It is here that we find two ways to put ourselves in control of our lives immediately. Wecan make a promise -- and keep it. Or we can set a goal -- and work to achieve it. As wemake and keep commitments, even small commitments, we begin to establish an innerintegrity that gives us the awareness of self-control and the courage and strength toaccept more of the responsibility for our own lives. By making and keeping promises toourselves and others, little by little, our honor becomes greater than our moods.The power to make and keep commitments to ourselves is the essence of developing thebasic habits of effectiveness. Knowledge, skill, and desire are all within our control. Wecan work on any one to improve the balance of the three. As the area of intersectionbecomes larger, we more deeply internalize the principles upon which the habits arebased and create the strength of character to move us in a balanced way towardincreasing effectiveness in our lives.
- Jul 2025
-
ia801900.us.archive.org ia801900.us.archive.org
-
- May 2025
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
i couldn't 4:50 get into the typewriter the screws were 4:52 in there so tight that there was no way 4:54 i could get that bottom off of the 4:55 machine so i did the only logical thing 4:58 i could think of i set it upside down 4:59 and then forgot about it for a really 5:01 long time i then went back in once i got 5:03 the confidence to go into this machine
Confidence is a (the?) key ingredient of typewriter repair.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Mar 2025
-
elixir.bootlin.com elixir.bootlin.com
-
#ifdef CONFIG_TRANSPARENT_HUGEPAGE #define NR_MAX_BATCHED_MIGRATION HPAGE_PMD_NR #else #define NR_MAX_BATCHED_MIGRATION 512 #endif #define NR_MAX_MIGRATE_PAGES_RETRY 10 #define NR_MAX_MIGRATE_ASYNC_RETRY 3 #define NR_MAX_MIGRATE_SYNC_RETRY \ (NR_MAX_MIGRATE_PAGES_RETRY - NR_MAX_MIGRATE_ASYNC_RETRY)
Policy that determines batch of pages that can be migrated in one migration cycle and also specifies on the number of retries that are possible for re-migration (async vs sync)
-
int migrate_pages(struct list_head *from, new_folio_t get_new_folio, free_folio_t put_new_folio, unsigned long private, enum migrate_mode mode, int reason, unsigned int *ret_succeeded) { int rc, rc_gather; int nr_pages; struct folio *folio, *folio2; LIST_HEAD(folios); LIST_HEAD(ret_folios); LIST_HEAD(split_folios); struct migrate_pages_stats stats; trace_mm_migrate_pages_start(mode, reason); memset(&stats, 0, sizeof(stats)); rc_gather = migrate_hugetlbs(from, get_new_folio, put_new_folio, private, mode, reason, &stats, &ret_folios); if (rc_gather < 0) goto out; again: nr_pages = 0; list_for_each_entry_safe(folio, folio2, from, lru) { /* Retried hugetlb folios will be kept in list */ if (folio_test_hugetlb(folio)) { list_move_tail(&folio->lru, &ret_folios); continue; } nr_pages += folio_nr_pages(folio); if (nr_pages >= NR_MAX_BATCHED_MIGRATION) break; } if (nr_pages >= NR_MAX_BATCHED_MIGRATION) list_cut_before(&folios, from, &folio2->lru); else list_splice_init(from, &folios); if (mode == MIGRATE_ASYNC) rc = migrate_pages_batch(&folios, get_new_folio, put_new_folio, private, mode, reason, &ret_folios, &split_folios, &stats, NR_MAX_MIGRATE_PAGES_RETRY); else rc = migrate_pages_sync(&folios, get_new_folio, put_new_folio, private, mode, reason, &ret_folios, &split_folios, &stats); list_splice_tail_init(&folios, &ret_folios); if (rc < 0) { rc_gather = rc; list_splice_tail(&split_folios, &ret_folios); goto out; } if (!list_empty(&split_folios)) { /* * Failure isn't counted since all split folios of a large folio * is counted as 1 failure already. And, we only try to migrate * with minimal effort, force MIGRATE_ASYNC mode and retry once. */ migrate_pages_batch(&split_folios, get_new_folio, put_new_folio, private, MIGRATE_ASYNC, reason, &ret_folios, NULL, &stats, 1); list_splice_tail_init(&split_folios, &ret_folios); } rc_gather += rc; if (!list_empty(from)) goto again; out: /* * Put the permanent failure folio back to migration list, they * will be put back to the right list by the caller. */ list_splice(&ret_folios, from); /* * Return 0 in case all split folios of fail-to-migrate large folios * are migrated successfully. */ if (list_empty(from)) rc_gather = 0; count_vm_events(PGMIGRATE_SUCCESS, stats.nr_succeeded); count_vm_events(PGMIGRATE_FAIL, stats.nr_failed_pages); count_vm_events(THP_MIGRATION_SUCCESS, stats.nr_thp_succeeded); count_vm_events(THP_MIGRATION_FAIL, stats.nr_thp_failed); count_vm_events(THP_MIGRATION_SPLIT, stats.nr_thp_split); trace_mm_migrate_pages(stats.nr_succeeded, stats.nr_failed_pages, stats.nr_thp_succeeded, stats.nr_thp_failed, stats.nr_thp_split, mode, reason); if (ret_succeeded) *ret_succeeded = stats.nr_succeeded; return rc_gather; }
Might.... be main func for migrating pages maintained by a folio to another free folio. No indication of policy... Except for the macros. Also worth looking into how list data structs are used. Overall not an interesting func despite linux kernel documentation (not the comments in here)
-
- Jan 2025
-
elixir.bootlin.com elixir.bootlin.com
-
static unsigned int zswap_max_pool_percent = 20;
Max percentage of total system RAM that can be used by the pool. Also a user controlled policy recognized by the Linux kernel documentation
-
- Nov 2024
-
elixir.bootlin.com elixir.bootlin.com
-
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_PTE_DEVMAP) && defined(CONFIG_TRANSPARENT_HUGEPAGE) static int __gup_device_huge(unsigned long pfn, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { int nr_start = *nr; struct dev_pagemap *pgmap = NULL; do { struct page *page = pfn_to_page(pfn); pgmap = get_dev_pagemap(pfn, pgmap); if (unlikely(!pgmap)) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); break; } if (!(flags & FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA) && is_pci_p2pdma_page(page)) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); break; } SetPageReferenced(page); pages[*nr] = page; if (unlikely(try_grab_page(page, flags))) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); break; } (*nr)++; pfn++; } while (addr += PAGE_SIZE, addr != end); put_dev_pagemap(pgmap); return addr == end; } static int __gup_device_huge_pmd(pmd_t orig, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long fault_pfn; int nr_start = *nr; fault_pfn = pmd_pfn(orig) + ((addr & ~PMD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); if (!__gup_device_huge(fault_pfn, addr, end, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; if (unlikely(pmd_val(orig) != pmd_val(*pmdp))) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); return 0; } return 1; } static int __gup_device_huge_pud(pud_t orig, pud_t *pudp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long fault_pfn; int nr_start = *nr; fault_pfn = pud_pfn(orig) + ((addr & ~PUD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); if (!__gup_device_huge(fault_pfn, addr, end, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; if (unlikely(pud_val(orig) != pud_val(*pudp))) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); return 0; } return 1; } #else static int __gup_device_huge_pmd(pmd_t orig, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { BUILD_BUG(); return 0; } static int __gup_device_huge_pud(pud_t pud, pud_t *pudp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { BUILD_BUG(); return 0; } #endif
seems like a check to see if pages can be grabbed. A quick skim maybe hints possible checks if huge pages can be grabbed?
-
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_HUGEPD static unsigned long hugepte_addr_end(unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned long sz) { unsigned long __boundary = (addr + sz) & ~(sz-1); return (__boundary - 1 < end - 1) ? __boundary : end; } static int gup_hugepte(pte_t *ptep, unsigned long sz, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long pte_end; struct page *page; struct folio *folio; pte_t pte; int refs; pte_end = (addr + sz) & ~(sz-1); if (pte_end < end) end = pte_end; pte = huge_ptep_get(ptep); if (!pte_access_permitted(pte, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; /* hugepages are never "special" */ VM_BUG_ON(!pfn_valid(pte_pfn(pte))); page = nth_page(pte_page(pte), (addr & (sz - 1)) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pte_val(pte) != pte_val(ptep_get(ptep)))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pte_write(pte) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_huge_pd(hugepd_t hugepd, unsigned long addr, unsigned int pdshift, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { pte_t *ptep; unsigned long sz = 1UL << hugepd_shift(hugepd); unsigned long next; ptep = hugepte_offset(hugepd, addr, pdshift); do { next = hugepte_addr_end(addr, end, sz); if (!gup_hugepte(ptep, sz, addr, end, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (ptep++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } #else static inline int gup_huge_pd(hugepd_t hugepd, unsigned long addr, unsigned int pdshift, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { return 0; } #endif /* CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_HUGEPD */ static int gup_huge_pmd(pmd_t orig, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { struct page *page; struct folio *folio; int refs; if (!pmd_access_permitted(orig, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; if (pmd_devmap(orig)) { if (unlikely(flags & FOLL_LONGTERM)) return 0; return __gup_device_huge_pmd(orig, pmdp, addr, end, flags, pages, nr); } page = nth_page(pmd_page(orig), (addr & ~PMD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pmd_val(orig) != pmd_val(*pmdp))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pmd_write(orig) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_huge_pud(pud_t orig, pud_t *pudp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { struct page *page; struct folio *folio; int refs; if (!pud_access_permitted(orig, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; if (pud_devmap(orig)) { if (unlikely(flags & FOLL_LONGTERM)) return 0; return __gup_device_huge_pud(orig, pudp, addr, end, flags, pages, nr); } page = nth_page(pud_page(orig), (addr & ~PUD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pud_val(orig) != pud_val(*pudp))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pud_write(orig) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_huge_pgd(pgd_t orig, pgd_t *pgdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { int refs; struct page *page; struct folio *folio; if (!pgd_access_permitted(orig, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; BUILD_BUG_ON(pgd_devmap(orig)); page = nth_page(pgd_page(orig), (addr & ~PGDIR_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pgd_val(orig) != pgd_val(*pgdp))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pgd_write(orig) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_pmd_range(pud_t *pudp, pud_t pud, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; pmd_t *pmdp; pmdp = pmd_offset_lockless(pudp, pud, addr); do { pmd_t pmd = pmdp_get_lockless(pmdp); next = pmd_addr_end(addr, end); if (!pmd_present(pmd)) return 0; if (unlikely(pmd_trans_huge(pmd) || pmd_huge(pmd) || pmd_devmap(pmd))) { /* See gup_pte_range() */ if (pmd_protnone(pmd)) return 0; if (!gup_huge_pmd(pmd, pmdp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(pmd_val(pmd))))) { /* * architecture have different format for hugetlbfs * pmd format and THP pmd format */ if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(pmd_val(pmd)), addr, PMD_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (!gup_pte_range(pmd, pmdp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (pmdp++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } static int gup_pud_range(p4d_t *p4dp, p4d_t p4d, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; pud_t *pudp; pudp = pud_offset_lockless(p4dp, p4d, addr); do { pud_t pud = READ_ONCE(*pudp); next = pud_addr_end(addr, end); if (unlikely(!pud_present(pud))) return 0; if (unlikely(pud_huge(pud) || pud_devmap(pud))) { if (!gup_huge_pud(pud, pudp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(pud_val(pud))))) { if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(pud_val(pud)), addr, PUD_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (!gup_pmd_range(pudp, pud, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (pudp++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } static int gup_p4d_range(pgd_t *pgdp, pgd_t pgd, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; p4d_t *p4dp; p4dp = p4d_offset_lockless(pgdp, pgd, addr); do { p4d_t p4d = READ_ONCE(*p4dp); next = p4d_addr_end(addr, end); if (p4d_none(p4d)) return 0; BUILD_BUG_ON(p4d_huge(p4d)); if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(p4d_val(p4d))))) { if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(p4d_val(p4d)), addr, P4D_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (!gup_pud_range(p4dp, p4d, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (p4dp++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } static void gup_pgd_range(unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; pgd_t *pgdp; pgdp = pgd_offset(current->mm, addr); do { pgd_t pgd = READ_ONCE(*pgdp); next = pgd_addr_end(addr, end); if (pgd_none(pgd)) return; if (unlikely(pgd_huge(pgd))) { if (!gup_huge_pgd(pgd, pgdp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return; } else if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(pgd_val(pgd))))) { if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(pgd_val(pgd)), addr, PGDIR_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return; } else if (!gup_p4d_range(pgdp, pgd, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return; } while (pgdp++, addr = next, addr != end); } #else static inline void gup_pgd_range(unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { }
policy use functions for gup_huge pte policy code function above (not right above, gotta scroll probably to find it)
-
