contagions, a type of social contagion which requires social reinforcement from multiple adopting neighbors.
-
- Nov 2022
-
library.oapen.org library.oapen.org
-
Modern science is, to a large extent, a model-building activity. In the natural and engineering sciences as well as in the social sciences, models are constructed, tested and revised, they are compared with other models, applied, interpreted and sometimes rejected or replaced by a better model.
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Computers can only deal with well-structured problems
ie, "well-defined problems" in John Vervaeke's language. Cultivation of wisdom, per Vervaeke, is developing the capacity to navigate a ill-defined problem space, and realize (ie, recognize, and make real) what is relevant to resolving the situation.
Examples of ill-defined problems: - how to take good notes? - how to tell a funny joke? - how to go on a successful 1st date? - how to be a good friend?
May relate to Shapiro's "role theory". Needs further research
-
-
-
As the British prime minister WilliamGladstone put it at the time in the Edinburgh Review, speaking of the remarkablePrussian success in the Franco-Prussian War: ‘Undoubtedly, the conduct of thecampaign, on the German side, has given a marked triumph to the cause ofsystematic popular education.’
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Additionally, Henry Giroux claims that it was originally "military–industrial–academic complex".[16]
-
- Sep 2022
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
we can kind of make an assumption that 00:04:22 complex brains and by extension complex intelligence should also be somewhat common in terms of evolutionary success and assuming that it's evolutionary preferential or basically that evolves many times throughout the history of the 00:04:35 planet we can then make a conjecture that it should exist somewhere out there where life exists on other planets okay just to rephrase this if we truly believe that extraterrestrial intelligence exists out there and that 00:04:48 it kind of evolved in the same way that it evolved here on planet earth it's pretty safe to assume that it might have evolved several times on the planet because we're making an assumption here that this is an evolutionary advantage 00:05:00 that all planets that potentially have life on them are going to end up with some kind of a species that's going to become super intelligent and that's going to be self-aware able to use technology and essentially kind of communicate in the same way that we 00:05:13 communicate using for example radio waves
!- in other words : there should be signs of complex intelligence like ours in the paleontological records
-
- Aug 2022
-
medium.com medium.com
-
Mayer says time-restricted eating — a form of intermittent fasting that requires you to squeeze all your daily calories into a compressed feeding window — may be helpful. “The migrating motor complex is rarely mentioned in these articles on intermittent fasting, which is surprising because it’s so well-studied,” he says.To ensure the MMC has enough time to perform its duties, aiming for 14 hours without caloric foods or drinks is a good target, he says. For example, you could avoid all calories between 8 p.m. and 10 a.m. “The 14 hours without food intake would allow the MMC to kick in and not only cleanse your gut of any undigestible, unabsorbable food components, but also to reestablish the normal proximal-to-distal gradient of gut microbial density,” he says.
!- For : microbiome health - fasting for 14 hours helps the migrating motor complex (MMC) maintain gut health
-
-
impedagogy.com impedagogy.com
-
I am going to add some optional 'reading and doing' directions to my posts. Might be helpful.
- You might listen to the poem first.
- You might answer the question that Trethewey asks first. Maybe you can engage in the margins with it.
- You can make all or part of your responses public or private.
- You can start a group to consider the question.
- You can have at it in the order presented: my intro--> Twitter thread--> my response to the thread-->check out the link-->listen to the poem.
- Perch in the margins with the withered wild grapes and the black haw and the redbuds.
- Join in the work of forecasting your own life.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
could you share with us how you learn new complex topics
This is worthwhile for all of us who share complex topics with others and want to get better at that.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Jun 2022
- Feb 2022
-
-
In the research phase, you’re just creating a disorganized pile of cards, with quotes, ideas, links, fragments, hunches. There’s no order, no sequence; just a non-linear collection of vaguely related ideas. But as the project takes shape, certain themes begin to emerge, and those become folders housing other cards. Eventually those themes start to map onto actual sections of the book, or individual chapters. At this point, sequence does begin to matter, but you can change the sequence just by dragging cards and folders around in the left hand outline view.
Example of writing advice that builds the links in after-the-fact instead of cross-linking ideas into initial networks as they're finding them. Compare/contrast this to the creation of these networks in the zettelkasten tradition as well as Sönke Ahrens description.
There's less upfront work in creating these links at the start than there is in reloading the context in one's brain to create these links after the fact. Collecting ideas without filing, linking, or organizing them upfront also means that one is more likely to only use these ideas in the context of specific projects which one already has in mind rather than keeping them for a lifetime's work which might also create generative projects one hadn't expected.
