n a recent laboratory study, Robert Jagiello, also at Warwick, found that socially shared information not only bolsters our biases but also becomes more resilient to correction.
- Sep 2022
-
www.scientificamerican.com www.scientificamerican.com
-
-
We confuse popularity with quality and end up copying the behavior we observe.
Popularity ≠ quality in social media.
-
Even our ability to detect online manipulation is affected by our political bias, though not symmetrically: Republican users are more likely to mistake bots promoting conservative ideas for humans, whereas Democrats are more likely to mistake conservative human users for bots.
-
Unable to process all this material, we let our cognitive biases decide what we should pay attention to.
In a society consumed with information overload, it is easier for our brains to allow our well evolved cognitive biases to decide not only what to pay attention to, but what to believe.
-
-
-
I've recently run across a few examples of a pattern that should have a name because it would appear to dramatically change the outcomes. I'm going to term it "decisions based on possibilities rather than realities". It's seen frequently in economics and politics and seems to be a form of cognitive bias. People make choices (or votes) about uncertain futures, often when there is a confluence of fear, uncertainty, and doubt, and these choices are dramatically different than when they're presented with the actual circumstances in practice.
A recent example was a story about a woman who was virulently pro-life who when presented with a situation required her to switch her position to pro-choice.
Another relates to choices that people want to make about where their children might go to school versus where they actually send them, and the damage this does to public education.
Let's start collecting examples of these quandaries at all levels of making choices in the real world.
What is the relationship to this with the mental exercise of "descending into the particular"?
Does this also potentially cause decision fatigue in cases of voting spaces when constituents are forced to vote for candidates on thousands of axes which they may or may not agree with?
-
-
macwright.com macwright.com
-
a bigger source tree
Someone is going to need to eventually explain their convoluted reasons for labeling this a downside.
Sure, strictly speaking, a bigger source tree is bad, but delegating to package.json and
npm installdoesn't actually change anything here. It's the same amount of code whether you eagerly fetch all of it at the same time or whether you resort to late fetching.Almost none of the hypothetical benefits apply to the way development is handled in practice. There was one arguably nice benefit, but it was a benefit for the application author's repo host (not the application author), and the argument in favor of it evaporated when GitHub acquired NPM, Inc.
-
Vendoring means that you aren’t going to get automatic bugfixes, or new bugs, from dependencies
No, those are orthogonal. Whether you obtain the code for your dependency* at the same time you clone your repo or whether you get it by binding by name and then late-fetching it after the clone finishes, neither approach has any irreversible, distinct consequences re bugs/fixes.
* and it still is a dependency, even when it's "vendored"...
-
-
www.retrievalpractice.org www.retrievalpractice.org
- Aug 2022
-
www.medrxiv.org www.medrxiv.org
-
Caspersen, I. H., Magnus, P., & Trogstad, L. (2021). Excess risk and clusters of symptoms after COVID-19 in a large Norwegian cohort (p. 2021.10.15.21265038). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.15.21265038
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Anthony Costello. (2022, February 24). The risks of cognitive symptoms lasting at least 12 MONTHS were much higher in the infected group. 4.8x higher for fatigue, 3.2x for brain fog, 5.3x for poor memory, and an incredible 51x for altered taste and smell. We need data on children, but it could easily be similar. (17) https://t.co/JC1qYyW2Xc [Tweet]. @globalhlthtwit. https://twitter.com/globalhlthtwit/status/1496957266016313348
-
-
www.bps.org.uk www.bps.org.uk
-
Decision-making in uncertainty | BPS. (n.d.). Retrieved November 22, 2021, from https://www.bps.org.uk/events/decision-making-uncertainty
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Weiss, D. J., & Shanteau, J. (2021). The futility of decision making research. Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part A, 90, 10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.shpsa.2021.08.018
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
You can use terribly slow scripting and techniques and get something working, not because the tooling is genius, but because the hardware is so incredibly fast.
If the thesis is sound, then logically we should expect the instances where people have decided to "use terribly slow scripting and techniques" to produce better programs; the not-slow (non-"scripting") stuff to be worse.
You can only pick one:
- software is worse because hardware improvements mean that what were previously noticeable inefficiencies are no longer noticeable
- programs that are written in low-level languages and don't as much incur runtime overheads are better on average because they're written in low-level languages that aren't as wasteful
-
-
-
Holford, D. L., Juanchich, M., & Sirota, M. (2021). Ambiguity and unintended inferences about risk messages for COVID - 19. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/w5rd6
-
-
theinformed.life theinformed.life
-
And it’s like, no, no, you know? This is an adaptation thing. You know, computers are almost as old as television now, and we’re still treating them like, “ooh, mysterious technology thing.” And it’s like, no, no, no! Okay, we’re manipulating information. And everybody knows what information is. When you bleach out any technical stuff about computers, everybody understands the social dynamics of telling this person this and not telling that person that, and the kinds of decorum and how you comport yourself in public and so on and so forth. Everybody kind of understands how information works innately, but then you like you try it in the computer and they just go blank and you know, like 50 IQ points go out the window and they’re like, “doh, I don’t get it?” And it’s the same thing, it’s just mediated by a machine.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Desai, S. C., & Reimers, S. (2022). Does explaining the origins of misinformation improve the effectiveness of a given correction? PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/fxkzc
-
-
-
Seaman, K. L., Christensen, A. P., Senn, K., Cooper, J., & Cassidy, B. S. (2022). Age Differences in the Social Associative Learning of Trust Information. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/b38rd
Tags
- social science
- social cognition
- trust
- working memory
- lang:en
- personality psychology
- learning
- social cue
- age difference
- fMRI
- is:preprint
- social psychology
- behavioral science
- social associative learning
- aging
- cognitive psychology
- judgement
- social processing
- developmental psychology
- decision making
- trust information
- research
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.joelonsoftware.com www.joelonsoftware.com
-
Corollary: Spolsky (at least at the time of this article) didn't really understand types, having about the same grasp on computing fundamentals as your average C programmer.
-
-
wiki.arnaudcys.com wiki.arnaudcys.com
-
It should be dead simple to distribute content (eg. static content).It should be easy to build apps.It should be not too hard to build a platform.
The thing that gets me about takes like this is that it's all the stuff below the Web content layer that accounts for what makes all this stuff harder than it needs to be.
What's the hard part about distributing content (static or not, but let's go with static for simplicity)? It's registering a domain, updating DNS, and keeping a Web server up—all systems that have nothing to do with the "infernal" trio and also generally programmed in what are typically described as saner languages and their traditions. It's either that, or it's relying on somebody else, like GitHub Pages, and integrating the implementation details/design decisions for their value-add into your workflow.
To "build a platform" is ambiguous, but it sounds a lot like "creating a server-side application to serve non-static content and handle associated requests". Is the infernal trio to blame for the difficulties of that, too?
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
Dynamic typing makes that harder
So run a typechecker on the code to check your work if you want type checking. That is what TypeScript does, after all. And it's been around long enough that people shouldn't be making the mistake that a runtime that support dynamic types at runtime means that you can't use a static typechecker at "compile time" (i.e. while the code is still on the developer workstation).
-
The point is to write bug-free code.
With this comment, the anti-JS position is becoming increasingly untenable. The author earlier suggested C as an alternative. So their contention is that it's easier to write bug-free code in C than it is in JS. This is silly.
C hackers like Fabrice Bellard don't choose C for the things they do because it's easier to write bug-free code in C.
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
Other examples of tech stacks that are very stable are C, C++, and Fortran.
Category error; C, C++, and Fortran are programming languages, not tech stacks.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
blog.khinsen.net blog.khinsen.net
-
What is not OK is what I perceive as the dominant attitude today: sell SciPy as a great easy-to-use tool for all scientists, and then, when people get bitten by breaking changes, tell them that it’s their fault for not having a solid maintenance plan for their code.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
particular branch of cognitive psychologyknown as linguistics
Chomsky categorized linguistics as a branch of cognitive psychology.
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
I avoided using languages that I don't know how to bootstrap like node.js
There's a weird (read: "weirdly obvious") category error here. NodeJS is not a language. (This wouldn't be so notable if the comment didn't go on to say "The key point is writing to an interface and not an implementation.")
The puzzle piece that fits the shape of the hole here is "JS". JS is the language, NodeJS is one of its implementations—and chubot knew both of these things already, so it's odd that it was expressed this way. Plus, there's a lot more diversity of JS implementations than exist for e.g. Python...
-
-
gbracha.blogspot.com gbracha.blogspot.com
-
they're called objects, and everybody has them
Even most ostensible FP practitioners who swear they don't.