static int internal_get_user_pages_fast(unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { unsigned long len, end; unsigned long nr_pinned; int locked = 0; int ret; if (WARN_ON_ONCE(gup_flags & ~(FOLL_WRITE | FOLL_LONGTERM | FOLL_FORCE | FOLL_PIN | FOLL_GET | FOLL_FAST_ONLY | FOLL_NOFAULT | FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA | FOLL_HONOR_NUMA_FAULT))) return -EINVAL; if (gup_flags & FOLL_PIN) mm_set_has_pinned_flag(¤t->mm->flags); if (!(gup_flags & FOLL_FAST_ONLY)) might_lock_read(¤t->mm->mmap_lock); start = untagged_addr(start) & PAGE_MASK; len = nr_pages << PAGE_SHIFT; if (check_add_overflow(start, len, &end)) return -EOVERFLOW; if (end > TASK_SIZE_MAX) return -EFAULT; if (unlikely(!access_ok((void __user *)start, len))) return -EFAULT; nr_pinned = lockless_pages_from_mm(start, end, gup_flags, pages); if (nr_pinned == nr_pages || gup_flags & FOLL_FAST_ONLY) return nr_pinned; /* Slow path: try to get the remaining pages with get_user_pages */ start += nr_pinned << PAGE_SHIFT; pages += nr_pinned; ret = __gup_longterm_locked(current->mm, start, nr_pages - nr_pinned, pages, &locked, gup_flags | FOLL_TOUCH | FOLL_UNLOCKABLE); if (ret < 0) { /* * The caller has to unpin the pages we already pinned so * returning -errno is not an option */ if (nr_pinned) return nr_pinned; return ret; } return ret + nr_pinned; } /** * get_user_pages_fast_only() - pin user pages in memory * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying pin behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Like get_user_pages_fast() except it's IRQ-safe in that it won't fall back to * the regular GUP. * * If the architecture does not support this function, simply return with no * pages pinned. * * Careful, careful! COW breaking can go either way, so a non-write * access can get ambiguous page results. If you call this function without * 'write' set, you'd better be sure that you're ok with that ambiguity. */ int get_user_pages_fast_only(unsigned long start, int nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { /* * Internally (within mm/gup.c), gup fast variants must set FOLL_GET, * because gup fast is always a "pin with a +1 page refcount" request. * * FOLL_FAST_ONLY is required in order to match the API description of * this routine: no fall back to regular ("slow") GUP. */ if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_GET | FOLL_FAST_ONLY)) return -EINVAL; return internal_get_user_pages_fast(start, nr_pages, gup_flags, pages); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(get_user_pages_fast_only); /** * get_user_pages_fast() - pin user pages in memory * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying pin behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Attempt to pin user pages in memory without taking mm->mmap_lock. * If not successful, it will fall back to taking the lock and * calling get_user_pages(). * * Returns number of pages pinned. This may be fewer than the number requested. * If nr_pages is 0 or negative, returns 0. If no pages were pinned, returns * -errno. */ int get_user_pages_fast(unsigned long start, int nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { /* * The caller may or may not have explicitly set FOLL_GET; either way is * OK. However, internally (within mm/gup.c), gup fast variants must set * FOLL_GET, because gup fast is always a "pin with a +1 page refcount" * request. */ if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_GET)) return -EINVAL; return internal_get_user_pages_fast(start, nr_pages, gup_flags, pages); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(get_user_pages_fast); /** * pin_user_pages_fast() - pin user pages in memory without taking locks * * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying pin behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Nearly the same as get_user_pages_fast(), except that FOLL_PIN is set. See * get_user_pages_fast() for documentation on the function arguments, because * the arguments here are identical. * * FOLL_PIN means that the pages must be released via unpin_user_page(). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for further details. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page() will not remove pins from it. */ int pin_user_pages_fast(unsigned long start, int nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN)) return -EINVAL; return internal_get_user_pages_fast(start, nr_pages, gup_flags, pages); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(pin_user_pages_fast); /** * pin_user_pages_remote() - pin pages of a remote process * * @mm: mm_struct of target mm * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying lookup behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * @locked: pointer to lock flag indicating whether lock is held and * subsequently whether VM_FAULT_RETRY functionality can be * utilised. Lock must initially be held. * * Nearly the same as get_user_pages_remote(), except that FOLL_PIN is set. See * get_user_pages_remote() for documentation on the function arguments, because * the arguments here are identical. * * FOLL_PIN means that the pages must be released via unpin_user_page(). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for details. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page*() will not remove pins from it. */ long pin_user_pages_remote(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages, int *locked) { int local_locked = 1; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, locked, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN | FOLL_TOUCH | FOLL_REMOTE)) return 0; return __gup_longterm_locked(mm, start, nr_pages, pages, locked ? locked : &local_locked, gup_flags); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(pin_user_pages_remote); /** * pin_user_pages() - pin user pages in memory for use by other devices * * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying lookup behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Nearly the same as get_user_pages(), except that FOLL_TOUCH is not set, and * FOLL_PIN is set. * * FOLL_PIN means that the pages must be released via unpin_user_page(). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for details. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page*() will not remove pins from it. */ long pin_user_pages(unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { int locked = 1; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN)) return 0; return __gup_longterm_locked(current->mm, start, nr_pages, pages, &locked, gup_flags); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(pin_user_pages); /* * pin_user_pages_unlocked() is the FOLL_PIN variant of * get_user_pages_unlocked(). Behavior is the same, except that this one sets * FOLL_PIN and rejects FOLL_GET. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page*() will not remove pins from it. */ long pin_user_pages_unlocked(unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, struct page **pages, unsigned int gup_flags) { int locked = 0; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN | FOLL_TOUCH | FOLL_UNLOCKABLE)) return 0; return __gup_longterm_locked(current->mm, start, nr_pages, pages, &locked, gup_flags); }
fast gup functions
-
/** * unpin_user_pages() - release an array of gup-pinned pages. * @pages: array of pages to be marked dirty and released. * @npages: number of pages in the @pages array. * * For each page in the @pages array, release the page using unpin_user_page(). * * Please see the unpin_user_page() documentation for details. */ void unpin_user_pages(struct page **pages, unsigned long npages) { unsigned long i; struct folio *folio; unsigned int nr; /* * If this WARN_ON() fires, then the system *might* be leaking pages (by * leaving them pinned), but probably not. More likely, gup/pup returned * a hard -ERRNO error to the caller, who erroneously passed it here. */ if (WARN_ON(IS_ERR_VALUE(npages))) return; sanity_check_pinned_pages(pages, npages); for (i = 0; i < npages; i += nr) { folio = gup_folio_next(pages, npages, i, &nr); gup_put_folio(folio, nr, FOLL_PIN); } }
gup unpin function, not actual logic
-
void unpin_user_page_range_dirty_lock(struct page *page, unsigned long npages, bool make_dirty) { unsigned long i; struct folio *folio; unsigned int nr; for (i = 0; i < npages; i += nr) { folio = gup_folio_range_next(page, npages, i, &nr); if (make_dirty && !folio_test_dirty(folio)) { folio_lock(folio); folio_mark_dirty(folio); folio_unlock(folio); } gup_put_folio(folio, nr, FOLL_PIN); } }
unpin logic but for dirty pages
-
if ((flags & FOLL_DUMP) && (vma_is_anonymous(vma) || !vma->vm_ops->fault)) return ERR_PTR(-EFAULT); return NULL;
explained in comments
-
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_PTE_SPECIAL /* * Fast-gup relies on pte change detection to avoid concurrent pgtable * operations. * * To pin the page, fast-gup needs to do below in order: * (1) pin the page (by prefetching pte), then (2) check pte not changed. * * For the rest of pgtable operations where pgtable updates can be racy * with fast-gup, we need to do (1) clear pte, then (2) check whether page * is pinned. * * Above will work for all pte-level operations, including THP split. * * For THP collapse, it's a bit more complicated because fast-gup may be * walking a pgtable page that is being freed (pte is still valid but pmd * can be cleared already). To avoid race in such condition, we need to * also check pmd here to make sure pmd doesn't change (corresponds to * pmdp_collapse_flush() in the THP collapse code path). */ static int gup_pte_range(pmd_t pmd, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { struct dev_pagemap *pgmap = NULL; int nr_start = *nr, ret = 0; pte_t *ptep, *ptem; ptem = ptep = pte_offset_map(&pmd, addr); if (!ptep) return 0; do { pte_t pte = ptep_get_lockless(ptep); struct page *page; struct folio *folio; /* * Always fallback to ordinary GUP on PROT_NONE-mapped pages: * pte_access_permitted() better should reject these pages * either way: otherwise, GUP-fast might succeed in * cases where ordinary GUP would fail due to VMA access * permissions. */ if (pte_protnone(pte)) goto pte_unmap; if (!pte_access_permitted(pte, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) goto pte_unmap; if (pte_devmap(pte)) { if (unlikely(flags & FOLL_LONGTERM)) goto pte_unmap; pgmap = get_dev_pagemap(pte_pfn(pte), pgmap); if (unlikely(!pgmap)) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); goto pte_unmap; } } else if (pte_special(pte)) goto pte_unmap; VM_BUG_ON(!pfn_valid(pte_pfn(pte))); page = pte_page(pte); folio = try_grab_folio(page, 1, flags); if (!folio) goto pte_unmap; if (unlikely(folio_is_secretmem(folio))) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } if (unlikely(pmd_val(pmd) != pmd_val(*pmdp)) || unlikely(pte_val(pte) != pte_val(ptep_get(ptep)))) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } if (!pte_write(pte) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } /* * We need to make the page accessible if and only if we are * going to access its content (the FOLL_PIN case). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for * details. */ if (flags & FOLL_PIN) { ret = arch_make_page_accessible(page); if (ret) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } } folio_set_referenced(folio); pages[*nr] = page; (*nr)++; } while (ptep++, addr += PAGE_SIZE, addr != end); ret = 1; pte_unmap: if (pgmap) put_dev_pagemap(pgmap); pte_unmap(ptem); return ret; } #else /* * If we can't determine whether or not a pte is special, then fail immediately * for ptes. Note, we can still pin HugeTLB and THP as these are guaranteed not * to be special. * * For a futex to be placed on a THP tail page, get_futex_key requires a * get_user_pages_fast_only implementation that can pin pages. Thus it's still * useful to have gup_huge_pmd even if we can't operate on ptes. */ static int gup_pte_range(pmd_t pmd, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { return 0; } #endif /* CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_PTE_SPECIAL */
non concurrent fast gup approach that checks for pinned page and unmaps pte or clears it
-
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_FAST_GUP /* * Used in the GUP-fast path to determine whether a pin is permitted for a * specific folio. * * This call assumes the caller has pinned the folio, that the lowest page table * level still points to this folio, and that interrupts have been disabled. * * Writing to pinned file-backed dirty tracked folios is inherently problematic * (see comment describing the writable_file_mapping_allowed() function). We * therefore try to avoid the most egregious case of a long-term mapping doing * so. * * This function cannot be as thorough as that one as the VMA is not available * in the fast path, so instead we whitelist known good cases and if in doubt, * fall back to the slow path. */ static bool folio_fast_pin_allowed(struct folio *folio, unsigned int flags) { struct address_space *mapping; unsigned long mapping_flags; /* * If we aren't pinning then no problematic write can occur. A long term * pin is the most egregious case so this is the one we disallow. */ if ((flags & (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_LONGTERM | FOLL_WRITE)) != (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_LONGTERM | FOLL_WRITE)) return true; /* The folio is pinned, so we can safely access folio fields. */ if (WARN_ON_ONCE(folio_test_slab(folio))) return false; /* hugetlb mappings do not require dirty-tracking. */ if (folio_test_hugetlb(folio)) return true; /* * GUP-fast disables IRQs. When IRQS are disabled, RCU grace periods * cannot proceed, which means no actions performed under RCU can * proceed either. * * inodes and thus their mappings are freed under RCU, which means the * mapping cannot be freed beneath us and thus we can safely dereference * it. */ lockdep_assert_irqs_disabled(); /* * However, there may be operations which _alter_ the mapping, so ensure * we read it once and only once. */ mapping = READ_ONCE(folio->mapping); /* * The mapping may have been truncated, in any case we cannot determine * if this mapping is safe - fall back to slow path to determine how to * proceed. */ if (!mapping) return false; /* Anonymous folios pose no problem. */ mapping_flags = (unsigned long)mapping & PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS; if (mapping_flags) return mapping_flags & PAGE_MAPPING_ANON; /* * At this point, we know the mapping is non-null and points to an * address_space object. The only remaining whitelisted file system is * shmem. */ return shmem_mapping(mapping); }
policy logic. avoids locks unlike get user pages unlocked/locked which seems risky so its not supposed to be used on concurrent gup logic
-
long get_user_pages(unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { int locked = 1; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_TOUCH)) return -EINVAL; return __get_user_pages_locked(current->mm, start, nr_pages, pages, &locked, gup_flags); }
policy logic.