-
-
thinkzone.wlonk.com thinkzone.wlonk.com
-
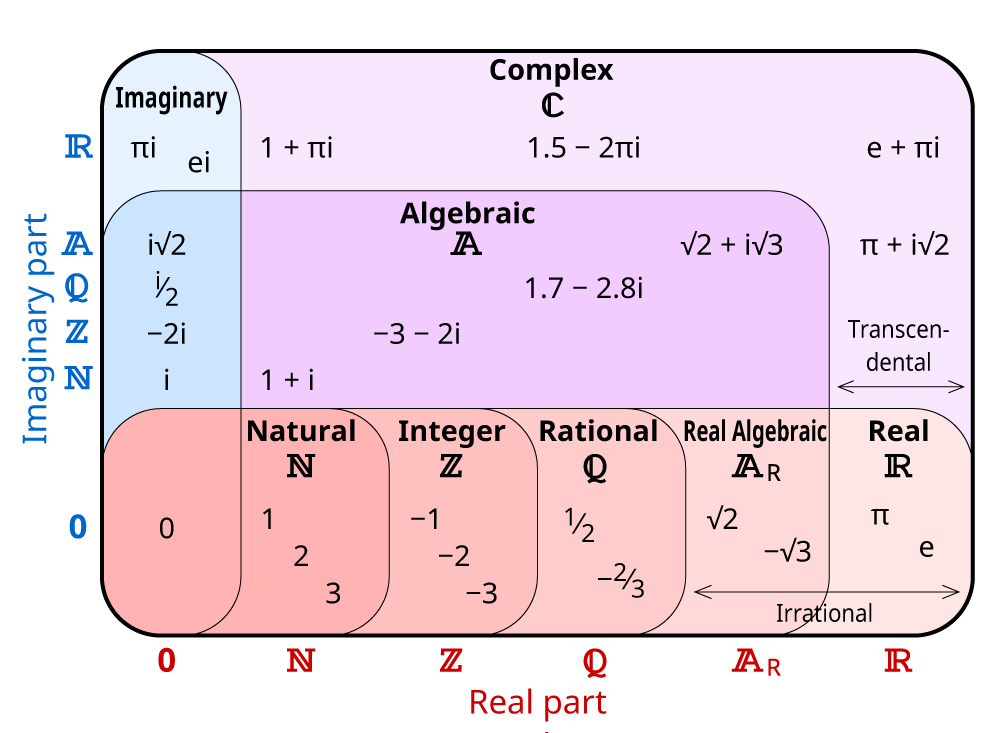
https://thinkzone.wlonk.com/Numbers/NumberSets.htm
A relatively clear explanation of the types of numbers and their properties.
I particularly like this diagram:
-
-
archive.org archive.org
-
Diesen gebrochenen Zahlen, welche zunächst als reine Zeichen auftreten, kann in vielen Fällen eine actuelle Bedeutung beigelegt werden.
A presented meaning can in many cases be attributed to these rational numbers, which at first appear as pure signs,
-
Wie wir die Regeln der rein formalen Verknüpfungen, d. h. der mit den mentalen Objecten vorzunehmenden Operationen definiren, steht in unserer Willkühr, nur muss eine Bedingung als wesentlich festgehalten werden: nämlich dass irgend welche logische Widersprüche in den- selben nicht implicirt sein dürfen.
How we define the rules of purely formal operations (Verknüpfungen), i.e., of carrying out operations (Operationen) with mental objects, is our arbitrary choice, except that one essential condition must be adhered to: namely that no logical contradiction may be implied in these same rules.
-
man sich zu der gegebenen Reihe von Ob- jecten eine inverse hinzudenkt
one adds an inverse in thought to the given series of objects
-
Man sieht aber nicht, wie unter — 3 eine reale Substanz verstanden werden kann, wenn das ursprünglich gesetzte Object eine solche ist, und würde im Rechte sein, wenn man — 3 als eine nicht reelle, imaginäre Zahl als eine „falsche" bezeichnete.
one cannot see how a real substance can be understood by -3... and would be within his rights if he refers to -3 as a non-real, imaginary number, as a "false" one.
-
Eine andere Definition des Begriffes der formalen Zahlen kann nicht gegeben werden; jede andere muss aus der Anschauung oder Erfahrung Vorstellungen zu Hilfe nehmen, welche zu dem Begriffe in einer nur zufälligen Beziehung stehen, und deren Beschränktheit einer allgemeinen Untersuchung der Rechnungsoperationen unüber- steigliche Hindemisse in den Weg legt..
A different definition of the concept of the formal numbers cannot be given; every other definition must rely on ideas from intuition or experience, which stand in only an accidental relation to the concept, and the limitations of which place insurmountable obstacles in the way of a general investigation of the arithmetic operations.
-
Die Bedingung zur Aufstellung einer allgemeinen Arithmetik ist daher eine von aller Anschauung losgelöste, rein intellectuelle Mathem&tik, eine reine Formenlehre, in welcher nicht Quanta oder ihre Bilder, die Zahlen verknüpft werden, sondern intellectuelle Objecte, Gedankendinge, denen actuelle Objecte oder Relationen solcher entsprechen kön- nen, aber nicht müssen.
The condition for the establishment of a general arithmetic is therefore a purely intellectual mathematics detached from all intuition, a pure theory of form, in which quanta or their images, the numbers, are not combined, but rather intellectual objects, thought-things, to which presented objects or relations of such objects can, but need not, correspond.