-
- Jul 2022
-
bafybeiac2nvojjb56tfpqsi44jhpartgxychh5djt4g4l4m4yo263plqau.ipfs.dweb.link bafybeiac2nvojjb56tfpqsi44jhpartgxychh5djt4g4l4m4yo263plqau.ipfs.dweb.link
-
Should something new be experienced, it will be unexpected, may beoverwhelming and may not fit into any meaningful representation or expression at all. The new assuch, the possible source of transformation, regeneration and vision, does not submit to the orderimposed by the personware, it is naturally on a collision course with it and a source to various degreesof cognitive dissonance. As such, it poses a threat that a well-functioning cognitive system mustmediate.
!- for : climate change, rapid whole system change * This is a common response of people conditioned to the status quo personware - it is overwhelming and threatening * Defensiveness and conservatism to preserve the familiar elements of the status quo is a common response, including all forms of climate denialism * Early stages of pandemic in which people were afraid to don masks for fear of being ostracized
-
In summary, X, Y and Z clearly occupy entirely different positions in the social fabric andeach experiences life entirely differently. They live with entirely different sets of constraints andopportunities and consequently face different challenges both psychologically and in their interactionswith the rest of the world. And yet, all three of them suffer from a cognitive dissonance between theirindividual drives and dispositions and the demands of the social roles they feel obliged to play.
!- example ; lebenswelt, lebenslage, multi-meaningverse, perspectival knowing, situatedness
!- key insight : social dissonance between their aspirations and demand of social roles they feel compelled to obey.
-
A cognitiveagent is needed to perform this very action (that needs to be recurrent)—and another agent is neededto further build on that (again recurrently and irrespective to the particular agents involved).
This appears to be setting up the conditions for an artificial cognitive agent to be able to play a role (ie Artificial Intelligence)
-
A decision takes place when the encoding of a cognitive selection triggers, upondecoding, an occurrence of a difference that is, a state change within the system [11 ].
!- explanation : symbol-anchored encoding and decoding of cognitive selections
- In other words, people think, imagine, conceptualize
- and then encode that into live or recorded words
- that are then heard or read by others (decoded)
- and then a governance decisions subsequently results.
- !- gloss : cognitive selection trigger
- !- gloss : symbol-anchored encoding
- !- gloss : decoding cognitive selection
Tags
- ostracized
- cognitive dissonance
- cognitive agent
- lebenslage
- AI cognitive agent
- climate denialism
- symbol-anchored encoding
- whole system change
- cognitive selection triggers
- climate change
- decoding cognitive selection
- pandemic
- AI governing agent
- artificial intelligence
- personware
- multi-meaningverse
- perspectival knowing
- Situatedness
- lebenswelt
Annotators
URL
-
-
tomcritchlow.com tomcritchlow.com
-
Yes, it’s making it easier than ever to write code collaboratively in the browser with zero configuration and setup. That’s amazing! I’m a HUGE believer in this mission.
Until those things go away.
A case study: DuckDuckHack used Codio, which "worked" until DDG decided to call it a wrap on accepting outside contributions. DDG stopped paying for Codio, and because of that, there was no longer an easy way to replicate the development environment—the DuckDuckHack repos remained available (still do), but you can't pop over into Codio and play around with it. Furthermore, because Codio had been functioning as a sort of crutch to paper over the shortcomings in the onboarding/startup process for DuckDuckHack, there was never any pressure to make sure that contributors could easily get up and running without access to a Codio-based development environment.
It's interesting that, no matter how many times cloud-based Web IDEs have been attempted and failed to displace traditional, local development, people keep getting suckered into it, despite the history of observable downsides.
What's also interesting is the conflation of two things:
-
software that works by treating the Web browser as a ubiquitous, reliable interpreter (in a way that neither
/usr/local/bin/nodenor/usr/bin/python3are reliably ubiquitous)—NB: and running locally, just like Node or Python (orgo buildormake runor...)—and -
the idea that development toolchains aiming for "zero configuration and setup" should defer to and depend upon the continued operation of third-party servers
That is, even though the Web browser is an attractive target for its consistency (in behavior and availability), most Web IDE advocates aren't actually leveraging its benefits—they still end up targeting (e.g.)
/usr/local/bin/nodeand/usr/local/python3—except the executables in question are expected to run on some server(s) instead of the contributor's own machine. These browser-based IDEs aren't so browser-based after all, since they're just shelling out to some non-browser process (over RPC over HTTP). The "World Wide Wruntime" is relegated to merely interpreting the code for a thin client that handles its half of the transactions to/from said remote processes, which end up handling the bulk of the computing (even if that computing isn't heavyweight and/or the client code on its own is full of bloat, owing to the modern trends in Web design).It's sort of crazy how common it is to encounter this "mental slippery slope": "We can lean on the Web browser, since it's available everywhere!" → "That involves offloading it to the cloud (because that's how you 'do' stuff for the browser, right?)".
So: want to see an actual boom in collaborative development spurred by zero-configuration dev environments? The prescription is straightforward: make all these tools truly run in the browser. The experience we should all be shooting for resemble something like this: Step 1: clone the repo Step 2: double click README.html Step 3: you're off to the races—because project upstream has given you all the tools you need to nurture your desire to contribute
You can also watch this space for more examples of the need for an alternative take on working to actually manage to achieve the promise of increased collaboration through friction-free (or at least friction-reduced) development: * https://hypothes.is/search?q=%22the+repo+is+the+IDE%22 * https://hypothes.is/search?q=%22builds+and+burdens%22
-
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
We also tend to preferinformation we have seen more recently to informationwe learned a long time ago.
Does this effect have a name? references?
Apparently called the recency bias: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recency_bias which may be entangled with availability bias or heuristic.
Are both recency and availability biases the foundations for causing the Baader–Meinhof phenomenon or frequency bias?
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
what happens um when we're thinking about our inner states one of the things that we need to recognize is that our introspection when 00:22:54 we we become aware of our beliefs our desires and our hopes and our fears and so forth is all done through language and on the model of language when i decide that i believe that john dunn 00:23:07 gave a great talk this morning when i believe that hal roth is a great scholar of zen and when i believe that alan wallace gave us a beautifully inspirational talk about the role of practice and contemplation in the 00:23:19 understanding of the self and i introspect that way i'm using those sentences alan gave that great talk john gave us a great talk about pramana and so forth as models for my inner states and i'm not 00:23:32 doing that because i looked inside and saw little english sentences in my brain i'm looking i'm doing that by using language as a kind of introspective model that's a matter of self-interpretation 00:23:44 it's easy to forget that because it feels so immediate so language gives us the concepts that we use to think about the world but it is also the model for the concepts of our propositional attitudes like belief 00:23:58 desire knowledge and so forth and as a model we have to recognize that the model the map isn't the reality to go back to what john uh reminded us of he reminded us of earlier introspection in 00:24:11 terms of language gives us an interpretation it doesn't give us an independent reality that is being interpreted and when we think about the madhyamaka 00:24:23 of nagarjuna and chandrakiri we remember that to be empty is to be empty of any intrinsic nature and if we follow chandra charity as i suggested earlier that means that it is to exist only 00:24:37 dependent on conceptual imputation and what i am suggesting now is that all of our inner cognitive states that we introspect we encounter only through a conceptual imputation only through 00:24:50 interpretation only through language and that is they exist conventionally not intrinsically even though they might appear to us to exist just as we see 00:25:02 them and to do so intrinsically
Another key point:
Language is the tool we use for introspection and as Nagarjuna and Chandrakirti hold, are empty of intrinsic nature. All inner cognitive states that we introspect are attained only through linguistic conceptual imputation so can only exist conventionally and not intrinsically.
This underscores the importance of the symbolosphere, of symbols and language.
-
another aspect to cognitive illusion here is the illusion um that our sense perception is something that 00:22:02 is transparent and simply delivering us a world as a telescope does and not as a cognitive not as a kaleidoscope does as a consequence then the sense that we 00:22:15 know our own cognitive states directly and accurately through inner sense as well of outer sense has got to be a cognitive illusion as well are of the the sortals or the concepts that we use 00:22:28 in order to introspect are just as opaque to us as our senses are and give us just as a non-transparent access to our inner world as our senses give to the outer 00:22:42 world
Jay reiterates a key point: we are under the spell of a cognitive illusion whereby the concepts we use to introspect are as non-transparent to us as the cognitive faculties used to organize sensations.
-
the illusion that pervades our sense perception is that what we experience is something external to us that somehow 00:20:10 we've got a world that exists as it is independent of us and that we simply happen to be perfect world detectors and we wander through it detecting things just as they are
This is a key statement of our illusion. We sense that what we experience is the way the world actually is, not seeing that our bodies play a huge role in what we observe. We don't know what it's like to be a bat!