-
static void __maybe_unused undo_dev_pagemap(int *nr, int nr_start, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages) { while ((*nr) - nr_start) { struct page *page = pages[--(*nr)]; ClearPageReferenced(page); if (flags & FOLL_PIN) unpin_user_page(page); else put_page(page); } }
policy use function that undoes mapping
-
#ifdef CONFIG_MIGRATION /* * Returns the number of collected pages. Return value is always >= 0. */ static unsigned long collect_longterm_unpinnable_pages( struct list_head *movable_page_list, unsigned long nr_pages, struct page **pages) { unsigned long i, collected = 0; struct folio *prev_folio = NULL; bool drain_allow = true; for (i = 0; i < nr_pages; i++) { struct folio *folio = page_folio(pages[i]); if (folio == prev_folio) continue; prev_folio = folio; if (folio_is_longterm_pinnable(folio)) continue; collected++; if (folio_is_device_coherent(folio)) continue; if (folio_test_hugetlb(folio)) { isolate_hugetlb(folio, movable_page_list); continue; } if (!folio_test_lru(folio) && drain_allow) { lru_add_drain_all(); drain_allow = false; } if (!folio_isolate_lru(folio)) continue; list_add_tail(&folio->lru, movable_page_list); node_stat_mod_folio(folio, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + folio_is_file_lru(folio), folio_nr_pages(folio)); } return collected; }
-
#ifdef CONFIG_ELF_CORE struct page *get_dump_page(unsigned long addr) { struct page *page; int locked = 0; int ret; ret = __get_user_pages_locked(current->mm, addr, 1, &page, &locked, FOLL_FORCE | FOLL_DUMP | FOLL_GET); return (ret == 1) ? page : NULL; } #endif /* CONFIG_ELF_CORE */
part of policy use code likely
-
int __mm_populate(unsigned long start, unsigned long len, int ignore_errors) { struct mm_struct *mm = current->mm; unsigned long end, nstart, nend; struct vm_area_struct *vma = NULL; int locked = 0; long ret = 0; end = start + len; for (nstart = start; nstart < end; nstart = nend) { /* * We want to fault in pages for [nstart; end) address range. * Find first corresponding VMA. */ if (!locked) { locked = 1; mmap_read_lock(mm); vma = find_vma_intersection(mm, nstart, end); } else if (nstart >= vma->vm_end) vma = find_vma_intersection(mm, vma->vm_end, end); if (!vma) break; /* * Set [nstart; nend) to intersection of desired address * range with the first VMA. Also, skip undesirable VMA types. */ nend = min(end, vma->vm_end); if (vma->vm_flags & (VM_IO | VM_PFNMAP)) continue; if (nstart < vma->vm_start) nstart = vma->vm_start; /* * Now fault in a range of pages. populate_vma_page_range() * double checks the vma flags, so that it won't mlock pages * if the vma was already munlocked. */ ret = populate_vma_page_range(vma, nstart, nend, &locked); if (ret < 0) { if (ignore_errors) { ret = 0; continue; /* continue at next VMA */ } break; } nend = nstart + ret * PAGE_SIZE; ret = 0; } if (locked) mmap_read_unlock(mm); return ret; /* 0 or negative error code */ }
policy use function that populates pages like the func before this.
-
long populate_vma_page_range(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long start, unsigned long end, int *locked) { struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm; unsigned long nr_pages = (end - start) / PAGE_SIZE; int local_locked = 1; int gup_flags; long ret; VM_BUG_ON(!PAGE_ALIGNED(start)); VM_BUG_ON(!PAGE_ALIGNED(end)); VM_BUG_ON_VMA(start < vma->vm_start, vma); VM_BUG_ON_VMA(end > vma->vm_end, vma); mmap_assert_locked(mm); /* * Rightly or wrongly, the VM_LOCKONFAULT case has never used * faultin_page() to break COW, so it has no work to do here. */ if (vma->vm_flags & VM_LOCKONFAULT) return nr_pages; gup_flags = FOLL_TOUCH; /* * We want to touch writable mappings with a write fault in order * to break COW, except for shared mappings because these don't COW * and we would not want to dirty them for nothing. */ if ((vma->vm_flags & (VM_WRITE | VM_SHARED)) == VM_WRITE) gup_flags |= FOLL_WRITE; /* * We want mlock to succeed for regions that have any permissions * other than PROT_NONE. */ if (vma_is_accessible(vma)) gup_flags |= FOLL_FORCE; if (locked) gup_flags |= FOLL_UNLOCKABLE; /* * We made sure addr is within a VMA, so the following will * not result in a stack expansion that recurses back here. */ ret = __get_user_pages(mm, start, nr_pages, gup_flags, NULL, locked ? locked : &local_locked); lru_add_drain(); return ret; }
policy use code.
-
long get_user_pages_remote(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages, int *locked) { int local_locked = 1; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, locked, &gup_flags, FOLL_TOUCH | FOLL_REMOTE)) return -EINVAL; return __get_user_pages_locked(mm, start, nr_pages, pages, locked ? locked : &local_locked, gup_flags); }
policy logic
-
static __always_inline long __get_user_pages_locked(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, struct page **pages, int *locked, unsigned int flags) { long ret, pages_done; bool must_unlock = false; /* * The internal caller expects GUP to manage the lock internally and the * lock must be released when this returns. */ if (!*locked) { if (mmap_read_lock_killable(mm)) return -EAGAIN; must_unlock = true; *locked = 1; } else mmap_assert_locked(mm); if (flags & FOLL_PIN) mm_set_has_pinned_flag(&mm->flags); /* * FOLL_PIN and FOLL_GET are mutually exclusive. Traditional behavior * is to set FOLL_GET if the caller wants pages[] filled in (but has * carelessly failed to specify FOLL_GET), so keep doing that, but only * for FOLL_GET, not for the newer FOLL_PIN. * * FOLL_PIN always expects pages to be non-null, but no need to assert * that here, as any failures will be obvious enough. */ if (pages && !(flags & FOLL_PIN)) flags |= FOLL_GET; pages_done = 0; for (;;) { ret = __get_user_pages(mm, start, nr_pages, flags, pages, locked); if (!(flags & FOLL_UNLOCKABLE)) { /* VM_FAULT_RETRY couldn't trigger, bypass */ pages_done = ret; break; } /* VM_FAULT_RETRY or VM_FAULT_COMPLETED cannot return errors */ if (!*locked) { BUG_ON(ret < 0); BUG_ON(ret >= nr_pages); } if (ret > 0) { nr_pages -= ret; pages_done += ret; if (!nr_pages) break; } if (*locked) { /* * VM_FAULT_RETRY didn't trigger or it was a * FOLL_NOWAIT. */ if (!pages_done) pages_done = ret; break; } /* * VM_FAULT_RETRY triggered, so seek to the faulting offset. * For the prefault case (!pages) we only update counts. */ if (likely(pages)) pages += ret; start += ret << PAGE_SHIFT; /* The lock was temporarily dropped, so we must unlock later */ must_unlock = true; retry: /* * Repeat on the address that fired VM_FAULT_RETRY * with both FAULT_FLAG_ALLOW_RETRY and * FAULT_FLAG_TRIED. Note that GUP can be interrupted * by fatal signals of even common signals, depending on * the caller's request. So we need to check it before we * start trying again otherwise it can loop forever. */ if (gup_signal_pending(flags)) { if (!pages_done) pages_done = -EINTR; break; } ret = mmap_read_lock_killable(mm); if (ret) { BUG_ON(ret > 0); if (!pages_done) pages_done = ret; break; } *locked = 1; ret = __get_user_pages(mm, start, 1, flags | FOLL_TRIED, pages, locked); if (!*locked) { /* Continue to retry until we succeeded */ BUG_ON(ret != 0); goto retry; } if (ret != 1) { BUG_ON(ret > 1); if (!pages_done) pages_done = ret; break; } nr_pages--; pages_done++; if (!nr_pages) break; if (likely(pages)) pages++; start += PAGE_SIZE; } if (must_unlock && *locked) { /* * We either temporarily dropped the lock, or the caller * requested that we both acquire and drop the lock. Either way, * we must now unlock, and notify the caller of that state. */ mmap_read_unlock(mm); *locked = 0; } return pages_done; }
same as gup but sets/unsets mmap_lock
-
if (!(flags & FOLL_INTERRUPTIBLE)) return false;
fatal fault signal handler
-
int fixup_user_fault(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long address, unsigned int fault_flags, bool *unlocked) { struct vm_area_struct *vma; vm_fault_t ret; address = untagged_addr_remote(mm, address); if (unlocked) fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_ALLOW_RETRY | FAULT_FLAG_KILLABLE; retry: vma = gup_vma_lookup(mm, address); if (!vma) return -EFAULT; if (!vma_permits_fault(vma, fault_flags)) return -EFAULT; if ((fault_flags & FAULT_FLAG_KILLABLE) && fatal_signal_pending(current)) return -EINTR; ret = handle_mm_fault(vma, address, fault_flags, NULL); if (ret & VM_FAULT_COMPLETED) { /* * NOTE: it's a pity that we need to retake the lock here * to pair with the unlock() in the callers. Ideally we * could tell the callers so they do not need to unlock. */ mmap_read_lock(mm); *unlocked = true; return 0; } if (ret & VM_FAULT_ERROR) { int err = vm_fault_to_errno(ret, 0); if (err) return err; BUG(); } if (ret & VM_FAULT_RETRY) { mmap_read_lock(mm); *unlocked = true; fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_TRIED; goto retry; } return 0; }
resolves user page fault. policy logic
-