-
Wie überhaupt die Entwicklung mathematischer Begriffe und Vorstellungen historisch zwei entgegengesetzte Phasen zu durchlaufen pflegt, so auch die des Imaginären. Zunächst erschien dieser Begriff' als paradox, streng genommen unzulässig, unmög- lich;
As the development of mathematical concepts and ideas generally goes historically through two opposed phases, so goes also that of the imaginary numbers. At first this concept appeared as a paradox, strictly inadmissible, impossible;
-
Wissenschaft leistete, im Laufe der Zeit alle Zweifel an seiner Legitimität nieder und es bildete sich die Ueberzeugung seiner inneren Wahrheit und Nothwendigkeit in solcher Entschiedenheit aus, dass die Schwierigkeiten und Widersprüche, welche man anfangs in ihm bemerkte, kaum noch gefühlt wurden. In diesem zweiten Stadium befindet sich die Frage des Imaginären heut zu Tage ; — indessen bedarf es keines Beweises, dass die eigentliche Natur von Begriffen und Vorstellungen erst dann hinreichend auf- geklärt ist, wenn man unterscheiden kann, was an ihnen noth- wendig ist, und was arbiträr, d. h. zu einem gewissen Zwecke in sie hineingelegt ist.
however, in the course of time, the essential services which it affords to science subdue all doubts of its legitimacy, and one is convinced in such decisiveness of its inner truth and necessity, that the difficulties and contradictions which one noticed in it at the beginning are hardly felt. Today, the question of imaginary numbers is in this second stage; --- however it needs no proof that the actual nature of concepts and ideas is only sufficiently clarified when one can distinguish what is necessary in them, and what is arbitrary, i.e., is put to a certain purpose in them.
-
- Jan 2022
-
eleanorkonik.com eleanorkonik.com
-
For most people, the most efficient method to get a quality paper done is to sit down and write it. Short of a project like a dissertation, most people can handle the organization of an essay without a lot of front-loading. Predictably, then, kids start resenting being forced to outline for no reason. Ditto studying habits or notetaking; most of my “good” students hate taking notes because … why should they bother? They’re going to remember most of what they actually need to know without having to study, not least of which because they’re more likely to be tested on skills than knowledge.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Chambon, M., Kammeraad, W., Harreveld, F. van, Dalege, J., Elberse, J., & Maas, H. van der. (2022). Why COVID-19 vaccination intention is so hard to change: A longitudinal study. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/b9qrj
-
-
-
At Packlane, we're all about quality without compromise. Our team of experts will work with you to take your custom packaging concept from proof to press at a steep volume discount. For orders of 2,000 boxes or more, please send us your contact information and we'll get right back to you. For smaller orders, you can get an instant quote with our easy-to-use box designer. To get started, choose your style. You're in good company.
As I mentioned in a previous comment, I find it interesting to filter a discount or differentiated value by a larger target.
-
-
-
Liu, C., Yang, Y., Chen, B., Cui, T., Shang, F., & Li, R. (2022). Revealing spatio-temporal interaction patterns behind complex cities. ArXiv:2201.02117 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2201.02117
-
- Nov 2021
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
i think the focus was very much on energy supply and to a limited extent on things like um yeah technologies and like vehicle 01:00:07 technologies for example but um much much less in terms of getting people to particularly in developed countries to use less energy and to change diet and to travel less and fly less and all these these things and i think part of 01:00:19 that and it is also reflected in the fact that it was fairly much absent in the uk's net zero strategy is that it is seen as being politically difficult that it might be a you know it might mean that they that politicians lose votes that 01:00:33 it's just too difficult to get people to change their behavior that it's threatening that it might mean lower standards of living um in developed countries etc so i think kind of it's still it's still seen as something and that that was quite explicit i think in 01:00:45 the forward to the uk strategy um so i think in terms of how we move beyond that that's that's difficult but i think it is about reframing behavior change and demand demand management in 01:00:58 much more positive terms to say this isn't a threat there are actually opportunities there are opportunities to improve people's health and well-being to create green jobs to reskill people in new sectors and 01:01:09 and so on and it is not about you know reducing uh quality of life or well-being it's not about people losing jobs etc so this is i think there's a job here to kind of reframe it in terms of those those opportunities and those 01:01:22 co-benefits so that would be my my initial thought
Reframing loss as gain is one strategy worth exploring for behavior change. Also explore social tipping points of complex contagion.
-
-
www.yesmagazine.org www.yesmagazine.org
-
social change typically spreads as ‘complex contagions,’ requiring multiple sources of social reinforcement to induce adoption,”
Climate change requires large investment in behavior change. It is a case of complex contagion, not simple contagion. Wide bridges are the key to bringing about social tipping points of complex contagion.
-
-
journals-sagepub-com.scsuproxy.mnpals.net journals-sagepub-com.scsuproxy.mnpals.net
-
Politically and legally, the principle of subsidiarity ensures that education remains a national competence for EU Member States (Ertl, 2006), while, theoretically, scholarly research points to the continued relevance of the state within a multi-scalar governance complex (Levinson et al., 2020; Tröhler, 2020).
multi-scalar governance complex (Levinson et al.,<br> 2020; Tröhler, 2020).
-
-
drive.google.com drive.google.com
-
Politically and legally, the principle of subsidiarity ensures that education remains a nationalcompetence for EU Member States (Ertl, 2006), while, theoretically, scholarly research points tothe continued relevance of the state within a multi-scalar governance complex
multi-scalar governance complex
-
-
learn2.open.ac.uk learn2.open.ac.uk
-
We are also concerned primarily with human activity systems. One individual alone can rarely affect a situation that they are part of, in ways that bring about improvements. This is partly because of the unpredictable way in which human activity systems function, which cannot be anticipated, and partly because bringing about such improvements often requires collaboration or negotiation among individuals – interactions of a particular kind.
community is more likely to make large-scale change than a single voice.