-
our mind functions as dharma yearly 00:19:43 emphasized as an instrument through which we have access to the world
the mind has faculties that construct our cognitions about the world.
-
when we attribute sensory experiences to 00:06:39 ourselves for instance like the experience of red or the experience of seeing blue the model is external properties and we think of there as being inner properties just like those external properties that somehow we are 00:06:52 um we are seeing immediately
This comment suggests a Color BEing Journey. How can we demonstrate in a compelling way that color is an attribute of the neural architecture of the person and NOT a property of the object we are viewing?
See Color Constancy Illusion here:
David Eagleman in WIRED interview https://hyp.is/go?url=http%3A%2F%2Fdocdrop.org%2Fvideo%2FMJBfn07gZ30%2F&group=world
Beau Lotto, TED Talk https://hyp.is/go?url=http%3A%2F%2Fdocdrop.org%2Fvideo%2Fmf5otGNbkuc%2F&group=world
Andrew Stockman, TEDx talk on how we see color: https://hyp.is/go?url=http%3A%2F%2Fdocdrop.org%2Fvideo%2F_l607r2TSwg%2F&group=world
Science shows that color is an experience of the subject, not a property of the object: https://youtu.be/fQczp0wtZQQ but what Jay will go on to argue, is that this explanation itself is part of the COGNITIVE IMMEDIACY OF EXPERIENCE that we also take for granted.
-
cognitive illusion and immediate experience perspectives 00:01:44 from buddhist philosophy
Title: cognitive illusion and immediate experience perspectives from buddhist philosophy Author: Jay L. Garfield Year: 2022
This is a very important talk outlining a number of key concepts that Stop Reset Go and Deep Humanity are built upon and also a rich source of BEing Journeys.
In brief, this talk outlines key humanistic (discoverable by a modern human being regardless of any cultural, gender, class, etc difference) concepts of Buddhist philosophy that SRG / DH embeds into its framework to make more widely accessible..
The title of the talk refers to the illusions that our own cognition produces of both outer and inner appearances because the mechanisms that produce them area opaque to us. Their immediacy feels as if they are real.
If what we sense and think is real is an illusion, then what is real? "Real" in this case implies ultimate truth. As we will see, Nagarjuna's denial of any argument that claims to be the ulitmate is denied. What is left after such a complete denial? Still something persists.
Tags
- Stop Reset Go
- Deep Humanity
- immediacy of experience
- SRG
- Beau Lotto
- BEing journey
- cognitive illusions
- David Eagleman
- cognitive science
- language
- DH
- color constancy
- symbolosphere
- What's it like to be a bat?
- Chandrakurti
- color illusion
- inner cognitive states
- Cognitive illusions
- color
- neuroscience
- Nagarjuna
- conceptual imputation.
- Jay Garfield
- Jay. L. Garfield
- Andrew Stockman
Annotators
URL
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
so here's a straightforward question what color are the strawberries in this photograph the red right wrong those strawberries are gray if you don't 00:00:12 believe me we look for one of the reddest looking patches on this image cut it out now what color is that it's great right but when you put it back on 00:00:25 the image it's red again it's weird right this illusion was created by a Japanese researcher named Akiyoshi Kitaoka and it hinges on something called color constancy it's an incredible visual 00:00:39 phenomenon by which the color of an object appears to stay more or less the same regardless of the lighting conditions under which you see it or the lighting conditions under which your brain thinks you're seeing it
Title: Why your brain thinks these strawberries are red Author: WIRED Date:2022
Color Constancy
Use this for BEing journey
-
-
-
i want to take you back to our lecture on cognitivism where we surveyed among other things the origins of this notion of a psychological subject within our inner architecture 00:05:52 that comes into being in 1896 john dewey wrote a very famous article called the reflex arc concept in psychology you may have missed it it's listed it's provided on 00:06:06 the page for cognitivism and what dewey was doing was surveying the very many very diverse uh research activities that were beginning to bring into being something like a 00:06:19 psychological science there was so many questions so many methods and a single theoretical construct had emerged that many people were leaning on to and was acting as a kind of a unified 00:06:32 construct with which notions of mind and body might be brought together that notion is the reflex arc now the reflex arc you may be familiar with from physiology if you touch something hot 00:06:45 then we can follow a physiological path from the receptors in the skin in this case if you touch a hot stove we can follow a very short path that goes through the spinal cord and immediately causes you 00:06:58 to move your hand away no thinking involved that's a reflex and you're familiar with the notion of reflex but that notion had been elaborated and was being developed by many people into a picture of the an account of the 00:07:11 embedding of the entire body and nervous system in the world john dewey was saying don't do that stop doing that it's a serious critique of this input output model and the 00:07:25 reflex arc starts with a stimulus and results in action and as a one-way throughput john dewey correctly said that an input output model reduces 00:07:40 the intervene the thing in the middle into a puppet there is no subjectivity possible here now this is a fundamental critique as the fundamental shift in perspective we're adopting in 00:07:53 this module which is to get away from the silly notion of the body and person and subject as being driven by inputs producing the 00:08:05 ghost of the cognitive sandwich there we go you've got the cognitive sandwich you've got sensation providing input you've got action on the output in between you have a great big mystery stuffed into the head it's very easy to make fun of this as 00:08:18 susan hurley does with her term cognitive sandwich it's much more difficult to make fun of exactly the same thing when we draw it like this there is an orthodox belief in our 00:08:30 society our society works on the assumption that there is the psychological subject who has inner processes of perception feeding into inner processes of higher cognition 00:08:43 all fueled by the world through senses and this model doesn't even have an output such constructive psychological representational stories typically 00:08:55 ignore action altogether so the cognitive sandwich may be ridiculous when we look at it in one way but it is also the most wide held belief in our society about the person and we 00:09:08 institute our laws our education systems our workplaces are built on this problematic model
In 1896, John Dewey wrote a famous paper called "The reflex arc concept in psychology". At that time, psychology was nascent and the reflex arc began to emerge as a framework to synthesis the many disparate findings.
the notion of the "cognitive sandwich" emerged which claimed that sensory inputs fed a mysterious cognitive function sandwiched between the input and motor system outputs.
Dewey said that the input output models relegates subjectivity to something trivial so cannot be correct.
This crude model still manifests in today's common belief that after sensing, there is a process of perception that feeds into higher cognition.
-
-
ocw.mit.edu ocw.mit.edu
-
This course is an introduction to computational theories of human cognition. Drawing on formal models from classic and contemporary artificial intelligence, we will explore fundamental issues in human knowledge representation, inductive learning and reasoning. What are the forms that our knowledge of the world takes?
When?
-
-
-
the 1911 paper by william morton wheeler is called the ant colony as an organism not a super organism because superorganism implies that nest mate would be the true organism
Check out the 1911 William Morton Wheeler paper on Ant Colonies as organisms. Does Wheeler actually call the colony an organism rather than a superorganism?
-
the six 00:48:41 six big systems i've mentioned can be viewed as a cognitive architecture it's the it's the means by which the society learns decides adapts and 00:48:54 and this society's efforts this is the third underlying position the society's efforts to learn decide and adapt and be viewed as being driven by an intrinsic purpose and that's really key also 00:49:08 because it's not just that we're learning deciding and adapting willy-nilly i mean i mean maybe it seems that way in the world you know in the sense we're so dysfunctional it kind of is billy nilly but 00:49:20 but what really matters is that we learn decide and adapt in relation to whatever intrinsic purpose we actually have as as a society as individuals in a 00:49:34 society it's that it's it's it's it's as i will use the the term uh maybe several times today it's solving problems that matter that really that really 00:49:45 matter that's what we're after
Second Proposition: The six thrusts or prmary societal systems are the cognitive architecture of the superorganism which it uses to sense the world
-
- Jun 2022
-
www.scientificamerican.com www.scientificamerican.com
-
Instead of hiking the trail yourself, the trees, rocks and moss move past you in flashes with no trace of what came before and no way to see what lies ahead.
Just as there are deficits like dyslexia in the literate world, are there those who have similar deficits relating to location in the oral world? What do these look like? What are they called specifically?
There are definitely memory deficits withing cognitive neuropsychology. Is there a comprehensive list one could look at?
Some people aren't as good at spatial orientation as others. Women are stereotyped as being less good at direction and direction finding.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
If we overlay the four steps of CODE onto the model ofdivergence and convergence, we arrive at a powerful template forthe creative process in our time.
The way that Tiago Forte overlaps the idea of C.O.D.E. (capture/collect, organize, distill, express) with the divergence/convergence model points out some primary differences of his system and that of some of the more refined methods of maintaining a zettelkasten.