static long __get_user_pages(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages, int *locked) { long ret = 0, i = 0; struct vm_area_struct *vma = NULL; struct follow_page_context ctx = { NULL }; if (!nr_pages) return 0; start = untagged_addr_remote(mm, start); VM_BUG_ON(!!pages != !!(gup_flags & (FOLL_GET | FOLL_PIN))); do { struct page *page; unsigned int foll_flags = gup_flags; unsigned int page_increm; /* first iteration or cross vma bound */ if (!vma || start >= vma->vm_end) { /* * MADV_POPULATE_(READ|WRITE) wants to handle VMA * lookups+error reporting differently. */ if (gup_flags & FOLL_MADV_POPULATE) { vma = vma_lookup(mm, start); if (!vma) { ret = -ENOMEM; goto out; } if (check_vma_flags(vma, gup_flags)) { ret = -EINVAL; goto out; } goto retry; } vma = gup_vma_lookup(mm, start); if (!vma && in_gate_area(mm, start)) { ret = get_gate_page(mm, start & PAGE_MASK, gup_flags, &vma, pages ? &page : NULL); if (ret) goto out; ctx.page_mask = 0; goto next_page; } if (!vma) { ret = -EFAULT; goto out; } ret = check_vma_flags(vma, gup_flags); if (ret) goto out; } retry: /* * If we have a pending SIGKILL, don't keep faulting pages and * potentially allocating memory. */ if (fatal_signal_pending(current)) { ret = -EINTR; goto out; } cond_resched(); page = follow_page_mask(vma, start, foll_flags, &ctx); if (!page || PTR_ERR(page) == -EMLINK) { ret = faultin_page(vma, start, &foll_flags, PTR_ERR(page) == -EMLINK, locked); switch (ret) { case 0: goto retry; case -EBUSY: case -EAGAIN: ret = 0; fallthrough; case -EFAULT: case -ENOMEM: case -EHWPOISON: goto out; } BUG(); } else if (PTR_ERR(page) == -EEXIST) { /* * Proper page table entry exists, but no corresponding * struct page. If the caller expects **pages to be * filled in, bail out now, because that can't be done * for this page. */ if (pages) { ret = PTR_ERR(page); goto out; } } else if (IS_ERR(page)) { ret = PTR_ERR(page); goto out; } next_page: page_increm = 1 + (~(start >> PAGE_SHIFT) & ctx.page_mask); if (page_increm > nr_pages) page_increm = nr_pages; if (pages) { struct page *subpage; unsigned int j; /* * This must be a large folio (and doesn't need to * be the whole folio; it can be part of it), do * the refcount work for all the subpages too. * * NOTE: here the page may not be the head page * e.g. when start addr is not thp-size aligned. * try_grab_folio() should have taken care of tail * pages. */ if (page_increm > 1) { struct folio *folio; /* * Since we already hold refcount on the * large folio, this should never fail. */ folio = try_grab_folio(page, page_increm - 1, foll_flags); if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!folio)) { /* * Release the 1st page ref if the * folio is problematic, fail hard. */ gup_put_folio(page_folio(page), 1, foll_flags); ret = -EFAULT; goto out; } } for (j = 0; j < page_increm; j++) { subpage = nth_page(page, j); pages[i + j] = subpage; flush_anon_page(vma, subpage, start + j * PAGE_SIZE); flush_dcache_page(subpage); } } i += page_increm; start += page_increm * PAGE_SIZE; nr_pages -= page_increm; } while (nr_pages); out: if (ctx.pgmap) put_dev_pagemap(ctx.pgmap); return i ? i : ret; }
Literally the actual policy logic of gup. Most important piece of code right here for gup
-
#ifdef CONFIG_STACK_GROWSUP return vma_lookup(mm, addr); #else static volatile unsigned long next_warn; struct vm_area_struct *vma; unsigned long now, next; vma = find_vma(mm, addr); if (!vma || (addr >= vma->vm_start)) return vma; /* Only warn for half-way relevant accesses */ if (!(vma->vm_flags & VM_GROWSDOWN)) return NULL; if (vma->vm_start - addr > 65536) return NULL; /* Let's not warn more than once an hour.. */ now = jiffies; next = next_warn; if (next && time_before(now, next)) return NULL; next_warn = now + 60*60*HZ; /* Let people know things may have changed. */ pr_warn("GUP no longer grows the stack in %s (%d): %lx-%lx (%lx)\n", current->comm, task_pid_nr(current), vma->vm_start, vma->vm_end, addr); dump_stack(); return NULL;
helper func to lookup vma(virtual mem area) that warns per hour about half way relevant acc and changes in stack
-
static bool writable_file_mapping_allowed(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long gup_flags) { /* * If we aren't pinning then no problematic write can occur. A long term * pin is the most egregious case so this is the case we disallow. */ if ((gup_flags & (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_LONGTERM)) != (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_LONGTERM)) return true; /* * If the VMA does not require dirty tracking then no problematic write * can occur either. */ return !vma_needs_dirty_tracking(vma); }
Def policy code. checks if we can write to a map
-
if (*flags & FOLL_NOFAULT) return -EFAULT; if (*flags & FOLL_WRITE) fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_WRITE; if (*flags & FOLL_REMOTE) fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_REMOTE; if (*flags & FOLL_UNLOCKABLE) { fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_ALLOW_RETRY | FAULT_FLAG_KILLABLE; /* * FAULT_FLAG_INTERRUPTIBLE is opt-in. GUP callers must set * FOLL_INTERRUPTIBLE to enable FAULT_FLAG_INTERRUPTIBLE. * That's because some callers may not be prepared to * handle early exits caused by non-fatal signals. */ if (*flags & FOLL_INTERRUPTIBLE) fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_INTERRUPTIBLE; } if (*flags & FOLL_NOWAIT) fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_ALLOW_RETRY | FAULT_FLAG_RETRY_NOWAIT; if (*flags & FOLL_TRIED) { /* * Note: FAULT_FLAG_ALLOW_RETRY and FAULT_FLAG_TRIED * can co-exist */ fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_TRIED; } if (unshare) { fault_flags |= FAULT_FLAG_UNSHARE; /* FAULT_FLAG_WRITE and FAULT_FLAG_UNSHARE are incompatible */ VM_BUG_ON(fault_flags & FAULT_FLAG_WRITE); } ret = handle_mm_fault(vma, address, fault_flags, NULL); if (ret & VM_FAULT_COMPLETED) { /* * With FAULT_FLAG_RETRY_NOWAIT we'll never release the * mmap lock in the page fault handler. Sanity check this. */ WARN_ON_ONCE(fault_flags & FAULT_FLAG_RETRY_NOWAIT); *locked = 0; /* * We should do the same as VM_FAULT_RETRY, but let's not * return -EBUSY since that's not reflecting the reality of * what has happened - we've just fully completed a page * fault, with the mmap lock released. Use -EAGAIN to show * that we want to take the mmap lock _again_. */ return -EAGAIN; } if (ret & VM_FAULT_ERROR) { int err = vm_fault_to_errno(ret, *flags); if (err) return err; BUG(); } if (ret & VM_FAULT_RETRY) { if (!(fault_flags & FAULT_FLAG_RETRY_NOWAIT)) *locked = 0; return -EBUSY; }
Seems it's just setting flags for page faults based on flags param
-
/* user gate pages are read-only */ if (gup_flags & FOLL_WRITE) return -EFAULT; if (address > TASK_SIZE) pgd = pgd_offset_k(address); else pgd = pgd_offset_gate(mm, address); if (pgd_none(*pgd)) return -EFAULT; p4d = p4d_offset(pgd, address); if (p4d_none(*p4d)) return -EFAULT; pud = pud_offset(p4d, address); if (pud_none(*pud)) return -EFAULT; pmd = pmd_offset(pud, address); if (!pmd_present(*pmd)) return -EFAULT; pte = pte_offset_map(pmd, address); if (!pte) return -EFAULT; entry = ptep_get(pte); if (pte_none(entry)) goto unmap; *vma = get_gate_vma(mm); if (!page) goto out; *page = vm_normal_page(*vma, address, entry); if (!*page) { if ((gup_flags & FOLL_DUMP) || !is_zero_pfn(pte_pfn(entry))) goto unmap; *page = pte_page(entry); } ret = try_grab_page(*page, gup_flags); if (unlikely(ret)) goto unmap;
Most of these seem like sanity checks right up until line 897 i.e, 'if(!page)'* after which we seem to unmap the page.
-
static struct page *follow_page_mask(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long address, unsigned int flags, struct follow_page_context *ctx) { pgd_t *pgd; struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm; ctx->page_mask = 0; /* * Call hugetlb_follow_page_mask for hugetlb vmas as it will use * special hugetlb page table walking code. This eliminates the * need to check for hugetlb entries in the general walking code. */ if (is_vm_hugetlb_page(vma)) return hugetlb_follow_page_mask(vma, address, flags, &ctx->page_mask); pgd = pgd_offset(mm, address); if (pgd_none(*pgd) || unlikely(pgd_bad(*pgd))) return no_page_table(vma, flags); return follow_p4d_mask(vma, address, pgd, flags, ctx); }
places mask after following page into pte
-
struct page *follow_page(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long address, unsigned int foll_flags) { struct follow_page_context ctx = { NULL }; struct page *page; if (vma_is_secretmem(vma)) return NULL; if (WARN_ON_ONCE(foll_flags & FOLL_PIN)) return NULL; /* * We never set FOLL_HONOR_NUMA_FAULT because callers don't expect * to fail on PROT_NONE-mapped pages. */ page = follow_page_mask(vma, address, foll_flags, &ctx); if (ctx.pgmap) put_dev_pagemap(ctx.pgmap); return page; }
finds page
-
if (flags & FOLL_SPLIT_PMD) { spin_unlock(ptl); split_huge_pmd(vma, pmd, address); /* If pmd was left empty, stuff a page table in there quickly */ return pte_alloc(mm, pmd) ? ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM) : follow_page_pte(vma, address, pmd, flags, &ctx->pgmap); } page = follow_trans_huge_pmd(vma, address, pmd, flags); spin_unlock(ptl); ctx->page_mask = HPAGE_PMD_NR - 1; return page;
we're finding the page again but storing page mask in ctx
-
if (likely(!pmd_trans_huge(pmdval))) return follow_page_pte(vma, address, pmd, flags, &ctx->pgmap); if (pmd_protnone(pmdval) && !gup_can_follow_protnone(vma, flags)) return no_page_table(vma, flags); ptl = pmd_lock(mm, pmd); if (unlikely(!pmd_present(*pmd))) { spin_unlock(ptl); return no_page_table(vma, flags); } if (unlikely(!pmd_trans_huge(*pmd))) { spin_unlock(ptl); return follow_page_pte(vma, address, pmd, flags, &ctx->pgmap); }
branch prediction to check if pmd is there and if it's big
-
if (pmd_none(pmdval)) return no_page_table(vma, flags); if (!pmd_present(pmdval)) return no_page_table(vma, flags); if (pmd_devmap(pmdval)) { ptl = pmd_lock(mm, pmd); page = follow_devmap_pmd(vma, address, pmd, flags, &ctx->pgmap); spin_unlock(ptl); if (page) return page; }
checks if pmd is there. im assuming it's page middle dir.