-
-
rupress.org rupress.org
-
a stoichiometry of approximately one complex molecule per actin monomer
This seems like an unreasonably high stoichiometry of Arp2/3 complexes per actin subunit; we now know that each Arp2/3 complex covers a few subunits, so there shouldn't be enough room on the filament to fit 1:1 Arp2/3 complex/actin
-
- Oct 2021
-
www.cambridge.org www.cambridge.org
-
Lagnado, D. A. (2022). Explaining the evidence: How the mind investigates the world. Cambridge University Press.
-
- Aug 2021
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Murphy, C., Laurence, E., & Allard, A. (2021). Deep learning of contagion dynamics on complex networks. Nature Communications, 12(1), 4720. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24732-2
-
- Jul 2021
-
github.com github.com
-
apart from [Websockets], which is unnecessarily complex for non-browser applications
-
-
link.aps.org link.aps.org
-
Ghavasieh, A., Nicolini, C., & De Domenico, M. (2020). Statistical physics of complex information dynamics. Physical Review E, 102(5), 052304. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.102.052304
-
-
-
Ingale, M., & Shekatkar, S. M. (2020). Resource dependency and survivability in complex networks. Physical Review E, 102(6), 062304. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.102.062304
-
- Jun 2021
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Zhong, L., Diagne, M., Wang, W., & Gao, J. (2021). Country distancing increase reveals the effectiveness of travel restrictions in stopping COVID-19 transmission. Communications Physics, 4(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-021-00620-5
-
-
www.migrationencounters.org www.migrationencounters.org
-
The apartment that we moved into in California was a one-bedroom apartment. It was a big complex and I remember it. There was a pool in the middle and there were a lot of families like us that shared a one-bedroom apartment. And there were eight to twelve people in this one space, and we were trying to find something bigger, but it was impossible.
Time in the US, Arriving in the United States, Living Situation
-
- Apr 2021
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Chambon, Monique, Jonas Dalege, Lourens Waldorp, Han van der Maas, Denny Borsboom, and Frenk van Harreveld. ‘A Complex Systems Perspective on Compliance with Behavioral Measures during the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Netherlands: How Psychological Networks Can Inform Interventions.’ PsyArXiv, 31 March 2021. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/fmu9w.
-
- Mar 2021
-
bugs.ruby-lang.org bugs.ruby-lang.org
-
A one-liner alternative for hash-only cases can be implemented using Enumerable#reduce: root = {} [:a, :b, :c].reduce(root){@1[@2]||={}}[:d] = 'E' # root => {:a=>{:b=>{:c=>{:d=>"E"}}}}
-
I think the issues/problems specified in the comments are not present with a Hash-only implementation. :) I would be supportive of re-considering this feature just for use with a Hash, where I believe 80% of the real-life use cases would (and do) exist. I have encountered this need before in the wild, but not with Arrays.
-
-
-
Wang, Xiangrong, Alejandro Tejedor, Yi Wang, and Yamir Moreno. ‘Unique Superdiffusion Induced by Directionality in Multiplex Networks’. ArXiv:2011.00991 [Physics], 2 November 2020. http://arxiv.org/abs/2011.00991.
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
There’s typically a complex tree of dependencies, where packages all tend to rely on each other in order to function.
-
- Feb 2021
-
www.cbc.ca www.cbc.ca
-
Pennycook, Gordon. ‘How the COVID-19 Crisis Exposes Widespread Climate Change Hypocrisy’. CBC, 22 May 2020. https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/saskatchewan/opinion-climate-change-should-believe-dont-understand-1.5482416.
-
-
-
Aminpour, P., Gray, S. A., Singer, A., Scyphers, S. B., Jetter, A. J., Jordan, R., Murphy, R., & Grabowski, J. H. (2021). The diversity bonus in pooling local knowledge about complex problems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(5). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2016887118
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
AI agents can acquire novel behaviors as they interact with the world around them and with other agents. The behaviors learned from such interactions are virtually impossible to predict, and even when solutions can be described mathematically, they can be “so lengthy and complex as to be indecipherable,” according to the paper.
The sheer number of interacting variables that you'd need to track makes it impossible to make any accurate predictions.
-
-
copyheart.org copyheart.org
-
Instead of trying to educate everyone on the complexities of copyright law, we’d rather make our intentions clear with this simple statement:
-
- Jan 2021
-
covid-19.iza.org covid-19.iza.org
-
Grözinger. N., Irlenbusch ., B., Laske. K., Schröder., M (2020) Innovation and Communication Media in Virtual Teams – An Experimental Study. Institute of Labor Economics. https://covid-19.iza.org/publications/dp13218/
-
- Nov 2020
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Edward J. Alessi, P. D., Courtney Hutchison, L. M., & Sarilee Kahn, P. D. (2020). Understanding COVID-19 through a complex trauma lens: Implications for effective psychosocial responses. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/8kmqb
-
-
www.plymouth.edu www.plymouth.edu
-
active site
This is the part of the enzyme where the substrate binds. The substrate enters the active site to form an enzyme-substrate complex.
-
- Oct 2020
-
www.plymouth.edu www.plymouth.edu
-
catabolic
This is the process of breaking down complex substances within a living organism into smaller ones. This process also releases energy unlike anabolism.