 <small>Overlapping ideas of C.O.D.E. and divergence/convergence from Tiago Forte's book Building a Second Brain (Atria Books, 2022) </small>
<small>Overlapping ideas of C.O.D.E. and divergence/convergence from Tiago Forte's book Building a Second Brain (Atria Books, 2022) </small>Forte's focus on organizing is dedicated solely on to putting things into folders, which is a light touch way of indexing them. However it only indexes them on one axis—that of the folder into which they're being placed. This precludes them from being indexed on a variety of other axes from the start to other places where they might also be used in the future. His method requires more additional work and effort to revisit and re-arrange (move them into other folders) or index them later.
Most historical commonplacing and zettelkasten techniques place a heavier emphasis on indexing pieces as they're collected.
Commonplacing creates more work on the user between organizing and distilling because they're more dependent on their memory of the user or depending on the regular re-reading and revisiting of pieces one may have a memory of existence. Most commonplacing methods (particularly the older historic forms of collecting and excerpting sententiae) also doesn't focus or rely on one writing out their own ideas in larger form as one goes along, so generally here there is a larger amount of work at the expression stage.
Zettelkasten techniques as imagined by Luhmann and Ahrens smooth the process between organization and distillation by creating tacit links between ideas. This additional piece of the process makes distillation far easier because the linking work has been done along the way, so one only need edit out ideas that don't add to the overall argument or piece. All that remains is light editing.
Ahrens' instantiation of the method also focuses on writing out and summarizing other's ideas in one's own words for later convenient reuse. This idea is also seen in Bruce Ballenger's The Curious Researcher as a means of both sensemaking and reuse, though none of the organizational indexing or idea linking seem to be found there.
This also fits into the diamond shape that Forte provides as the height along the vertical can stand in as a proxy for the equivalent amount of work that is required during the overall process.
This shape could be reframed for a refined zettelkasten method as an indication of work
Forte's diamond shape provided gives a visual representation of the overall process of the divergence and convergence.
But what if we change that shape to indicate the amount of work that is required along the steps of the process?!
Here, we might expect the diamond to relatively accurately reflect the amounts of work along the path.
If this is the case, then what might the relative workload look like for a refined zettelkasten? First we'll need to move the express portion between capture and organize where it more naturally sits, at least in Ahren's instantiation of the method. While this does take a discrete small amount of work and time for the note taker, it pays off in the long run as one intends from the start to reuse this work. It also pays further dividends as it dramatically increases one's understanding of the material that is being collected, particularly when conjoined to the organization portion which actively links this knowledge into one's broader world view based on their notes. For the moment, we'll neglect the benefits of comparison of conjoined ideas which may reveal flaws in our thinking and reasoning or the benefits of new questions and ideas which may arise from this juxtaposition.

This sketch could be refined a bit, but overall it shows that frontloading the work has the effect of dramatically increasing the efficiency and productivity for a particular piece of work.
Note that when compounded over a lifetime's work, this diagram also neglects the productivity increase over being able to revisit old work and re-using it for multiple different types of work or projects where there is potential overlap, not to mention the combinatorial possibilities.
--
It could be useful to better and more carefully plot out the amounts of time, work/effort for these methods (based on practical experience) and then regraph the resulting power inputs against each other to come up with a better picture of the efficiency gains.
Is some of the reason that people are against zettelkasten methods that they don't see the immediate gains in return for the upfront work, and thus abandon the process? Is this a form of misinterpreted-effort hypothesis at work? It can also be compounded at not being able to see the compounding effects of the upfront work.
What does research indicate about how people are able to predict compounding effects over time in areas like money/finance? What might this indicate here? Humans definitely have issues seeing and reacting to probabilities in this same manner, so one might expect the same intellectual blindness based on system 1 vs. system 2.
Given that indexing things, especially digitally, requires so little work and effort upfront, it should be done at the time of collection.
I'll admit that it only took a moment to read this highlighted sentence and look at the related diagram, but the amount of material I was able to draw out of it by reframing it, thinking about it, having my own thoughts and ideas against it, and then innovating based upon it was incredibly fruitful in terms of better differentiating amongst a variety of note taking and sense making frameworks.
For me, this is a great example of what reading with a pen in hand, rephrasing, extending, and linking to other ideas can accomplish.
-
If you ignore that inner voice of intuition, over time it will slowlyquiet down and fade away. If you practice listening to what it is tellingyou, the inner voice will grow stronger. You’ll start to hear it in allkinds of situations. It will guide you in what choices to make andwhich opportunities to pursue. It will warn you away from people andsituations that aren’t right for you. It will speak up and take a standfor your convictions even when you’re afraid.I can’t think of anything more important for your creative life—andyour life in general—than learning to listen to the voice of intuitioninside. It is the source of your imagination, your confidence, and yourspontaneity
While we have evolved a psychological apparatus that often gives us good "gut feelings" (an actual physical "second brain"), we should listen careful to them, but we should also learn to think about, analyze, and verify these feelings so we don't fall prey to potential cognitive biases.
Tags
- trust but verify
- innovation
- productivity
- cognitive bias
- knowledge work
- behavioral economics
- compounding value
- gut feelings
- putting in the work
- efficiency
- commonplace books vs. zettelkasten
- C.O.D.E.
- work
- Tiago Forte
- writing
- zettelkasten
- writing for understanding
- second brain
- divergence/convergence
- visualizations
- system one versus system two
- imitation for innovation
- commonplace books
- misinterpreted-effort hypothesis
- time
Annotators
-
-
-
you get so used to the way things are you don't think of the obvious next step and you know that can be so frustrating
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
the human brain is an energy hog like and you can learn a lot about a lot of our uh biases and problems from the kinds of shortcuts that the brain takes 00:06:41 in the name of energy conservation well it looks like estimating group consensus is one of those shortcuts right because all it's equal your brain tends to assume that the loudest voices repeated 00:06:53 the most are the majority and and i think about that i think wow that doesn't seem like a good a good shortcut at all but i guess if you go back and f through evolution and when most of our time was spent and like 00:07:05 seeing like the dumbar number kind of you know groups it probably it obviously had to work well enough right to just be here with us but now when you think about with social media 00:07:18 and these massive imaginary communities like nations where you're never going to meet more than a tiny tiny percentage of the people in your group that shortcut becomes problematic um and 00:07:31 we can talk about it like i mean social media in particular makes it very very easy to distort perceived group consensus
This is the key problem that makes current social media dangerous, it can be easily gamed due to this evolutionary shortcut of the brain, the fast system of biases aka Daniel Kahneman's research.
-
- May 2022
-
blog.webb.page blog.webb.page
-
I think adding automated deployments would be a nice quality-of-life feature and would definitely encourage me to write more. Currently, I have to upload a new text file to my server and refresh the pm2 job.
Is "automated deployments" really the solution?
-
-
Local file Local file
-
new result, test it against each of your twelve problems to seewhether it helps. Every once in a while there will be a hit, andpeople will say, “How did he do it? He must be a genius!”
You have to keep a dozen of your favorite problems constantly present in your mind, although by and large they will lay in a dormant state. Every time you hear or read a new trick or a
Gian-Carlo Rota, Indiscrete Thoughts (Boston: Birkhäuser Boston, 1997), 202.
Richard Feynman indicated in an interview that he kept a dozen of his favorite problems at the top of his mind. As he encountered new results and tricks, he tried applying them to those problems in hopes of either solving them or in coming up with new ideas. Over time by random but combinatorial chance, solutions or ideas would present themselves as ideas were juxtaposed.
One would suspect that Feynman hadn't actually read Raymond Llull, but this technique sounds very similar to the Llullan combinatorial arts from centuries earlier, albeit in a much more simplified form.
Can we find evidence of Feynman having read or interacted with Llull? Was it independently created or was he influenced?
I had an example of this on 2022-05-28 in Dan Allosso's book club on Equality in the closing minutes where a bit of inspiration hit me to combine the ideas of memes, evolution, and Indigenous knowledge and storytelling to our current political situation. Several of them are problems and ideas I've been working with over years or months, and they came together all at once to present a surprising and useful new combination. #examples
Link this also to the idea of diffuse thinking as a means of solving problems. One can combine the idea of diffuse thinking with combinatorial creativity to super-charge one's problem solving and idea generation capacity this way. What would one call this combination? It definitely needs a name. Llullan combinatorial diffusion, perhaps? To some extent Llull was doing this already as part of his practice, it's just that he didn't know or write explicitly about the diffuse thinking portion (to my knowledge), though this doesn't mean that he wasn't the beneficiary of it in actual practice, particularly when it's known that many of his time practiced lectio divina and meditated on their ideas. Alternately meditating on ideas and then "walking away" from them will by force cause diffuse thinking to be triggered.