-
/* FOLL_GET and FOLL_PIN are mutually exclusive. */ if (WARN_ON_ONCE((flags & (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_GET)) == (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_GET))) return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); ptep = pte_offset_map_lock(mm, pmd, address, &ptl); if (!ptep) return no_page_table(vma, flags); pte = ptep_get(ptep); if (!pte_present(pte)) goto no_page; if (pte_protnone(pte) && !gup_can_follow_protnone(vma, flags)) goto no_page; page = vm_normal_page(vma, address, pte); /* * We only care about anon pages in can_follow_write_pte() and don't * have to worry about pte_devmap() because they are never anon. */ if ((flags & FOLL_WRITE) && !can_follow_write_pte(pte, page, vma, flags)) { page = NULL; goto out; } if (!page && pte_devmap(pte) && (flags & (FOLL_GET | FOLL_PIN))) { /* * Only return device mapping pages in the FOLL_GET or FOLL_PIN * case since they are only valid while holding the pgmap * reference. */ *pgmap = get_dev_pagemap(pte_pfn(pte), *pgmap); if (*pgmap) page = pte_page(pte); else goto no_page; } else if (unlikely(!page)) { if (flags & FOLL_DUMP) { /* Avoid special (like zero) pages in core dumps */ page = ERR_PTR(-EFAULT); goto out; } if (is_zero_pfn(pte_pfn(pte))) { page = pte_page(pte); } else { ret = follow_pfn_pte(vma, address, ptep, flags); page = ERR_PTR(ret); goto out; } } if (!pte_write(pte) && gup_must_unshare(vma, flags, page)) { page = ERR_PTR(-EMLINK); goto out; } VM_BUG_ON_PAGE((flags & FOLL_PIN) && PageAnon(page) && !PageAnonExclusive(page), page); /* try_grab_page() does nothing unless FOLL_GET or FOLL_PIN is set. */ ret = try_grab_page(page, flags); if (unlikely(ret)) { page = ERR_PTR(ret); goto out; } /* * We need to make the page accessible if and only if we are going * to access its content (the FOLL_PIN case). Please see * Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for details. */ if (flags & FOLL_PIN) { ret = arch_make_page_accessible(page); if (ret) { unpin_user_page(page); page = ERR_PTR(ret); goto out; } } if (flags & FOLL_TOUCH) { if ((flags & FOLL_WRITE) && !pte_dirty(pte) && !PageDirty(page)) set_page_dirty(page); /* * pte_mkyoung() would be more correct here, but atomic care * is needed to avoid losing the dirty bit: it is easier to use * mark_page_accessed(). */ mark_page_accessed(page); }
finds page in pte. Judging by the complexity of the logic this is most likely policy code because we're literally getting user page
-
if (flags & FOLL_TOUCH) { pte_t orig_entry = ptep_get(pte); pte_t entry = orig_entry; if (flags & FOLL_WRITE) entry = pte_mkdirty(entry); entry = pte_mkyoung(entry); if (!pte_same(orig_entry, entry)) { set_pte_at(vma->vm_mm, address, pte, entry); update_mmu_cache(vma, address, pte); }
uses pte to mark dirty pages and finds pfn in pte
-
void unpin_user_pages_dirty_lock(struct page **pages, unsigned long npages, bool make_dirty) { unsigned long i; struct folio *folio; unsigned int nr; if (!make_dirty) { unpin_user_pages(pages, npages); return; } sanity_check_pinned_pages(pages, npages); for (i = 0; i < npages; i += nr) { folio = gup_folio_next(pages, npages, i, &nr); /* * Checking PageDirty at this point may race with * clear_page_dirty_for_io(), but that's OK. Two key * cases: * * 1) This code sees the page as already dirty, so it * skips the call to set_page_dirty(). That could happen * because clear_page_dirty_for_io() called * page_mkclean(), followed by set_page_dirty(). * However, now the page is going to get written back, * which meets the original intention of setting it * dirty, so all is well: clear_page_dirty_for_io() goes * on to call TestClearPageDirty(), and write the page * back. * * 2) This code sees the page as clean, so it calls * set_page_dirty(). The page stays dirty, despite being * written back, so it gets written back again in the * next writeback cycle. This is harmless. */ if (!folio_test_dirty(folio)) { folio_lock(folio); folio_mark_dirty(folio); folio_unlock(folio); } gup_put_folio(folio, nr, FOLL_PIN); } }
unpins and dirties page
-
static inline struct folio *gup_folio_next(struct page **list, unsigned long npages, unsigned long i, unsigned int *ntails) { struct folio *folio = page_folio(list[i]); unsigned int nr; for (nr = i + 1; nr < npages; nr++) { if (page_folio(list[nr]) != folio) break; } *ntails = nr - i; return folio; }
gets folio of next page along with reference to end of folio
-
static inline struct folio *gup_folio_range_next(struct page *start, unsigned long npages, unsigned long i, unsigned int *ntails) { struct page *next = nth_page(start, i); struct folio *folio = page_folio(next); unsigned int nr = 1; if (folio_test_large(folio)) nr = min_t(unsigned int, npages - i, folio_nr_pages(folio) - folio_page_idx(folio, next)); *ntails = nr; return folio; }
gets the folio of the next page from start to 'i' range. also gets the tail folio/reference
-
folio_ref_add(folio, GUP_PIN_COUNTING_BIAS);
function for adding reference
-
void unpin_user_page(struct page *page) { sanity_check_pinned_pages(&page, 1); gup_put_folio(page_folio(page), 1, FOLL_PIN); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(unpin_user_page);
actual policy use logic
-
struct folio *folio = page_folio(page); if (WARN_ON_ONCE(folio_ref_count(folio) <= 0)) return -ENOMEM; if (unlikely(!(flags & FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA) && is_pci_p2pdma_page(page))) return -EREMOTEIO; if (flags & FOLL_GET) folio_ref_inc(folio);
checks for code that is involved in policy but is not the actual logic
-
else if (flags & FOLL_PIN) { /* * Don't take a pin on the zero page - it's not going anywhere * and it is used in a *lot* of places. */ if (is_zero_page(page)) return 0; /* * Similar to try_grab_folio(): be sure to *also* * increment the normal page refcount field at least once, * so that the page really is pinned. */ if (folio_test_large(folio)) { folio_ref_add(folio, 1); atomic_add(1, &folio->_pincount); } else { folio_ref_add(folio, GUP_PIN_COUNTING_BIAS); } node_stat_mod_folio(folio, NR_FOLL_PIN_ACQUIRED, 1); }
Logic that actually tries to grab the folio. Also policy use code and not actual policy
-
if (!put_devmap_managed_page_refs(&folio->page, refs)) folio_put_refs(folio, refs);
Definitely a vital and straightforward policy use section of gup that simples places a reference on the folio
-
if (flags & FOLL_PIN) { if (is_zero_folio(folio)) return; node_stat_mod_folio(folio, NR_FOLL_PIN_RELEASED, refs); if (folio_test_large(folio)) atomic_sub(refs, &folio->_pincount); else refs *= GUP_PIN_COUNTING_BIAS; }
Checks if the folio is zero/large
-
if (folio_test_large(folio)) atomic_add(refs, &folio->_pincount); else folio_ref_add(folio, refs * (GUP_PIN_COUNTING_BIAS - 1))
maintaining reference counts. Part of policy logic most likely
-
if (unlikely((flags & FOLL_LONGTERM) && !folio_is_longterm_pinnable(folio))) { if (!put_devmap_managed_page_refs(&folio->page, refs)) folio_put_refs(folio, refs); return NULL;
checks for longterm folio pins.
-
if (WARN_ON_ONCE((flags & (FOLL_GET | FOLL_PIN)) == 0)) return NULL; if (unlikely(!(flags & FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA) && is_pci_p2pdma_page(page))) return NULL;
Time saving predictions(unlikely) and single time warning func(WARN_ON_ONCE) for flags. Not actual policy logic so low confidence.
-
if (unlikely(page_folio(page) != folio)) { if (!put_devmap_managed_page_refs(&folio->page, refs)) folio_put_refs(folio, refs); goto retry;
Uses prediction to check if a folio still points to the page. This is part of the function that tries to retrieve the folio to confirm that it is associated with a page.
-
folio = page_folio(page); if (WARN_ON_ONCE(folio_ref_count(folio) < 0)) return NULL; if (unlikely(!folio_ref_try_add(folio, refs))) return NULL;
These increment the reference count for the folio since you're returning a reference of the folio. Important function so important internal logic subsequently
-
if (is_zero_page(page) || !folio_test_anon(folio)) continue; if (!folio_test_large(folio) || folio_test_hugetlb(folio))
Sanity checks for pinned pages wouldn't classify as policy logic but common sense pre-checks for the actual policy. But I think it's worth tagging this to gain a sense of what is not policy code
-
if (is_zero_page(page)) return page_folio(page); folio = try_get_folio(page, refs); if (!folio) return NULL;
Just trying to check for zero pages and trying to retrieve folios. Unlikely policy logic
-
if (flags & FOLL_GET) return try_get_folio(page, refs);
Policy logic that determines and tries to retrieve folios based on given flags.
-
if (flags & FOLL_PIN) { ret = arch_make_page_accessible(page); if (ret) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } }
part of policy code
-
if (!(gup_flags & FOLL_LONGTERM)) return __get_user_pages_locked(mm, start, nr_pages, pages, locked, gup_flags);
policy decision to get locked page!
-
if (page_increm > nr_pages) page_increm = nr_pages;
next page logic
-
*/ if (gup_flags & FOLL_MADV_POPULATE) { vma = vma_lookup(mm, start); if (!vma) { ret = -ENOMEM; goto out; } if (check_vma_flags(vma, gup_flags)) { ret = -EINVAL; goto out; } goto retry; }
page populate flag for sure
-
- Oct 2024
-
munk.org munk.org
-
The hardest part of typewriter repair is believing you can do it. Everything else is just instructions plus a careful, thoughtful hand.<br /> —Theodore Munk
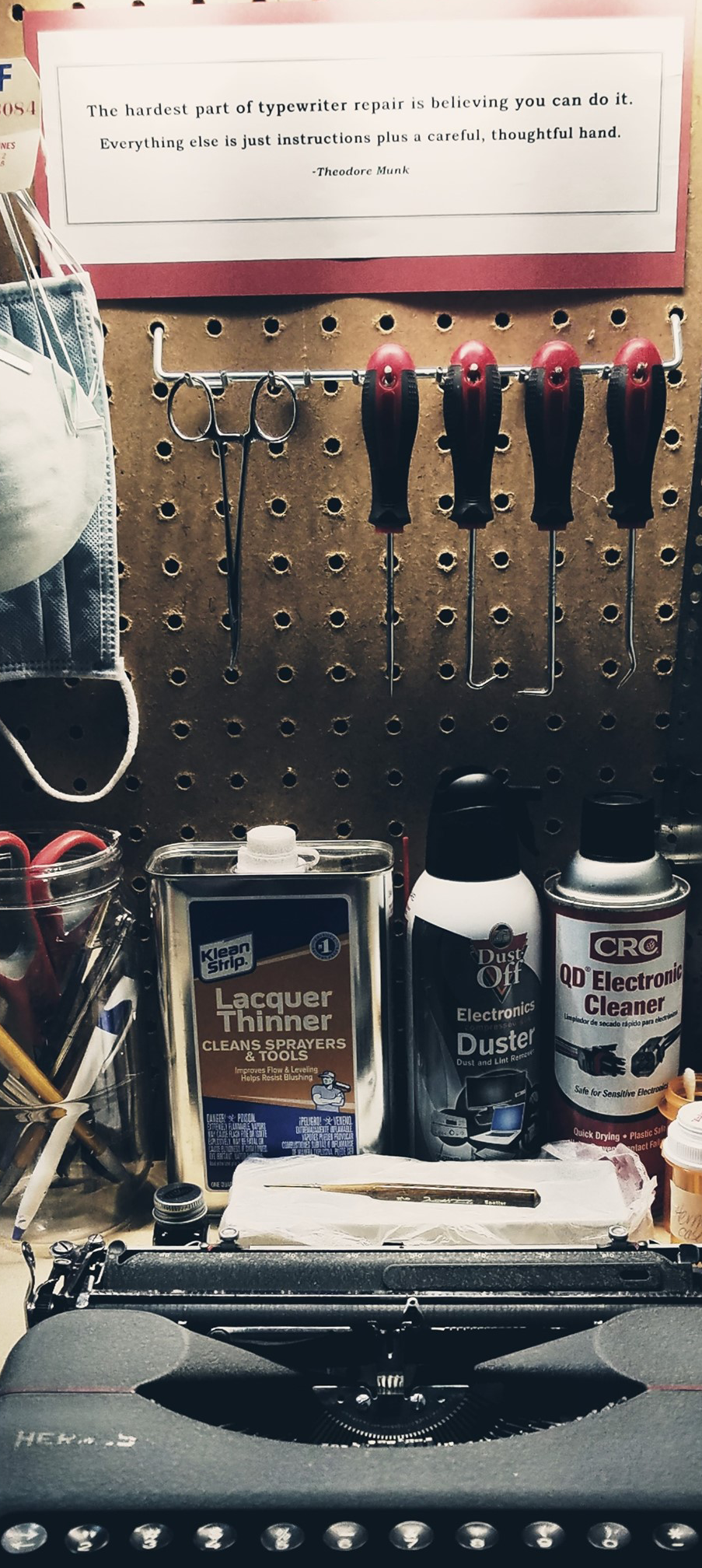

-
- Jul 2024
-
gemini.google.com gemini.google.com
-
The illusion of knowledge: The song questions the notion that speaking confidently on a subject equates to understanding it deeply.
There is a need for intellectual humility within the community of researchers, and society in general. Do not speak confident about that which you do not know.
Relation to Charlie Munger's principle.
-
- Apr 2024
-
apps.apple.com apps.apple.com
-
The Mzanzi kids multilingual language learning App was created for children between the ages of 2-6 years in South Africa. It was designed to stimulate visual, speech and language literacy skills at an early age by understanding basic everyday concepts and highlighting the correct pronunciation of speech in six (6) different languages; English, Afrikaans, IsiXhosa, IsiZulu, Sepedi and Setswana. The integration of images and phonetics provides a good foundation for children to learn and speak in their mother tongue or home language with confidence and fluency, but most importantly comprehend and appreciate the diversity of languages used by South Africans. This multilingual App provides a good introduction before entering a schooling environment, and offers a non-threatening, playful and fun way of learning languages using innovative technology.
This is an app for multilingual language learning. Mine will focus on the mother tongue.
I tried it out for a bit and found the audio very repetitive, which could be problematic. Minecraft had such good audio - C14 or C11? It is fantastically immersive, and the popularity of the game and audio is irrefutable if you look at longevity (games come and go often, and very few manage to stick and have a continuous impact, Minecraft is a good example of an exception to this, alongside other well adjusted and designed games.
I had fun learning the clicks in isiXhoso - something I want to practice, but the audio became too much as i hit the image repeatedly.
There's room for more resources. This application does not speak to all children, and no one application ever will, hence the need for many across a broad range of cultures and diversities.
-
-
archive.org archive.org
-
Beware of Mental-Itis! Industrial. The Calvin Company, 1937. http://archive.org/details/0800_Beware_of_Mental-itis_06_00_55_00.
-
-
thegaryhalbertletter.com thegaryhalbertletter.com
-
Besides that, we're an arrogant, surly lot most often more interested in dwelling on our divine wonderfulness than we are slaving away on your lowly project.
yes, an impeccable sense of confidence is REQUIRED in this level of success
-
- Sep 2023
-
github.com github.com
-
I'd suggest that you play around a little bit with a vanilla app. Create a brand new app without any additional files, just what rails new generates. See how bin/rails runner Models raises an error because there is no models directory in autoload_paths. Now, put config.autoload_paths += %W(#{config.root}/app) in config/application.rb and observe how bin/rails runner Models just returns a prompt. With the confidence of having that running, then transalate to your app.
-
- Jul 2023
-
academic.oup.com academic.oup.com
-
specific uses of the technology help develop what we call “relational confidence,” or the confidence that one has a close enough relationship to a colleague to ask and get needed knowledge. With greater relational confidence, knowledge sharing is more successful.