-
-
-
Ghavasieh, A., Nicolini, C., & De Domenico, M. (2020). Statistical physics of complex information dynamics. ArXiv:2010.04014 [Cond-Mat, Physics:Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.04014
-
-
link.aps.org link.aps.org
-
Burda, Z., Kotwica, M., & Malarz, K. (2020). Ageing of complex networks. Physical Review E, 102(4), 042302. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.102.042302
-
- Aug 2020
-
link.aps.org link.aps.org
-
Perez, I. A., Di Muro, M. A., La Rocca, C. E., & Braunstein, L. A. (2020). Disease spreading with social distancing: A prevention strategy in disordered multiplex networks. Physical Review E, 102(2), 022310. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.102.022310
-
-
jamanetwork.com jamanetwork.com
-
Mishra, V., & Dexter, J. P. (2020). Comparison of Readability of Official Public Health Information About COVID-19 on Websites of International Agencies and the Governments of 15 Countries. JAMA Network Open, 3(8), e2018033–e2018033. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.18033
-
-
-
Young, J.-G., Cantwell, G. T., & Newman, M. E. J. (2020). Robust Bayesian inference of network structure from unreliable data. ArXiv:2008.03334 [Physics, Stat]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2008.03334
-
-
covid-19.iza.org covid-19.iza.org
-
Grözinger. N., Irlenbusch. B., Laske. K., Schröder. M., (2020). Innovation and Communication Media in Virtual Teams – An Experimental Study. Institute of Labor Economics. Retrieved from: https://covid-19.iza.org/publications/innovation-and-communication-media-in-virtual-teams-an-experimental-study/
-
-
biorxiv.org biorxiv.org
-
Clausen, T. M., Sandoval, D. R., Spliid, C. B., Pihl, J., Painter, C. D., Thacker, B. E., Glass, C. A., Narayanan, A., Majowicz, S. A., Zhang, Y., Torres, J. L., Golden, G. J., Porell, R., Garretson, A. F., Laubach, L., Feldman, J., Yin, X., Pu, Y., Hauser, B., … Esko, J. D. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 Infection Depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2. BioRxiv, 2020.07.14.201616. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.14.201616
-
- Jul 2020
-
nautil.us nautil.us
-
West, D. K. & G. (2020, July 8). The Damage We’re Not Attending To. Nautilus. http://nautil.us/issue/87/risk/the-damage-were-not-attending-to
-
-
www.kqed.org www.kqed.org
-
is to make sure that students have sufficient background knowledge to stimulate interest and avoid confusion.
Scaffolding teaching? Providing those hints that are mentioned earlier in the article?
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Chambon, M., Dalege, J., Elberse, J., & van Harreveld, F. (2020). A psychological network approach to factors related to preventive behaviors during pandemics: A European COVID-19 study [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/es45v
-
- Jun 2020
-
behavioralscientist.org behavioralscientist.org
-
Gauri, V. (2020 April 30). Behavioral Public Policy Faces a Crisis. Behavioral Scientist. https://behavioralscientist.org/behavioral-public-policy-faces-a-crisis/
-
-
-
Murphy, C., Laurence, E., & Allard, A. (2020). Deep learning of stochastic contagion dynamics on complex networks. ArXiv:2006.05410 [Cond-Mat, Physics:Physics, Stat]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.05410
-
-
academic.oup.com academic.oup.com
-
Marshall, B. D. L., & Galea, S. (2015). Formalizing the Role of Agent-Based Modeling in Causal Inference and Epidemiology. American Journal of Epidemiology, 181(2), 92–99. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwu274
-
-
-
Jazayeri, A., & Yang, C. C. (2020). Motif Discovery Algorithms in Static and Temporal Networks: A Survey. ArXiv:2005.09721 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.09721
-
-
iopscience.iop.org iopscience.iop.org
-
Parisi, F., Squartini, T., & Garlaschelli, D. (2020). A faster horse on a safer trail: Generalized inference for the efficient reconstruction of weighted networks. New Journal of Physics, 22(5), 053053. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/ab74a7
-
-
-
Della Rossa, F., & DeLellis, P. (2020). Stochastic master stability function for noisy complex networks. Physical Review E, 101(5), 052211. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.101.052211
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
de Arruda, G. F., Méndez-Bermúdez, J. A., Rodrigues, F. A., & Moreno, Y. (2020). Universality of eigenvector delocalization and the nature of the SIS phase transition in multiplex networks. ArXiv:2005.08074 [Cond-Mat, Physics:Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.08074
-
-
royalsocietypublishing.org royalsocietypublishing.org
-
Ngo, S.-C., Percus, A. G., Burghardt, K., & Lerman, K. (2020). The transsortative structure of networks. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 476(2237), 20190772. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2019.0772
-
-
-
Torres, L., Blevins, A. S., Bassett, D. S., & Eliassi-Rad, T. (2020). The why, how, and when of representations for complex systems. ArXiv:2006.02870 [Cs, q-Bio]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.02870
-
-
iaciac.github.io iaciac.github.io
-
Iacopini, I. (2020, June 3). Networks beyond pairwise interactions: Structure and dynamics. Iacopo Iacopini. https://iaciac.github.io/post/beyond/
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Kraemer, M.U.G., Sadilek, A., Zhang, Q. et al. Mapping global variation in human mobility. Nat Hum Behav (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-020-0875-0
-
-
-
Mariani, M. S., & Lü, L. (2020). Network-based ranking in social systems: Three challenges. Journal of Physics: Complexity, 1(1), 011001. https://doi.org/10.1088/2632-072X/ab8a61
-
-
-
Eroglu, D. (2020). Revealing Dynamics, Communities, and Criticality from Data. Physical Review X, 10(2). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.10.021047