Are there people for whom diffuse thinking doesn't work from a physiological perspective? What type of neurodiversity does this cause?
-
.Adopting the habit of knowledge capture has immediate benefitsfor our mental health and peace of mind. We can let go of the fearthat our memory will fail us at a crucial moment. Instead of jumpingat every new headline and notification, we can choose to consumeinformation that adds value to our lives and consciously let go of therest.
Immediate knowledge capture by highlighting, annotating, or other means when taking notes can help to decrease cognitive load. This is similar to other productivity methods like quick logging within a bullet journal system, writing morning pages, or Getting Things Done (GTD). By putting everything down in one place, you can free your mind of the constant need to remember dozens of things. This frees up your working memory to decrease stress as you know you've captured the basic idea for future filtering, sorting, and work at a later date.
Tags
- bullet journals
- Richard Feynman
- diffuse thinking
- productivity
- morning pages
- flâneur
- lectio divina
- GTD
- cross-disciplinary studies
- information processing
- note taking
- combinatorial creativity
- neurodiversity
- Llullan combinatorial arts
- meditation
- psychology
- quotes
- cognitive neuropsychology
- cognitive load
- Feynman's 12 Favorite Problems
- Llullan combinatorial diffusion
Annotators
-
-
link.springer.com link.springer.com
-
Interesting sounding high level paper about the limits and constraints on general intelligence and how this might relate to the struggles AI/ML research has had historically.
-
-
www.usmcu.edu www.usmcu.edu
-
Humanity’s COG is assessed as its deep frames, prevalent and dominant worldviews that influence governance decisions across the public and private sectors (figure 3). Simply put, CEC presents a new type of threat—a Frankenstein-like killing and destruction phenomenon—that humanity struggles to conceive or perceive.
It would benefit the description by including the umwelt in the perception lens and cognitive biases and cognitive constructions in the cognitive lens.
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
There's a related phenomenon/paradox: the superinferiority of "native" applications.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.buildingasecondbrain.com www.buildingasecondbrain.com
-
The student doesn’t have a strong preference for any of these archetypes. Their notes serve a clear purpose that’s often based on a short-term priority (e.g, writing a paper or passing a test), with the goal to “get it done” as simply as possible.
The typical student note taking method of transcribing, using (or often not using at all), and keeping notes is doomed to failure.
Many students make the mistake of not making their own actual notes. By this I don't mean they're not writing information down. In fact many are writing information down, but we can't really call these notes. Notes by definition ought to transform something seen or heard into one's own words. Without the transformation, these students think that they're taking notes, but in reality they're focusing their efforts on being transcriptionists. They're attempting to capture something for later consumption. This is a deadly trap! By only transcribing, they're not taking advantage of transforming information by putting ideas down in their own words to test their understanding. Often worse, even if they do transcribe notes, they don't revisit them. If they do revisit them, they're simply re-reading them and not actively working with them. Only re-reading them will lead to the illusion that they're learning something when in fact they're falling into the mere-exposure effect.
Students who are acting as transcriptionists would be better off simply reading a textbook and taking notes directly from that.
A note that isn't revisited or revised, may as well be a note not taken. If we were to consider a spectrum of useful, valuable, and worthwhile notes, these notes would be at the lowest end of the spectrum.
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
That said, I've since realized I was wrong of course. Trying to maintain projects that haven't been touched in more than a year led to hours of fixing dependency issues.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
datagubbe.se datagubbe.se
-
Linux (and Wine) may prove to be an alternative here.
If what we're discussing here is the decision to no longer opt in to playing along with the "Western" regime for IP, then why would they limit themselves to Linux and Wine—two products of attempts to play by the rules of the now-deprioritized regime? Why wouldn't they react by shamelessly embracing "pirated" forms of the (Windows) systems that they clearly have a revealed preference for? If hackability is the issue*, then that's ameliorated by the fact that NT/2000 source code and XP source code was leaked awhile ago—again: the only thing stopping anyone from embracing those before was a willingness to play along and recognize that some game states are unreachable when (artificially) restricting one's own options to things that are considered legal moves. But that's not important anymore, right?
* i.e. malleability, and it's not obvious that it should be—it wasn't already, so what does this change?
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
State exact versions and checksums of all deps plus run your own server hosting the deps
In other words, do a lot of work to route around the problems introduced by the way that using npm routes around your existing version control system.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
all the exception handling these packages do
These packages don't/can't do the amount of exception handling suggested by this comment.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
The events list is created with JS, yes. But that's the only thing on the whole site (~25 pages) that works that way.Here's another site I maintain this way where the events list is plain HTML: https://www.kingfisherband.com
There's an unnecessary dichotomy here between uses JS and page is served as HTML. There's a middle ground, where the JS can do the same thing that it does now, but it only does so at edit time—in the post author's own browser, but not in others'. Once the post author is ready to publish an update, the client-side generated content is captured as plain HTML, and then they upload that. It still "uses JS", but crucially it doesn't require the visitor to have their browser do it (and for it to be repeated N times, once per page visit)...
-
- Apr 2022
-
datastation.multiprocess.io datastation.multiprocess.io
-
I'm not sure what $name is
This post is filled with programming/debugging missteps that are the result of nothing other than overlooking what's already right in front of the person who's writing.
-
-
www.irrodl.org www.irrodl.org
-
The consequences of student frustration (Borges, 2005) can generate a load that has to be borne by all the agents involved in the learning experiences: students, teachers, and institutions.
-
-
-
The way technologies like fMRI are applied is aproduct of our brainbound orientation; it has not seemed odd or unusual toexamine the individual brain on its own, unconnected to others.
In part because of modalities of studying the brain using methods like fMRI where the images are of an individual's head, we focus too much and too exclusively on single brains bound to individuals rather than on brains working in concert.
Greater flexibilities in tools and methods should help do studies of humans working in concert.
Link this to the anecdote:
I recall a radiology test within a medical school setting in which students were asked to diagnose an x-ray of a human patient's skull. Most either guessed small hairline fractures in the skull or that there was nothing wrong with the patient.
Can you diagnose the patient?
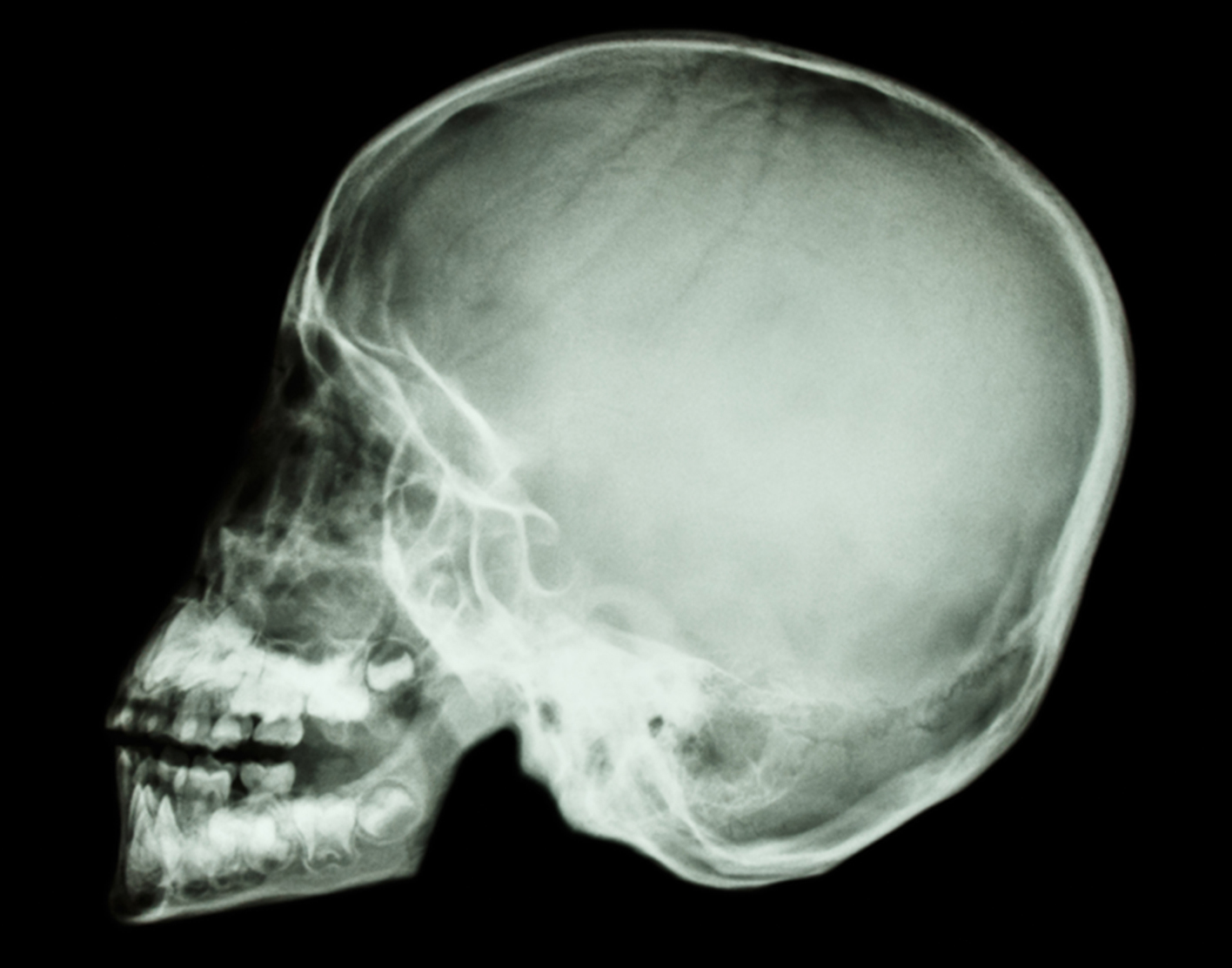
Almost all the students failed the question, and worse felt like idiots when the answer was revealed: the patient must be dead because the spinal column and the rest of the body are not attached. Compare:

-
imitation more generally. Emmanuel Roze hasfound that the experience of imitating patients makes the young doctors he trainsmore empathetic
Imitation can potentially help one become more empathetic.