-
- Apr 2023
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Vicky Zhao indirectly frames the answer for "why have a zettelkasten?", especially for learning, as overcoming the "illusion of competence" which is closely related to the mere-exposure effect and the Dunning–Kruger effect.
-
-
www.schoolofmotion.com www.schoolofmotion.com
-
reinforcing audio
Audio(music and sounds) within a video presentation is a tool that can help you engage more with your audience, unfortunately it is a double edged sword. There are times when the audio can fail or be delayed, which can throw off the rhythm of your presentation as well as your confidence. Using audio for edited videos gives the user more control as they can edit the audio to their liking.
-
- Mar 2023
-
www-nejm-org.manchester.idm.oclc.org www-nejm-org.manchester.idm.oclc.org
-
interval
The probabilyty that 95% of the populaton will fall within this range
-
- Jan 2023
-
philosophybreak.com philosophybreak.com
-
Confidence is the middle way between self-deprecation (deficiency) and arrogance (excess).
Уверенность — это средний путь между самоуничижением (недостаток) и высокомерием (избыток).
-
-
www.tri-cityherald.com www.tri-cityherald.com
-
In short, the agency put forth a rule that addresses the problem head-on without prevaricating or kowtowing to corporate America.
-
- Oct 2022
-
gamefound.com gamefound.com
-
After the first week of the campaign, we realized what are the main problematic pillars and fixed them right away. Nevertheless, even with these improvements and strong support from the Gamefound team, we’re not even close to achieving the backer numbers with which we could safely promise to create a game of the quality we think it deserves.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
To be able to trustone's own experience, even if it often turns out to beinadequate, is one mark of the mature workman. Suchconfidence in o n e ' s own experience is indispensable tooriginality in any intellectual pursuit, and the file is onetool by which I have tried to develop and justify suchconfidence.
The function of memory served by having written notes is what allows the serious researcher or thinker to have greater confidence in their work, potentially more free from cognitive bias as one idea can be directly compared and contrasted with another by direct juxtaposition.
Tags
Annotators
-
- Aug 2022
-
www.bps.org.uk www.bps.org.uk
-
Decision-making in uncertainty | BPS. (n.d.). Retrieved November 22, 2021, from https://www.bps.org.uk/events/decision-making-uncertainty
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
I'm currently in a second master's program with a thesis coming up in about 8 months. I could not write my reports without my ZK. No going back for me! I'm also now more confident that I could pursue a PhD.
https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/comment/7902/#Comment_7902
-
- Mar 2022
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. (2022, January 26). RT @PsyArXivBot: Confidence of others trumps confidence of self in social information use https://t.co/Tvanez1cjS [Tweet]. @SciBeh. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1502295445527277574
-
- Feb 2022
-
healthydebate.ca healthydebate.ca
-
Enough with the harassment: How to deal with anti-vax cults. (2022, January 26). Healthy Debate. https://healthydebate.ca/2022/01/topic/how-to-deal-with-anti-vax-cults/
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Gradassi, A., Bos, W. van den, & Molleman, L. (2022). Confidence of others trumps confidence of self in social information use. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/mqyu2
-
- Dec 2021
-
healthydebate.ca healthydebate.ca
-
Vaccination among the pregnant lagging despite growing evidence of safety and efficacy. (2021, December 10). Healthy Debate. https://healthydebate.ca/2021/12/topic/vaccination-pregnant-safe-efficacy/
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Kan, U., Feng, M., & Porter, M. A. (2021). An Adaptive Bounded-Confidence Model of Opinion Dynamics on Networks. ArXiv:2112.05856 [Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2112.05856
-
-
www.thelancet.com www.thelancet.com
-
Pickles, K., Copp, T., Dodd, R. H., Cvejic, E., Seale, H., Steffens, M. S., Meyerowitz-Katz, G., Bonner, C., & McCaffery, K. (2021). COVID-19 vaccine intentions in Australia. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 21(12), 1627–1628. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00686-1
-
- Nov 2021
-
www.cnbc.com www.cnbc.com
-
A list of useless filler phrases and softeners that are generally unnecessary. including the word "just". Worth exploring these in more depth.
I'm not sure I believe the "think"/"believe" one.
“I think this would ...” What to say instead: “I believe this would …”
-
-
drive.google.com drive.google.com
-
teachers’ confidencein their own basic IT skills promotes positive attitudes to online learning and that peer tutoring plays animportant role in teachers’ learning
- Disparities caused and/or exacerbated as a result of the forced transition to online learning.
-
-
acpinternist.org acpinternist.org
-
Frost, M. (n.d.). Busting COVID-19 vaccination myths. Retrieved November 2, 2021, from https://acpinternist.org/archives/2021/11/busting-covid-19-vaccination-myths.htm
Tags
- anti-vaccine
- misconception
- speaking engagement
- vaccine confidence
- lang:en
- public confidence
- risk
- data
- safety
- mortality
- BIPOC
- young people
- health information
- vaccine effectiveness
- trust
- immunization
- disinformation
- FDA
- is:webpage
- online
- misinformation
- campaign
- vaccine
- COVID-19
- USA
- infodemic
- social media
- vaccination rate
Annotators
URL
-
- Oct 2021
-
www.euro.who.int www.euro.who.int
-
Denmark campaign rebuilds confidence in HPV vaccination. (n.d.). Retrieved October 6, 2021, from https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/vaccines-and-immunization/news/news/2018/3/denmark-campaign-rebuilds-confidence-in-hpv-vaccination
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Larson, H. J., Hartigan-Go, K., & de Figueiredo, A. (2018). Vaccine confidence plummets in the Philippines following dengue vaccine scare: Why it matters to pandemic preparedness. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 15(3), 625–627. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2018.1522468
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Basol, M., Roozenbeek, J., & van der Linden, S. (n.d.). Good News about Bad News: Gamified Inoculation Boosts Confidence and Cognitive Immunity Against Fake News. Journal of Cognition, 3(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.5334/joc.91
-
-
orb-international.com orb-international.com
-
orb-developer. (2021, June 4). Vaccine Confidence Tracker: UK. ORB International. https://orb-international.com/2021/06/04/vaccine-confidence-tracker-uk/
-
-
link.springer.com link.springer.com
-
Shahsavari, S., Holur, P., Wang, T., Tangherlini, T. R., & Roychowdhury, V. (2020). Conspiracy in the time of corona: automatic detection of emerging COVID-19 conspiracy theories in social media and the news. Journal of Computational Social Science, 3(2), 279–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42001-020-00086-5
-
-
www.vaccinestoday.eu www.vaccinestoday.eu
-
Finnegan, G. (2021, September 8). How France overcame COVID-19 vaccine scepticism. VaccinesToday. https://www.vaccinestoday.eu/stories/how-france-overcame-covid-19-vaccine-scepticism/
-
- Sep 2021
-
docs.google.com docs.google.com
-
confidence
a feeling of being certain of your ability to do things well:
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Glenza, J. (2021, September 27). How the US vaccine effort derailed and why we shouldn’t be surprised. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2021/sep/27/us-vaccine-effort-derailed
-
- Aug 2021
-
cgdev.org cgdev.org
-
Center For Global Development. “Three New Estimates of India’s All-Cause Excess Mortality during the COVID-19 Pandemic.” Accessed August 11, 2021. https://cgdev.org/publication/three-new-estimates-indias-all-cause-excess-mortality-during-covid-19-pandemic.
Tags
- death
- India
- civil registration
- lang:en
- statistical confidence
- COVID-19
- age-specific infection fatality rates
- authoritative estimate
- is:article
- pandemic
- attendant accountability
- Consumer Pyramid Household Survey
- data source
- Coronavirus
Annotators
URL
cgdev.org/publication/three-new-estimates-indias-all-cause-excess-mortality-during-covid-19-pandemic -
-
thebulletin.org thebulletin.org
-
How to trash confidence in a COVID-19 vaccine: Brexit edition—Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. (n.d.). Retrieved August 10, 2021, from https://thebulletin.org/2021/08/how-to-trash-confidence-in-a-covid-19-vaccine-brexit-edition/#.YQwD9u6LazM.twitter
-
-
www.kff.org www.kff.org
-
Lopes, L., Stokes, M., & 2021. (2021, June 30). KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor: June 2021. KFF. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-june-2021/
-
- Jul 2021
-
allafrica.com allafrica.com
-
Leah Keating on Twitter: “This work with @DavidJPOS and @gleesonj is now on arXiv (https://t.co/hxjZnCmKcM): ‘A multi-type branching process method for modelling complex contagion on clustered networks’ Here is a quick overview of our paper: (1/6) https://t.co/3jQ2flhk71” / Twitter. (n.d.). Retrieved July 23, 2021, from https://twitter.com/leahakeating/status/1418150117106978816
-
-
www.journals.uchicago.edu www.journals.uchicago.edu
-
Heesen, R., & Bright, L. K. (2020). Is Peer Review a Good Idea? The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science, 000–000. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjps/axz029
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Jensen, U., Ayers, S., & Koskan, A. (2021). Video-based messages to reduce COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and nudge uptake. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/df9qw
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
It’s fun but when would we ever use things like this in actual code?When it’s well tested, commented, documented, and becomes an understood idiom of your code base.We focus so much on black magic and avoiding it that we rarely have a chance to enjoy any of the benefits. When used responsibly and when necessary, it gives a lot of power and expressiveness.
-
-
www.ecdc.europa.eu www.ecdc.europa.eu
-
Countering online vaccine misinformation in the EU/EEA. (n.d.). Retrieved July 2, 2021, from https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/countering-online-vaccine-misinformation-eu-eea
-
- Jun 2021
-
thisisourshot.ca thisisourshot.ca
-
Home—This Is Our Shot Canada. (n.d.). Retrieved June 28, 2021, from https://thisisourshot.ca/
-
-
science.sciencemag.org science.sciencemag.org
-
Larson, H. J., & Broniatowski, D. A. (2021). Volatility of vaccine confidence. Science, 371(6536), 1289–1289. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abi6488
-
-
www.bmj.com www.bmj.com
-
Mahase, E. (2021). Covid-19: UK has highest vaccine confidence and Japan and South Korea the lowest, survey finds. BMJ, n1439. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n1439
-
- May 2021
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Remmel, A. (2021). ‘It’s a minefield’: COVID vaccine safety poses unique communication challenge. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-01257-8
-
-
journals.sagepub.com journals.sagepub.com
-
Dunn, E. W., Chen, L., Proulx, J. D. E., Ehrlinger, J., & Savalei, V. (2021). Can Researchers’ Personal Characteristics Shape Their Statistical Inferences? Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 47(6), 969–984. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167220950522
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Vaccine confidence fears as under-30s in UK offered AstraZeneca alternative. (2021, April 7). The Guardian. http://www.theguardian.com/society/2021/apr/07/under-30s-in-uk-should-be-offered-alternative-covid-vaccine-to-astrazeneca-jab-says-regulator
Tags
- alternative
- young women
- is:news
- Oxford
- Europe
- vaccine confidence
- lang:en
- COVID-19
- under-30s
- blood clots
- UK
- AstraZeneca
- low risk
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Sturgis, P., Brunton-Smith, I., & Jackson, J. (2021). Trust in science, social consensus and vaccine confidence. Nature Human Behaviour. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01115-7
Tags
- science
- vaccination uptake
- vaccine confidence
- lang:en
- societal consensus
- vaccine hesitancy
- trust
- immunization
- epidemiology
- scientific trust
- country-level differences
- behavioral science
- scepticism
- vaccine
- COVID-19
- herd immunity
- anti-vaxxer
- social consensus
- is:article
- vaccine acceptance
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
Politicians must dial down the rhetoric over COVID vaccines. (2021). Nature, 591(7851), 502–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-00769-7
-
-
blogs.bmj.com blogs.bmj.com
-
How will covid-19 vaccine safety concerns impact vaccine confidence? (2021, April 16). The BMJ. https://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2021/04/16/how-will-the-uks-decision-to-offer-an-alternative-to-the-oxford-astrazeneca-covid-19-vaccine-for-under-30s-following-safety-signals-impact-vaccine-confidence/
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Ben Wakana. (2021, April 14). NEW POLL: The J&J pause makes people more confident in vaccines, not less. M-O-R-E C-O-N-F-I-D-E-N-T https://t.co/bqe6bTBwiR [Tweet]. @benwakana46. https://twitter.com/benwakana46/status/1382436908689657867
-
-
www.kff.org www.kff.org
-
KFF. “KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor – April 2021,” May 6, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-april-2021/.