-
- May 2020
-
www.futurelearn.com www.futurelearn.com
-
FutureLearn. Pandemics, Modelling, and Policy—Online Course. https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/pandemics-modelling-and-policy
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Katz, D. M., Coupette, C., Beckedorf, J., & Hartung, D. (2020). Complex Societies and the Growth of the Law. ArXiv:2005.07646 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.07646
-
-
www.nyteknik.se www.nyteknik.se
-
Forskare: ”Se upp med komplexa coronamodeller – de kan överträffa verkligheten”. (2020 April 24). Ny Teknik. https://www.nyteknik.se/opinion/forskare-se-upp-med-komplexa-coronamodeller-de-kan-overtraffa-verkligheten-6994339
-
-
-
Riolo, M. A., & Newman, M. E. J. (2020). Consistency of community structure in complex networks. Physical Review E, 101(5), 052306. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.101.052306
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Vespignani, A., Tian, H., Dye, C. et al. Modelling COVID-19. Nat Rev Phys (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42254-020-0178-4
Tags
- pharmaceutical
- policy
- intervention
- war time
- epidemiology
- antibody testing
- complex network
- containment measures
- modeling
- is:article
- public health
- challenge
- superspreading
- mathematics
- isolation
- quarentine
- infection
- COVID-19
- forecast
- computational modeling
- emergency
- prediction
- transmission dynamics
- open data
- contact tracing
- lang:en
- China
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
Liu, L., Wang, X., Tang, S., & Zheng, Z. (2020). Complex social contagion induces bistability on multiplex networks. ArXiv:2005.00664 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.00664
-
-
-
Pinto, S. F., & Ferreira, R. S. (2020). Analyzing course programmes using complex networks. ArXiv:2005.00906 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.00906
-
-
apolitical.co apolitical.co
-
Complex systems thinking is being used for policymaking. Is it the future? (2018, October 25). https://apolitical.co/en/solution_article/complex-systems-thinking-policymaking
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Olthof, M., Hasselman, F., & Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A. (2020, May 1). Complexity In Psychological Self-Ratings: Implications for research and practice. Retrieved from psyarxiv.com/fbta8
-
- Apr 2020
-
www.pnas.org www.pnas.org
-
Stavroglou, S. K., Pantelous, A. A., Stanley, H. E., & Zuev, K. M. (2020). Unveiling causal interactions in complex systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(14), 7599–7605. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1918269117
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Crutchfield, J. P. (2020). The Hidden Fragility of Complex Systems—Consequences of Change, Changing Consequences. ArXiv:2003.11153 [Cond-Mat, Physics:Nlin, Physics:Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2003.11153
-
- Jan 2020
-
quantum.country quantum.country
-
What does it mean for a matrix UUU to be unitary? It’s easiest to answer this question algebraically, where it simply means that U†U=IU^\dagger U = IU†U=I, that is, the adjoint of UUU, denoted U†U^\daggerU†, times UUU, is equal to the identity matrix. That adjoint is, recall, the complex transpose of UUU:
Starting to get a little bit more into linear algebra / complex numbers. I'd like to see this happen more gradually as I haven't used any of this since college.
-
-
www.adaptivecapacitylabs.com www.adaptivecapacitylabs.com
-
How Complex Systems Fail
-
- Nov 2019
-
davecormier.com davecormier.com
-
A large part of the ‘resources’ conversation in OER is this kind of problem. Cheaper access to books. More people using books. Nice measurable problems that can be fixed.
Lowering costs for learning materials via OER: A complicated problem vs what Dave calls complex problems, like open pedagogies.
-
- Oct 2019
- Aug 2019
-
zoia.org zoia.org
-
Context notes are used as a map to a series of notes. A context note that outlines a more complex concept or broader subject, using links to other notes in the process. For example, while I’m reading a book, I build an outline of the things I find relevant, based on my highlights and notes of the book. Each of the outline’s items links to a separate note explaining the idea in more detail, and usually contains the highlighted text of the book.
-
- Jul 2019
-
www.narst.org www.narst.org
-
How will all educators and society have a deliberate coming together to envision equity as a guiding framework for the implementation of NGSS?
question interrogates problem of... wow, hard for me to encapsulate in a sentence. How about: Us teachers and other stakeholders need to engage in dialogue/action around equity and NGSS in our own local connections yet be aware of and engage with other local dialogues and furthermore transform/be-transformed-by the emerging, higher level discourse. np
-
- Feb 2019
-
dougengelbart.org dougengelbart.org
-
The Two Sides of the H-LAM/T System
When I view this diagram, I am reminded of Robert Rosen's Modeling Relation, an image of which is here The Modeling Relation grew out of research in Relational Biology which was the first mathematical biology to recognize that relations among organism components and between those components and the environment are key to understanding complex adaptive systems.
-
It is the augmentation means that serve to break down a large problem in such a way that the human being can walk through it with his little steps, and it is the structure or organization of these little steps or actions that we discuss as process hierarchies.
As I begin to read this (as I did back in 2000 when I was introduced to Doug) I begin to think in terms of reductionism as a practice in the face of problems which are highly complex, nonlinear, and which do not submit to chunking.