Is there a relationship between this effect and one's mirror neurons?
Donald J. Trump is well known for is sad impersonation of impaired and disabled people. Obviously he has no empathy for them and it's unlikely that his re-enactments will create empathy for him. Is this a result of a neurological deficit on his part?
-
In these sessions, students didn’t listen to a description ofcomputer science concepts, or engage in a discussion about the work performedby computer scientists; they actually did the work themselves, under the tutors’close supervision.
The process seen in cognitive apprenticeships seems more akin to the sorts of knowledge transfer done in primary oral indigenous cultures by passing down stories and performing (song, dance, art, etc.) knowledge.
It shouldn't be surprising that cognitive apprenticeships work well given their general use by oral cultures over millennia.
link to: Writing out answers will show gaps in knowledge Performing actions will show gaps in knowledge
-
crucial difference between traditional apprenticeships and modern schooling: inthe former, “learners can see the processes of work,” while in the latter, “theprocesses of thinking are often invisible to both the students and the teacher.”Collins and his coauthors identified four features of apprenticeship that could beadapted to the demands of knowledge work: modeling, or demonstrating the taskwhile explaining it aloud; scaffolding, or structuring an opportunity for thelearner to try the task herself; fading, or gradually withdrawing guidance as thelearner becomes more proficient; and coaching, or helping the learner throughdifficulties along the way.
This is what’s known as a cognitive apprenticeship, a term coined by Allan Collins, now a professor emeritus of education at Northwestern University. In a 1991 article written with John Seely Brown and Ann Holum, Collins noted a
In a traditional apprenticeship, a learner watches and is able to imitate the master process and work. In a cognitive apprenticeship the process of thinking is generally invisible to both the apprentice and the teacher. The problem becomes how to make the thinking processes more tangible and visible to the learner.
Allan Collins, John Seely Brown, and Ann Holum identified four pedagogical methods in apprenticeships that can also be applied to cognitive apprenticeships: - modeling: demonstrating a task while focusing on describing and explaining the steps and general thinking about the problem out loud - scaffolding: structuring a task to encourage and allow the learner the ability to try it themself - fading: as the learner gains facility and confidence in the process, gradually removing the teacher's guidance - coaching: as necessary, the teacher provides tips and suggestions to the learner to prompt them through potential difficulties
Tags
- thinking with peers
- skulls
- gaps in knowledge
- cognitive bias
- knowledge work
- orality
- fading
- mirror neurons
- fMRI
- immitation
- performing knowledge
- pedagogy
- coaching
- apprenticeships
- knowledge scaffolding
- Donald J. Trump
- orality and memory
- radiology
- information gaps
- x-rays
- empathy
- anatomy
- cognitive neuropsychology
- cognitive apprenticeships
- modeling behavior
- individuals vs. groups
Annotators
-
-
Local file Local file
-
allow Jakobson to explain why the first person and its cognates are both thelast linguistic acquisition of the child and the first linguistic loss of the aphasiac.Jakobson’s first essays to be translated into French came out in 1963. Barthesrefers to them, the very same year, in the preface to the Critical Essays where heidentifies (if one may say so) both positively and negatively with those two invalidspeaking subjects whom, for not having yet (or having no longer) access to thefirst person, he promotes as models or examples for the writer, granted one differ-ence: the writer takes responsibility for not uttering the “I” that both the childand the aphasiac are constitutionally unable to use.
Is it broadly true that the first person and cognates are the last acquisitions of children and among the first losses of aphasiacs?
-
-
small-tech.org small-tech.orgHome1
-
Ongoing research Building on our work with Site.js, we’ve begun working on two interrelated tools: NodeKit The successor to Site.js, NodeKit brings back the original ease of buildless web development to a modern stack based on Node.js that includes a superset of Svelte called NodeScript, JSDB, automatic TLS support, WebSockets, and more.
"How much of your love of chocolate has to do with your designs for life that are informed by your religious creed? Is it incidental or essential?"
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
What do we know about Covid’s impact on the brain? (2022, March 9). The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2022/mar/09/covid-coronavirus-brain-study-eric-topol
-
-
quillette.com quillette.com
-
Interestingly, though, expertise appears to influence persuasion only if the individual is identified as an expert before they communicate their message. Research has found that when a person is told the source is an expert after listening to the message, this new information does not increase the person’s likelihood of believing the message.
-
-
www.donnelly-house.net www.donnelly-house.net
-
So far it works great. I can now execute my bookmarklets from Twitter, Facebook, Google, and anywhere else, including all https:// "secure" websites.
In addition to the note above about this being susceptible to sites that deny execution of inline scripts, this also isn't really solving the problem. At this point, these are effectively GreaseMonkey scripts (not bookmarklets), except initialized in a really roundabout way...
-
- Mar 2022
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Delz, Louise Aurora Katharina, Keith Gaynor, Ellen Somers, Rachel O. Connor, and Luisa Schmieder. ‘A CONFIRMATORY FACTOR ANALYSIS OF A COGNITIVE MODEL OF COVID-19 RELATED DISTRESS’. PsyArXiv, 18 February 2022. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/zmf5d.
-
-
-
what i don't really do 00:48:10 is having a checklist like going through possible biases i don't feel that's very helpful i think it's important to keep them in mind but i think it's more about detecting okay 00:48:25 what kind of question is [Music] the author trying to answer
Understanding the sorts of questions an author is looking at and attempting to answer are often more important than going through a checklist of biases which may come into play.
-
give the text your reading the opportunity to tell you something new and something 00:49:02 you have not expected so i'm worried a little bit of having fixed [Music] categories to look through 00:49:16 text because it might turn every text into something that is um already fitting your categories instead of expanding them 00:49:26 or adding to them
Coming to a text with too rigid a set of questions or preconceived categories may cause you to be blinded by what you expect to get out of it rather than allowing the text to surprise you with new and interesting insights you may not have anticipated.
-
-
matt.life matt.life
-
it's usually due to the misapplication of healthy open source principles
The effect of handling open source the way it's popularly practiced on GitHub does not get nearly enough scrutiny for its role in e.g. maintainer burnout. Pretty much every project I see on GitHub does things that are obviously bad—or at least it should be obvious*—and neither are they sustainable, nor even a particularly good way to try to get work done, assuming that that's your imperative. It is probably the case, however, that that assumption is a bad one.