-
-
thehill.com thehill.com
-
It’s too soon to declare vaccine victory—Four strategies for continued progress | TheHill. (n.d.). Retrieved May 12, 2021, from https://thehill.com/opinion/healthcare/552219-its-too-soon-to-declare-covid-vaccine-victory-four-strategies-for
-
-
-
Approaching email development this way transitions more of the quality assurance (QA) process to the browser instead of the email client. It gives email designers more power, control, and confidence in developing an email that will render gracefully across all email clients.
can mostly test with browser and have less need (but still not no need) to test with email client
-
- Apr 2021
-
-
Keenan, E. (2021, April 14). Doctors weigh in as U.S. pauses use of Johnson & Johnson vaccine. Toronto Star. https://www.thestar.com/news/world/2021/04/13/im-not-losing-sleep-over-this-doctors-weigh-in-as-us-pauses-use-of-johnson-johnson-vaccine.html
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. ‘RT @benwakana46: NEW POLL: The J&J Pause Makes People more Confident in Vaccines, Not Less. M-O-R-E C-O-N-F-I-D-E-N-T Https://T.Co/Bq…’. Tweet. @SciBeh (blog), 14 April 2021. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1382618891222925314.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Céline Gounder, MD, ScM, FIDSA. (2021, April 14). With all due respect to @NateSilver538, he is not an expert on the psychology of vaccine confidence. He is a poll aggregator and political pundit. He is not an infectious disease specialist, epidemiologist, vaccinologist, virologist, immunologist, or behavioral scientist. Https://t.co/HBrI6zj9aa [Tweet]. @celinegounder. https://twitter.com/celinegounder/status/1382299663269761024
-
- Mar 2021
-
www-sciencedirect.ez29.periodicos.capes.gov.br www-sciencedirect.ez29.periodicos.capes.gov.br
-
Larson, H. J., Cooper, L. Z., Eskola, J., Katz, S. L., & Ratzan, S. (2011). Addressing the vaccine confidence gap. The Lancet, 378(9790), 526–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60678-8
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Larson, H. J., Jarrett, C., Eckersberger, E., Smith, D. M. D., & Paterson, P. (2014). Understanding vaccine hesitancy around vaccines and vaccination from a global perspective: A systematic review of published literature, 2007–2012. Vaccine, 32(19), 2150–2159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.01.081
-
-
www.thelancet.com www.thelancet.com
-
Figueiredo, A. de, Simas, C., Karafillakis, E., Paterson, P., & Larson, H. J. (2020). Mapping global trends in vaccine confidence and investigating barriers to vaccine uptake: A large-scale retrospective temporal modelling study. The Lancet, 396(10255), 898–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31558-0
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Finnegan, G., Holt, D., English, P. M., Glismann, S., Thomson, A., Salisbury, D. M., Bogaerts, H., & Bonanni, P. (2018). Lessons from an online vaccine communication project. Vaccine, 36(44), 6509–6511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.05.007
-
-
www.biorxiv.org www.biorxiv.org
-
Bertana, A., Chetverikov, A., Bergen, R. S. van, Ling, S., & Jehee, J. F. M. (2020). Dual strategies in human confidence judgments. BioRxiv, 2020.09.17.299743. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.17.299743
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Rahnev, D. (2020). Confidence in the Real World. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2020.05.005
-
-
www.pewresearch.org www.pewresearch.org
-
NW, 1615 L. St, Suite 800Washington, and DC 20036USA202-419-4300 | Main202-857-8562 | Fax202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries. ‘Intent to Get a COVID-19 Vaccine Rises to 60% as Confidence in Research and Development Process Increases’. Pew Research Center Science & Society (blog), 3 December 2020. https://www.pewresearch.org/science/2020/12/03/intent-to-get-a-covid-19-vaccine-rises-to-60-as-confidence-in-research-and-development-process-increases/.
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Boseley, S. (2021, March 15). Coronavirus: report scathing on UK government’s handling of data. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/mar/15/mp-report-scathing-on-uk-goverment-handling-and-sharing-of-covid-data
-
-
www.pnas.org www.pnas.org
-
Mendels, D.-A., Dortet, L., Emeraud, C., Oueslati, S., Girlich, D., Ronat, J.-B., Bernabeu, S., Bahi, S., Atkinson, G. J. H., & Naas, T. (2021). Using artificial intelligence to improve COVID-19 rapid diagnostic test result interpretation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(12). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2019893118
-
- Feb 2021
-
www.wsj.com www.wsj.com
-
We’ll Have Herd Immunity by April
Overall scientific credibility: 'very low', according to scientists who analyzed this article.
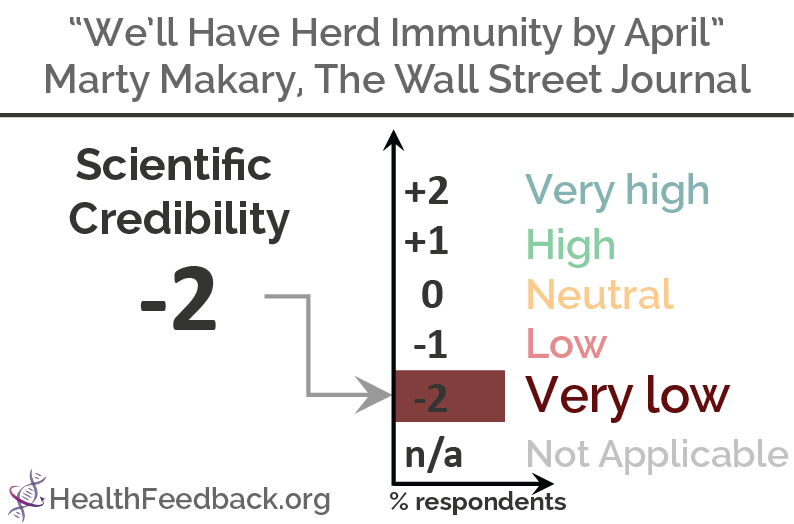
Find more details in Health Feedback's analysis
-
-
www.nejm.org www.nejm.org
-
Placebo-Controlled Trials of Covid-19 Vaccines—Why We Still Need Them. (2021). New England Journal of Medicine, 384(2), e2. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp2033538
-
-
-
Hickok, A., Kureh, Y., Brooks, H. Z., Feng, M., & Porter, M. A. (2021). A Bounded-Confidence Model of Opinion Dynamics on Hypergraphs. ArXiv:2102.06825 [Nlin, Physics:Physics]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2102.06825
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Vaccine experts defend UK decision to delay second Pfizer Covid jab. (2021, January 23). The Guardian. http://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/jan/23/vaccine-experts-defend-uk-decision-to-delay-second-pfizer-covid-jab
Tags
- dose
- lang:en
- vaccination
- UK
- delay
- international
- protection
- strategy
- government
- confidence
- public
- is:news
- isolated
- vaccine
- COVID-19
- population
- BMA
- policy
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Mega, E. R. (2021). Trust in COVID vaccines is growing. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-00368-6
-
- Jan 2021
-
sciencing.com sciencing.com
-
-
What is vaccine hesitancy and why do so many people have it? (n.d.). Vogue India. Retrieved 13 January 2021, from https://www.vogue.in/wellness/content/what-is-vaccine-hesitancy-and-why-do-so-many-people-have-it
-
- Oct 2020
-
metascience.com metascience.com
-
Fiona Fidler: Misinterpretations of evidence, and worse misinterpretations of evidence (Video). (n.d.). Metascience.com. Retrieved 29 October 2020, from https://metascience.com/events/metascience-2019-symposium/fiona-fidler-misinterpretations-of-evidence/
-
-
stackoverflow.com stackoverflow.com
-
Final Form makes the assumption that your validation functions are "pure" or "idempotent", i.e. will always return the same result when given the same values. This is why it doesn't run the synchronous validation again (just to double check) before allowing the submission: because it's already stored the results of the last time it ran it.
-
- Sep 2020
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Antoniou, Rea, Heather Romero-Kornblum, J. Clayton Young, Michelle You, Joel Kramer, and Winston Chiong. ‘No Utilitarians in a Pandemic? Shifts in Moral Reasoning during the COVID-19 Global Health Crisis’, 21 September 2020. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/yjn3u.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Susan Athey, July 22, 2020. (2020, August 2). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hqTOPrUxDzM
-
-
www.pmo.gov.sg www.pmo.gov.sg
-
katherine_chen. (2020, June 17). PMO | National Broadcast by PM Lee Hsien Loong on 7 June 2020 [Text]. Prime Minister’s Office Singapore; katherine_chen. http://www.pmo.gov.sg/Newsroom/National-Broadcast-PM-Lee-Hsien-Loong-COVID-19
-
-
-
Any typescript definitions exported from this library should be tested, otherwise it can cause real pain and doubt for ts users.
-
- Aug 2020
-
osf.io osf.io
-
Pickup, M., Stecula, D., & van der Linden, C. (2020). Novel coronavirus, old partisanship: COVID-19 attitudes and behaviors in the United States and Canada [Preprint]. SocArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/5gy3d
-
-
-
Gruijters, Stefan L.K. ‘The Fallacy of Manipulation “Checks” in Psychological Experiments’. Preprint. PsyArXiv, 20 August 2020. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/fkzv5.
-
-
jamanetwork.com jamanetwork.com
-
Califf, Robert M., Adrian F. Hernandez, and Martin Landray. ‘Weighing the Benefits and Risks of Proliferating Observational Treatment Assessments: Observational Cacophony, Randomized Harmony’. JAMA 324, no. 7 (18 August 2020): 625–26. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.13319.
Tags
- causation
- lang:en
- randomised clinical trials
- reliable truth
- confusion
- therapies
- observational
- nonrandomised studies
- RCTs
- is:report
- epidemiology
- benefits and risks
- treatment
- assessments
- proliferating observational treatment
- noise
- risks
- COVID-19
- clinical management
- false confidence
- benefits
Annotators
URL
-
-
academic.oup.com academic.oup.com
-
Lavoie, K. (2019). Applying behavioural science to improve physicians’ ability to help people improve their own health behaviours. European Journal of Public Health, 29(Supplement_4). https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckz185.812
-
- Jul 2020
-
www.nber.org www.nber.org
-
Aksoy, C. G., Eichengreen, B., & Saka, O. (2020). The Political Scar of Epidemics (Working Paper No. 27401; Working Paper Series). National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w27401
-
-
osf.io osf.io
-
Aksoy, C. G., Eichengreen, B., & Saka, O. (2020). The Political Scar of Epidemics [Preprint]. SocArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/p25nh
-
-
-
Aksoy, C. G., Eichengreen, B., & Saka, O. (2020). Revenge of the Experts: Will COVID-19 Renew or Diminish Public Trust in Science? [Preprint]. SocArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/5ym9n
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Kim, H., & Florack, A. (2020). When Social Interaction Backfires: Frequent Social Interaction during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period Is Associated with Decreased Well-Being and Higher Panic Buying. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/sg5vx
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Chan, H., Torgler, B., Brumpton, M., Macintyre, A., Arapoc, J., Savage, D. A., … Stadelmann, D. (2020, July 3). How confidence in health care systems affects mobility and compliance during the COVID-19 pandemic. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/86qxu
-
- Jun 2020
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Twitter. (n.d.). Twitter. Retrieved June 22, 2020, from https://twitter.com/JASPStats/status/1274764017752592384
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Henley, J. (2020, June 6). Merkel among winners as Europeans give verdict on anti-Covid battles. The Observer. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/jun/06/no-european-leader-is-safe-as-public-lose-faith-in-coronavirus-responses
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Angner, E. (2020, May 11). "Terrific assessment of projections of demand for Swedish ICU beds. The first two panels are model-based projections by academics; the third is a simple extrapolation by the public-health authority; the fourth is the actual outcome /1." Twitter. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1260121561861939200
-
-
psycnet.apa.org psycnet.apa.org
-
Attali, Y., Budescu, D., & Arieli-Attali, M. (2020). An item response approach to calibration of confidence judgments. Decision, 7(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1037/dec0000111
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Lunn, P. D., Timmons, S., Julienne, H., Belton, C., Barjaková, M., Lavin, C., & McGowan, F. P. (2020). Using Decision Aids to Support Self-Isolation During the COVID-19 Pandemic [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/fngx5
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Moore, D. A., & Schatz, D. (2020). Overprecision increases subsequent surprise [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/wfcbv
-
- May 2020
-
kellysutton.com kellysutton.com
-
The test is being marked as skipped because it has randomly failed. How much confidence do we have in that test and feature in the first place.