-
-
static1.squarespace.com static1.squarespace.com
-
nd often differs from his own-from that which he had yesterday, or WilJ have tomorrow.
this stands out to me that a complex idea in the mind of one person will be fluid and different from day to day, my gut reaction was that an individual's "complex ideas" would remain rather unaltered for extended periods of time, even a lifetime. Maybe as one develops throughout life (adolescence to adulthood) one's thoughts would change, but not day to day
-
- Sep 2018
-
osf.io osf.io
-
Whilespatial biases may contribute to these findings,asnodes belonging to the same module tend to be anatomically colocalized [7,8],they cannot explain these effects entirely [94,95].
Very nice review. Please note the reference [94] (Pantazatos et al.) is misplaced because they did not argue that spatial biases cannot entirely explain the putative links between CGE and functional segregation. Instead, they argued there was insufficient evidence in the original Richiardi et al. study linking elevated CGE with resting state functional networks, and that spatial biases may in fact entirely account for their findings. To describe the debate/exchange more accurately, I would suggest replacing the below sentence
“While spatial biases may contribute to these findings, as nodes belonging to the same module tend to be anatomically colocalized [7,8], they cannot explain these effects entirely [94,95].”
with the below paragraph:
“Spatial biases may contribute to these findings, as nodes belonging to the same module tend to be anatomically colocalized [7,8]. Pantazatos et al. argued that these findings are entirely explained by spatial biases [94]. They showed that elevated CGE, as defined in the original Richiardi et al. study, falls monotonically as longer distance edges are removed. Moreover, they showed that 1,000 sets of randomly spaced modules all have significantly high CGE when using the same null distribution defined in the original Richiardi et al. analyses. Therefore, elevated CGE is not specifically related to functional segregation as defined by resting state functional networks, which is in direct contradiction to the main conclusion of the original Richiardi et al. study. Since randomly placed modules do not align (spatially) with any distributed pattern of functional segregation, the finding of elevated CGE may instead be attributed entirely to anatomical colocalization of the nodes within each module. In their rebuttal to [94], Richiardi et al. argue spatial biases cannot explain their findings entirely [95]. However, the authors do not offer an explanation for significantly high CGE observed for randomly spaced sets of modules, other than to note that nodes tend to be closer on average compared to when modules are defined by resting state fMRI. Future work is required to dissociate the effects of spatially proximity on relationships between CGE and spatially distributed functional networks.”
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Feb 2018
-
science.sciencemag.org science.sciencemag.org
-
Shared molecular neuropathology across major psychiatric disorders parallels polygenic overlap
-
- Oct 2017
-
mcadams.posc.mu.edu mcadams.posc.mu.edu
-
Military Industrial Complex:
- Eisenhower has seen the consequences of this intersection of military power and his own "new look" policy
Presidential speeches can be measured by how long we talk about them. Still one of the most referenced presidential speeches ever given.
IRAN — Mohammed Mossafegh (1951–1954)
- First military Coup during CIA golden age
- US tells Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi (1941–1979) that they will take over the country unless he overthrows Mossafegh.
- For 20+ years we supported a dictator who murdered his own people
- Any nation state has the option to buy out foreign companies
Guatemala — Jacobo Arbenz Guzman (1951–1954)
- Democratically elected leader, called for Progressive Reform (second President to do so)
- Nationalizing land (US decided it looked like Communism)
- Guzman runs into problems with the United Fruit Company, who had been cheating on their taxes, undervaluing their land prices. Government seeks to purchase land to nationalize it, and wants to buy it for the price that the UFC valued their land for.
- UFC and US Government set up a military Coup. Using radio broadcast propaganda, pretending that an army is ravaging the countryside. Guzman believes the propaganda and flees. We set up a dictator.
-
- May 2017
-
static1.squarespace.com static1.squarespace.com
-
The dance (or, as I prefer to call it, the complex ecolo
This is an interesting move in terms of form. Hayles herself is the one who introduced the term "dance" and then immediately amends it parenthetically to comment that she prefers the term "complex ecology." I'm not sure why she chose to leave both of those thoughts in, but I like it.
-
- Apr 2017
-
waitbutwhy.com waitbutwhy.com
-
This is why people can play the piano with their fingers but not with their toes.
That does not really explain why there are very talented musicians that have limb defects, but I suppose that similar to a blind person being able to hear better, their brains adjust (like complex-adaptive systems do) and reassign a new input-element (e.g. the feet) to a left-over motoric system(e.g. the hands).
-
-
static1.squarespace.com static1.squarespace.com
-
complexofpersons,events,~obJeas;anarela-tionspresentinganactualorpotentialexigence
Sounds like one big happy family
-
- Mar 2017
-
environment.yale.edu environment.yale.edu
-
Interpretive Communities
Should be credited to Stanley Fish.
-
-
www.jstor.org www.jstor.org
-
There may well be a dominant reading, but this can erode over time if the “interpretive community” (Fish 1980) to which it speaks changes or the message lost entirely if that com-munity is decisively disrupted or displaced.14
-
- Oct 2016
-
journal.code4lib.org journal.code4lib.org
-
Oklahoma Correctional Industries; workers scan the original photos and prepare metadata
We can make the argument here that the University of North Texas, the Oklahoma Historical Society, and the Ethics in Journalism Foundation support de facto slave labor. Let's be honest here: "workers" = "prisoners"
-
- Jun 2016
-
www.bluecerealeducation.com www.bluecerealeducation.com
-
And now we’re besties again.