* I've slowly come to realize and accept that this stuff is not obvious to lots of people, because it's all they know—whether that means that that should affect whether its negative consequences are obvious is something that I'm inclined heavily to argue that "no, it shouldn't affect it; it should still be obvious that it's bad even then", but empirically, it seems that my instinct is wrong.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Arechar, A. A., Allen, J. N. L., berinsky, a., Cole, R., Epstein, Z., Garimella, K., … Rand, D. G. (2022, February 11). Understanding and Reducing Online Misinformation Across 16 Countries on Six Continents. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/a9frz
-
-
-
Halilova, J. G., Fynes-Clinton, S., Green, L., Myerson, J., Wu, J., Ruggeri, K., … Rosenbaum, R. (2022, January 28). Short-sighted decision-making by those not vaccinated against COVID-19. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/6uqky
-
-
-
Washington State mathteacher Brendan Jeffreys turned to gesture as a way of easing the mental loadcarried by his students, many of whom come from low-income households,speak English as a second language, or both. “Academic language—vocabularyterms like ‘congruent’ and ‘equivalent’ and ‘quotient’—is not something mystudents hear in their homes, by and large,” says Jeffreys, who works for theAuburn School District in Auburn, a small city south of Seattle. “I could see thatmy kids were stumbling over those words even as they were trying to keep trackof the numbers and perform the mathematical operations.” So Jeffreys devised aset of simple hand gestures to accompany, or even temporarily replace, theunfamiliar terms that taxed his students’ ability to carry out mental math.
Mathematics can often be more difficult compared to other subjects as students learning new concepts are forced not only to understand entirely new concepts, but simultaneously are required to know new vocabulary to describe those concepts. Utilizing gestures to help lighten the cognitive load of the new vocabulary to allow students to focus on the concepts and operations can be invaluable.
-
A familiar example ofsuch offloading is the way young children count on their fingers when workingout a math problem. Their fingers “hold” an intermediate sum so that their mindsare free to think about the mathematical operation they must execute (addition,subtraction) to reach the final answer.
Children counting on their fingers is an example of offloading cognitive load by using proprioception.
Different cultures use different finger sequences (particularly for the number 3) for counting up.
-
designed gestures can lighten our mentalload.
Designed (or intentional) gestures can function to lighten the cognitive load of teaching by engaging multiple pathways simultaneously.
-
Research shows that moving our hands advances our understanding ofabstract or complex concepts, reduces our cognitive load, and improves ourmemory.
movement and gesture as a mnemonic device
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Agrawal, M., Peterson, J., Cohen, J. D., & Griffiths, T. (2022). Stress, Intertemporal Choice, and Mitigation Behavior During the COVID-19 Pandemic. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/ureqg
-
-
www.psychologytoday.com www.psychologytoday.com
-
Newton arranged an experiment in which one person — a “tapper” — was asked to tap out the melody of a popular song, while another person — the “listener” — was asked to identify it. The tappers assumed that their listeners would correctly identify about 50% of their melodies; they were amazed to learn that the listeners only got about one out of 40 songs correct. To the tappers, their melodies sounded perfectly clear and obvious, but the listeners heard no music, no instrumentation in their heads — only the muffled noise of a finger tapping on a table.
An example of the curse of knowledge effect.
-
- Feb 2022
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Schreiber, M. (2022, February 18). Covid infection increases risk of mental health disorders, study finds. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/feb/18/covid-infection-increases-risk-mental-health-disorder-study
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Kevin Courtney #NEU💝NHS. (2022, January 5). Ventilation isn’t just for Covid.... ...It’s for Education This study looks at the impact of CO2 not just as a marker of pollution but as a pollutant in itself. It shows that as CO2 rises above 700/800 ppm cognitive function begins to be impaired https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/27662232/4892924.pdf?sequence=1&fbclid=IwAR2kWIHIJfssa_sw72MD6W1hnkDvSm4bikK5FOLxwQxhjYLEYjfPCfzXz3E [Tweet]. @cyclingkev. https://twitter.com/cyclingkev/status/1478778857536860170
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Read for Understanding
Ahrens goes through a variety of research on teaching and learning as they relate to active reading, escaping cognitive biases, creating understanding, progressive summarization, elaboration, revision, etc. as a means of showing and summarizing how these all dovetail nicely into a fruitful long term practice of using a slip box as a note taking method. This makes the zettelkasten not only a great conversation partner but an active teaching and learning partner as well. (Though he doesn't mention the first part in this chapter or make this last part explicit.)
-
Reading, especially rereading, caneasily fool us into believing we understand a text. Rereading isespecially dangerous because of the mere-exposure effect: Themoment we become familiar with something, we start believing wealso understand it. On top of that, we also tend to like it more(Bornstein 1989).
The mere-exposure effect can be dangerous when rereading a text because we are more likely to falsely believe we understand it. Robert Bornstein's research from 1989 indicates that we will tend to like the text more, which can pull us into confirmation bias.
Bornstein, Robert F. 1989. “Exposure and Affect: Overview and Meta-Analysis of Research, 1968-1987.” Psychological Bulletin 106 (2): 265–89.
-
psychologists call the mere-exposure effect: doing something many times makes us believe wehave become good at it – completely independent of our actualperformance (Bornstein 1989). We unfortunately tend to confusefamiliarity with skill.
The mere-exposure effect leads us to confuse familiarity with a process with actual skill.
-
Our brains work not that differently in terms of interconnectedness.Psychologists used to think of the brain as a limited storage spacethat slowly fills up and makes it more difficult to learn late in life. Butwe know today that the more connected information we alreadyhave, the easier it is to learn, because new information can dock tothat information. Yes, our ability to learn isolated facts is indeedlimited and probably decreases with age. But if facts are not kept
isolated nor learned in an isolated fashion, but hang together in a network of ideas, or “latticework of mental models” (Munger, 1994), it becomes easier to make sense of new information. That makes it easier not only to learn and remember, but also to retrieve the information later in the moment and context it is needed.
Our natural memories are limited in their capacities, but it becomes easier to remember facts when they've got an association to other things in our minds. The building of mental models makes it easier to acquire and remember new information. The down side is that it may make it harder to dramatically change those mental models and re-associate knowledge to them without additional amounts of work.
The mental work involved here may be one of the reasons for some cognitive biases and the reason why people are more apt to stay stuck in their mental ruts. An example would be not changing their minds about ideas of racism and inequality, both because it's easier to keep their pre-existing ideas and biases than to do the necessary work to change their minds. Similar things come into play with respect to tribalism and political party identifications as well.
This could be an interesting area to explore more deeply. Connect with George Lakoff.
-
Just followyour interest and always take the path that promises the mostinsight.
What specific factors does one evaluate for determining what particular paths will provide actual (measurable) insight?
Most people have a personal gut reaction about which directions to go in heuristically, but can these heuristics be broken down explicitly to enable better evaluating them? How can they be used to avoid cognitive biases?
Tags
- associative memory
- understanding
- teaching
- tribalism
- gut reactions
- cognitive bias
- elaboration
- familiarity
- inequality
- learning
- effects
- networked thought
- cognitive dissonance
- open questions
- mere-exposure effect
- George Lakoff
- pedagogy
- reading practices
- heuristics
- insight
- rereading
- mental models
- counterintuitive pedagogy
- confirmation bias
- identity
- Robert Bornstein
- psychology
- skill
- cognitive load
- progressive summarization
- racism
- political affiliation
Annotators
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Research is needed to determine the situations in which the redundancy principle does not hold
p. 144-145
The authors describe limits to the research (circa 2016) as follows: 1. Kinds of learners, 2. kinds of material, and 3. kinds of presentation methods. Each of these situations present interesting possibilities for research related to the use of closed captions used by first-year law students while watching course-related videos.
When considering how "kinds of learners" might be relevant, the authors ask how redundant on-screen text might hurt or help non-native speakers of a language or learners with very low prior knowledge. It is probably reasonable to consider first-year law students as having "very low prior knowledge". Is there any sense in which those same students could be understand as having overlapping characteristics with TBD
-
Principle 2: Consider Adding On‐Screen Text to Narration in Special Situations
p. 139-141
Clark and Mayer describe a key exception to the first principle they describe. One of the special situations they describe consists of when a learner must "exert greater cognitive effort to comprehend spoken text rather than printed text" (p. 140). This could be when the verbal material is complex and challenging, such as when learners are learning another language or when terminology is challenging such as might be encountered in scientific, technical, or legal(?) domains (p. 141).
[P]rinting unfamiliar technical terms on the screen may actually reduce cognitive processing because the learner does not need to grapple with decoding the spoken words.
However, it may be necessary to ensure that video is slow-paced or learner-controlled under circumstances where both audio narration and on-screen text are provided. Mayer, Lee, and Peebles (2014) found that when video is fast-paced, redundant text can cause cognitive overload, even when learners are non-native speakers.
Mayer, R. E., Lee, H., & Peebles, A. (2014). Multimedia Learning in a Second Language: A Cognitive Load Perspective. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 28(5), 653–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/acp.3050
-
boundary conditions.
p. 131-132
Clark and Mayer provide a brief summary of the boundary conditions, the situations in which learners benefit from the use redundant on-screen text. These situations include adding printed text when 1) there are no graphics, 2) the presentation rate of the on-screen text is slow or learner-controlled, 3) the narration includes technical or unfamiliar words, and the 3) on-screen text is shorter than the audio narration.