-
“Make it work” means shipping something that doesn’t break. The code might be ugly and difficult to understand, but we’re delivering value to the customer and we have tests that give us confidence. Without tests, it’s hard to answer “Does this work?”
-
-
-
Mandel, D. R., Collins, R. N., Risko, E. F., & Fugelsang, J. A. (2020). Effect of Confidence Interval Construction on Judgment Accuracy. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/mktgj
-
-
www.w3.org www.w3.org
-
The "'strict-dynamic'" source expression aims to make Content Security Policy simpler to deploy for existing applications who have a high degree of confidence in the scripts they load directly, but low confidence in their ability to provide a reasonable list of resources to load up front.
-
-
psycnet.apa.org psycnet.apa.org
-
Can we count on parents to help their children learn at home? (2020, May 8). Evidence for Action. https://blogs.unicef.org/evidence-for-action/can-we-count-on-parents-to-help-their-children-learn-at-home/
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Fischer, H., & Said, N. (2020, May 12). Metacognition_ClimateChange_Fischer&Said_Preprint. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/fd6gy
-
-
-
Van den Akker, O., Weston, S. J., Campbell, L., Chopik, W. J., Damian, R. I., Davis-Kean, P., Hall, A. N., Kosie, J. E., Kruse, E. T., Olsen, J., Ritchie, S. J., Valentine, K. D., van ’t Veer, A. E., & Bakker, M. (2019). Preregistration of secondary data analysis: A template and tutorial [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/hvfmr
-
- Apr 2020
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Sibley, C. G., Greaves, L., Satherley, N., Wilson, M., Lee, C., Milojev, P., … Barlow, F. (2020, April 20). Short-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and a nationwide lockdown on institutional trust, attitudes to government, health and wellbeing. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/cx6qa
-
-
behavioralscientist.org behavioralscientist.org
-
Epistemic Humility—Knowing Your Limits in a Pandemic—By Erik Angner. (2020, April 13). Behavioral Scientist. https://behavioralscientist.org/epistemic-humility-coronavirus-knowing-your-limits-in-a-pandemic/
-
-
www.troyhunt.com www.troyhunt.com
-
In the past, I've had people approach me with all sorts of creative means by which I could store this data and make it available to people. But no matter how good a crypto solution I come up with, being able to hand-on-heart say "I don't store passwords in HIBP" is enormously important. Not "I store them but I've been really, really, really careful with them" because that always leaves an element of doubt in people's minds.
-
- Mar 2020
-
www.thesun.co.uk www.thesun.co.uk
-
Melting glaciers reveal LOST island in Antarctica – and humans are already visiting it
Overall scientific credibility: 'low' according to the scientists who analyzed this article.
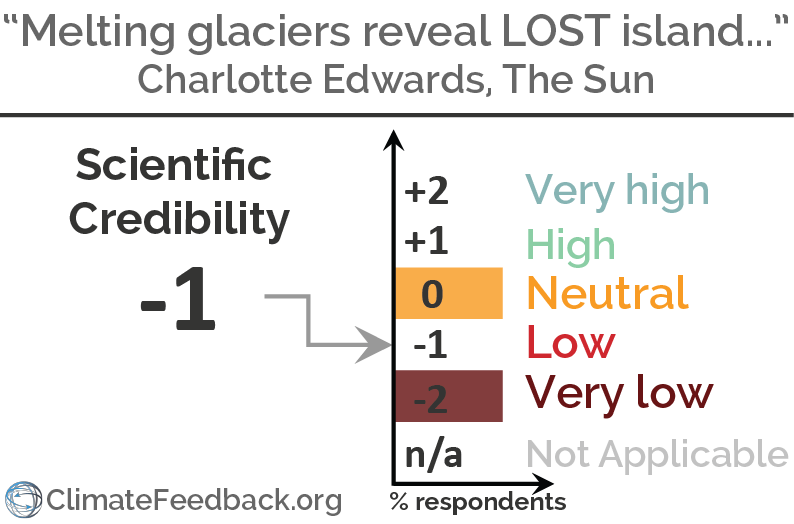
Find more details in Climate Feedback's analysis
-
- Feb 2020
-
about.gitlab.com about.gitlab.com
-
development is hard because you have to preserve the ability to quickly improve the product in the future
-
- Nov 2019
-
www.dailymail.co.uk www.dailymail.co.uk
-
Breakthrough as scientists create a new cowpox-style virus that can kill EVERY type of cancer
Overall scientific credibility: 'neutral', according to scientists who analyzed this article.
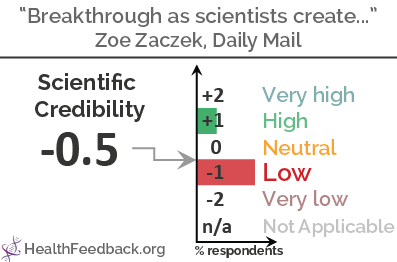
Find more details in Health Feedback's analysis
-
-
kentcdodds.com kentcdodds.com
-
Because they're more integrated and try to serialize an incomplete system (e.g. one with some kind of side effects: from browser/library/runtime versions to environment to database/API changes), they will tend to have high false-negatives (failing test for which the production code is actually fine and the test just needs to be changed). False negatives quickly erode the team's trust in a test to actually find bugs and instead come to be seen as a chore on a checklist they need to satisfy before they can move on to the next thing.
-
-
kentcdodds.com kentcdodds.com
-
But isn't the point of testing to be confident the application works? Who cares if your unit works if the app is broken? I definitely want to know if the third party component I'm using breaks my use case. I mean, I'm not going to rewrite their entire test base, but if I can easily test my use case by not mocking out their component then why not do that and get the extra confidence?
-
So finally I'm coming out with it and explaining why I never use shallow rendering and why I think nobody else should either. Here's my main assertion:With shallow rendering, I can refactor my component's implementation and my tests break. With shallow rendering, I can break my application and my tests say everything's still working.This is highly concerning to me because not only does it make testing frustrating, but it also lulls you into a false sense of security. The reason I write tests is to be confident that my application works and there are far better ways to do that than shallow rendering.
-
-
kickass.partners kickass.partners
-
We're not just fast, we know where we're going.
-
You’ll rest easy at night, knowing that the proper amount of automated test coverage is in place and protecting your product from unintentional breakage.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
Unit test coverage grants confidence that code logic is correct(and serves as great developer documentation!)
-
-
testing-library.com testing-library.com
-
You want to write maintainable tests for your React components. As a part of this goal, you want your tests to avoid including implementation details of your components and rather focus on making your tests give you the confidence for which they are intended. As part of this, you want your testbase to be maintainable in the long run so refactors of your components (changes to implementation but not functionality) don't break your tests and slow you and your team down.
-
The more your tests resemble the way your software is used, the more confidence they can give you.
-
- Sep 2019
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
The Best Probiotics
Overall scientific credibility: 'high', according to scientists who analyzed this article.
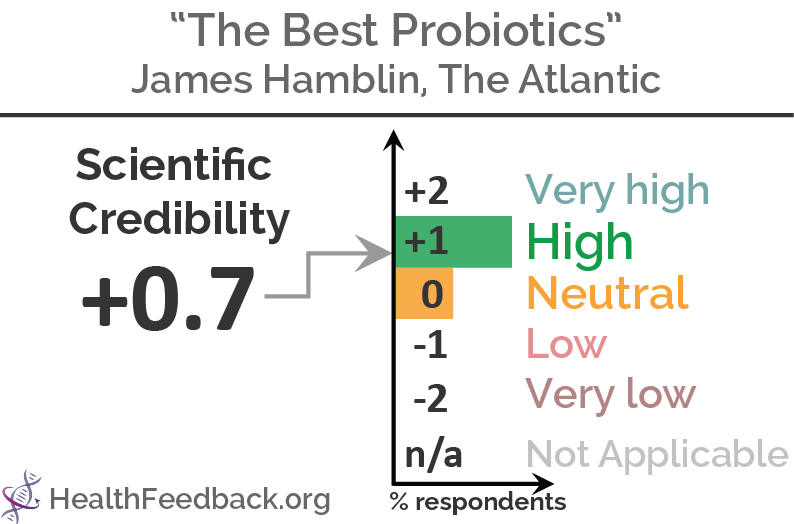
Find more details in Health Feedback's analysis
-
- Mar 2019
-
elearningindustry.com elearningindustry.com
-
This page describes a method of teaching designed specifically for adults. The instructional design theory is Keller's "ARCS," which stands for attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction--all features that adult learning experiences should be characterized by. The text on this page is readable but the popups and graphics are a bit annoying. rating 3/5
-
- Feb 2019
-
www.auccaravan.com www.auccaravan.com
-
the vote of no confidence
See the February 10, 2019 article in The Caravan about the AUC University Senate's 80% vote of no confidence in the AUC president and his administration.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Dec 2018
-
highline.huffingtonpost.com highline.huffingtonpost.com
-
Everything You Know About Obesity Is Wrong
Overall scientific credibility: 'debated', according to scientists who analyzed this article.
Find more details in Health Feedback's analysis
-
- Nov 2018
-
iphysresearch.github.io iphysresearch.github.io
-
Learning Confidence Sets using Support Vector Machines
也是一篇讨论“置信度”的文章。将二分类问题转化为一个分别独立的“三分类”问题,且分类边界可学习,而边界的取定用 SVM。文章里似乎有不少详尽的数学理论推导,值得练手推推看~
-
Inhibited Softmax for Uncertainty Estimation in Neural Networks
这种关乎网络“置信度confidence”或者叫“不确定度uncentainty”的 paper 还是挺有意义的,虽然现在还是婆说婆有理的阶段。文内综述了很多 Related 工作,还是挺值得 mark 下的。作者提的Inhibited Softmax蛮好理解的,另repo里放了不少ipynb文档[good]。
-
Learning Confidence for Out-of-Distribution Detection in Neural Networks
此文对我来说,值得好好看一看~
关键在于最后一层处,并行的多安排了一层表示学习confidence 的输出层。不过,总觉得这种操作很片面,有点以偏概全~
-
-
www.virclass.net www.virclass.net
-
blog is called Rebecca’s Pocket. In her oft-cited essay “Weblogs: a history and perspective”, she writes about how blogging not only helped her gain knowledge about herself and her own interests, blogging actually led her to value more highly her own opinion and her own point of view. Partly, this was because she carefully considered her ideas as she wrote.
This demonstrates how blogging is one of those informal yet vital places where people become great writers.
-
- Jul 2018
-
-
This result is consistent with analysis by the data science team at Quora, a site where users ask and answer questions. That team found that women use uncertain words and phrases more often than men do, even when they are just as confident.
-
- Jul 2016
-
thesocialwrite.com thesocialwrite.com
-
You might even notice that your confidence isn’t the only thing that goes up, this was my first step in growing internally, and you’ll find that in the end Social Development isn’t just about learning to talk to other people, it’s a deep discovery about who you truly are.
-
Basically it makes you go from walking in a mild pace towards your goals to sprinting at them full speed with a rocket pack strapped to your back!
-
Self-Acceptance + Self Assurance = Confidence
-
- Jan 2016
-
www.gutenberg.org www.gutenberg.org
-
I am now viewing the "Workman's Sandwich" and wondering what it would take humankind to provide the WorkWOMAN's Sandwich... Ladies on the job deserve just as much roast beef as any male laborer. If I may, I'd like to propose an ideal sandwich: it would include the contents of; Cheese churned from the breast milk of strong, independent mothers, Turkey of the female farmer's land, and mustard from a female CEO-owned grocery store on Wall Street.
-
- Oct 2013
-
rhetoric.eserver.org rhetoric.eserver.org
-
Let reading, therefore, be at first sure, then continuous, and for a long time slow, until, by exercise, a correct quickness is gained.
learning at their own pace and building confidence along the way.
-
-
rhetoric.eserver.org rhetoric.eserver.org
-
we believe that we cannot and shall not fail, or that we shall succeed completely
confidence is key to success
-
Confidence is, about what things we feel it, and under what conditions. It is the opposite of fear, and what causes it is the opposite of what causes fear; it is, therefore, the expectation associated with a mental picture of the nearness of what keeps us safe and the absence or remoteness of what is terrible: it may be due either to the near presence of what inspires confidence or to the absence of what causes alarm.
-
-
rhetoric.eserver.org rhetoric.eserver.org
-
the three, namely, that induce us to believe a thing apart from any proof of it: good sense, good moral character, and goodwill
these things are confidence builders
Tags
Annotators
URL
-