I can relate. I have deep respect for AK but often find myself flipping back and forth between strong agreement and feeling somewhat off-put by what he writes. That seems like a healthier relationship to have with any public intellectual though than 100% agreement 100% of the time. I'm so glad his writing exists in the world and I'm glad yours does too. Seems like this kind of layered relationship is just part of dealing with complex systems. :-)
-
-
www.jstor.org.proxyau.wrlc.org www.jstor.org.proxyau.wrlc.org
-
"complex adaptive system."
"the combination of multiple strange loops"
-
- Jan 2016
-
smaldino.com smaldino.com
-
Stupid models are extremely useful. They are usefulbecause humans are boundedly rational and because language is imprecise. It is often only by formalizing a complex system that we can make progress in understanding it. Formal models should be a necessary component of the behavioral scientist’s toolkit. Models are stupid, and we need more of them.
Formal models are explicit in the assumptions they make about how the parts of a system work and interact, and moreover are explicit in the aspects of reality they omit.
-
Microeconomic models based on rational choice theory are useful for developing intuition, and may even approximate reality in a fewspecial cases, but the history of behavioral economics shows that standard economic theory has also provided a smorgasbord of null hypotheses to be struck down by empirical observation.
-
Where differences between conditions are indicated, avoid the mistake of running statistical analyses as if you were sampling from a larger population.
You already have a generating model for your data – it’s your model. Statistical analyses on model data often involve modeling your model with a stupider model. Don’t do this. Instead, run enough simulations to obtain limiting distributions.
-
A model’s strength stemsfromits precision.
I have come across too many modeling papers in which the model – that is, the parts, all their components, the relationships between them, and mechanisms for change – is not clearly expressed. This is most common with computational models (such as agent-based models), which can be quite complicated, but also exists in cases of purely mathematical models.
-
However, I want to be careful not to elevate modelers above those scientists who employ other methods.
This is important for at least two reasons, the first and foremost of which is that science absolutely requires empirical data. Those data are often painstaking to collect, requiring clever, meticulous, and occasionally tedious labor. There is a certain kind of laziness inherent in the professional modeler, who builds entire worlds from his or her desk using only pen, paper, and computer. Relatedly, many scientists are truly fantastic communicators, and present extremely clear theories that advance scientific understanding without a formal model in sight. Charles Darwin, to give an extreme example, laid almost all the foundations of modern evolutionary biology without writing down a single equation.
-
Ultimately,the theory has been shown to be incorrect, and has been epistemically replaced by the theory of General Relativity. Nevertheless, the theory is able to make exceptionally good approximations of gravitational forces –so good that NASA’s moon missions have relied upon them.
General Relativity may also turn out to be a "dumb model". https://twitter.com/worrydream/status/672957979545571329
-
Table 1.Twelve functions served by false models. Adapted with permissionfrom Wimsatt
Twelve good uses for dumb models, William Wimsatt (1987).
-
To paraphrase Gunawardena (2014), a model is a logical engine for turning assumptions into conclusions.
By making our assumptions explicit, we can clearly assess their implied conclusions. These conclusions will inevitably be flawed, because the assumptions are ultimately incorrect or at least incomplete. By examining how they differ from reality, we can refine our models, and thereby refine our theories and so gradually we might become less wrong.
-
the stupidity of a model is often its strength. By focusing on some key aspects of a real-world system(i.e., those aspectsinstantiated in the model), we can investigate how such a system would work if, in principle, we really couldignore everything we are ignoring. This only sounds absurd until one recognizes that, in our theorizing about the nature of reality –both as scientists and as quotidianhumans hopelessly entangled in myriad webs of connection and conflict –weignore thingsall the time.
-
The generalized linear model, the work horse ofthe social sciences, models data as being randomly drawn from a distribution whose mean varies according to some parameter. The linear model is so obviously wrong yet so useful that the mathematical anthropologist Richard McElreathhas dubbed it “the geocentric model of applied statistics,”in reference to the Ptolemaic model of the solar system that erroneously placed the earth rather than the sun at the center but nevertheless produced accurate predictions of planetary motion as they appeared in the night sky(McElreath 2015).
A model that approximates some aspect of reality can be very useful, even if the model itself is flat-out wrong.
But on the other hand, we can't accept approximation of reality as hard proof that a model is correct.
-
Unfortunately, my own experience working with complex systems and working among complexity scientistssuggests that we are hardly immune to such stupidity. Consider the case of Marilyn Vos Savantand the Monty Hall problem.
Many people, including some with training in advanced mathematics, contradicted her smugly. But a simple computer program that models the situation can demonstrate her point.
2/3 times, your first pick will be wrong. Every time that happens, the door Monty didn't open is the winner. So switching wins 2/3 times.
-
Mitch Resnick, in his book Turtles, Termites, and Traffic Jams, details his experiences teaching gifted high school students about the dynamics of complex systems using artificial life models (Resnick 1994). He showed them how organized behavior could emerge when individualsresponded only to local stimuli using simple rules, without the need for a central coordinating authority. Resnick reports that even after weeks spent demonstrating the principles of emergence,using computer simulations that the students programmed themselves, many students still refused to believe that what they were seeing could really work without central leadership.
-
- Apr 2015
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
First, the domain is a poor candidate because the domain of all entities relevant to neurobiological function is extremely large, highly fragmented into separate subdisciplines, and riddled with lack of consensus (Shirky, 2005).
Probably a good thing to add to the Complex Data integration workshop write up
-
- Nov 2013
-
www.jstor.org www.jstor.org
-
German "military-industrial complex"--does m-i c have the same meaning in every country?
-