The first three conditions described bear some similarity to closed caption use by students in legal education watching class lecture videos, especially students in first-year courses. Typically, the students are viewing videos with very few detailed graphics, they have control over the speed, pause, review, and advance features of the video player, and the narration provides numerous legal terms.
Although closed captions are intended for hard of hearing and deaf viewers, they may have some benefits for other learners if the boundary conditions described by the authors turn out to be true. Dello Stritto and Linder (2017) shared findings from a large survey of post-secondary students reporting that a range of students found closed captions to be helpful.
Dello Stritto, M. E., & Linder, K. (2017). A Rising Tide: How Closed Captions Can Benefit All Students. Educause Review Online. https://er.educause.edu:443/articles/2017/8/a-rising-tide-how-closed-captions-can-benefit-all-students
-
graphics using words in both on‐screen text and audio narration in which the audio repeats the text. We call this technique redundant on‐screen text because the printed text (on‐screen text) is redundant with the spoken text (narration or audio).
Clark and Mayer provide a definition of redundant: Graphics accompanied by words in both on-screen text and audio narration in which that text is repeated. p. 131
The authors go on to provide guidance about concurrent graphics, audio, and on-screen text. Based upon the research that they summarize in Chapter Seven, they advise instructors not to add printed text to an on screen graphic.
p. 131
-
-
jamanetwork.com jamanetwork.com
-
Heesakkers, H., van der Hoeven, J. G., Corsten, S., Janssen, I., Ewalds, E., Simons, K. S., Westerhof, B., Rettig, T. C. D., Jacobs, C., van Santen, S., Slooter, A. J. C., van der Woude, M. C. E., van den Boogaard, M., & Zegers, M. (2022). Clinical Outcomes Among Patients With 1-Year Survival Following Intensive Care Unit Treatment for COVID-19. JAMA, 327(6), 559–565. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.0040
-
-
every.to every.to
-
I don't think it's a surprise to anyone to know that there are certain activities that help create that space, and it’s been widely commented upon. Doing the dishes, walking the dog, cleaning the house – you need to be doing something.For me, pruning trees in our olive grove is perfect. It takes a little bit of attention, but not that much attention.
This is related to the idea of diffuse thinking caused by taking breaks or doing things that don't require extreme concentration. Flaneuring... walking, etc.
You want an activity that requires a little bit of attention but not too much attention. Doing dishes, walking, errands, etc. are good examples.
Relate this to the
-
-
therebooting.substack.com therebooting.substack.com
-
a bias toward bad news
Is there a more technical term for the bias towards bad news?
-
- Jan 2022
-
-
Current approaches to improving digital well-being also promote tech solutionism, or the presumption that technology can fix social, cultural, and structural problems.
Tech solutionism is the presumption that technology (usually by itself) can fix a variety of social, cultural, and structural problems.
It fits into a category of problem that when one's tool is a hammer then every problem looks like a nail.
Many tech solutionism problems are likely ill-defined to begin with. Many are also incredibly complex and difficult which also tends to encourage bikeshedding, which is unlikely to lead us to appropriate solutions.
-
-
nationalpost.com nationalpost.com
-
Blackwell, T. (2022, January 18). Living for the moment: Study points to cognitive differences in people who are vaccine hesitant. National Post. https://nationalpost.com/health/living-for-the-moment-study-points-to-cognitive-differences-in-people-who-are-vaccine-hesitant
-
-
joeldare.com joeldare.com
-
it’s insecure unless the credentials are served over an encrypted HTTPS connection
The same is true for login systems that use cookies, but no one cites that as a downside. There's an asymmetric standard being applied to HTTP native authentication.
-
-
learn-us-east-1-prod-fleet01-xythos.content.blackboardcdn.com learn-us-east-1-prod-fleet01-xythos.content.blackboardcdn.com
-
Most of us simply take it for granted that ‘Western’observers, even seventeenth-century ones, are simply an earlierversion of ourselves;
It is likely a good broad generality that from a historical perspective, those looking at people from the past do so by considering them simply an earlier version of ourselves.
This sort of isocultural cognitive bias is something to be very cognizant of particularly in cases without extensive context as it is likely to cause massive context collapse.
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
The study of cognitive development suffers from a deep theoretical tension – one with ancient philosophical roots.
This could've been a good place to allow liberal arts folx some point of entry. Alas.
-
-
www.biorxiv.org www.biorxiv.org
-
Fernandez-Castaneda, A., Lu, P., Geraghty, A. C., Song, E., Lee, M.-H., Wood, J., Yalcin, B., Taylor, K. R., Dutton, S., Acosta-Alvarez, L., Ni, L., Contreras-Esquivel, D., Gehlhausen, J. R., Klein, J., Lucas, C., Mao, T., Silva, J., Pena-Hernandez, M., Tabachnikova, A., … Monje, M. (2022). Mild respiratory SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause multi-lineage cellular dysregulation and myelin loss in the brain (p. 2022.01.07.475453). https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.07.475453
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. (2022, January 4). “Importantly, higher study quality was associated with lower prevalence of all symptoms, except loss of smell & cognitive symptoms” ....as someone who studies cognition I didn’t find that as reassuring as possibly intended... [Tweet]. @SciBeh. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1478341731707981829
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Krueger, P., Callaway, F., Gul, S., Griffiths, T., & Lieder, F. (2022). Discovering Rational Heuristics for Risky Choice. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/mg7dn
-
- Dec 2021
-
learn-us-east-1-prod-fleet01-xythos.content.blackboardcdn.com learn-us-east-1-prod-fleet01-xythos.content.blackboardcdn.com
-
When we simply guess as to whathumans in other times and places might be up to, we almostinvariably make guesses that are far less interesting, far less quirky– in a word, far less human than what was likely going on.
Definitely worth keeping in mind, even for my own work. Providing an evidential structure for claims will be paramount.
Is there a well-named cognitive bias for the human tendency to see everything as nails when one has a hammer in their hand?
-
‘What is it about the ancients,’ Pinker asks at one point, ‘that theycouldn’t leave us an interesting corpse without resorting to foul play?’
Part of their point here seems to be that Pinker is suffering from a form of bias related to the most sensational cases which will tend to heighten the availability bias. (Is there a name for this sort of sensationalism effect?)
Is there also some survivorship bias at play here as well?
We don't have access to a wide statistical survey of dead bodies from a large swath of times and places which makes it difficult to determine actual numbers.
-
Now, this may seem counter-intuitive to anyone who spendsmuch time watching the news, let alone who knows much about thehistory of the twentieth century.
Are they suffering from potential availability heuristic (cognitive bias) here? Are they encouraging it in us? Just because we see violence on the news every day doesn't mean it's ubiquitous.
Apparently we'll need real evidence here to provide actual indications.
Does Steven Pinker provide archaeological evidence in his book? What are the per capita rates of violence and/or death over time?
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Cognitive Development
SAMPLE ANNOTATION
As an instructor with a background in K12, I came to post-secondary with a history of writing objectives as measurable skills. Now I see growth is a much better goal than some arbitrary skill and Fosnot & Perry (1996) agree.
Reference
Fosnot, C.T. & Perry, R.S. (1996). Constructivism: A psychological theory of learning. Galactic Challenge. https://gchallenge.org/constructivism-a-psychological-theory-of-learning-2/
-
-
crookedtimber.org crookedtimber.org
-
In a nutshell, then, there was never a time when humans uniformly lived in small, simple egalitarian hunter-gatherer societies, and a time when they started to switch to agriculture- thus inevitably switching to a sedentary, hierarchical, and more complex life style. This is not because the correct trajectory is a different one, but because there was never a linear trajectory to begin with.
Is there a reason or cognitive bias we've got that would tend to make us think that there's a teleological outcome in these cases?
Why should it seem like there would be a foregone conclusion to all of human life or history? Why couldn't/shouldn't it just keep evolving from its current context to the next
-
-
-
In fact, the methodical use of notebooks changed the relationship between natural memory and artificial memory, although contemporaries did not immediately realize it. Historical research supports the idea that what was once perceived as a memory aid was now used as secondary memory.18
During the 16th century there was a transition in educational centers from using the natural and artificial memories to the methodical use of notebooks and commonplace books as a secondary memory saved by means of writing.
This allows people in some sense to "forget" what they've read and learned and be surprised by it again later. They allow themselves to create liminal memories which may be refreshed and brought to the center later. Perhaps there is also some benefit in this liminal memory for allowing ideas to steep on the periphery before using them. Perhaps combinatorial creativity happens unconsciously?
Cross reference: learning research by Barbara Oakley and Terry Sejnowski.
-
-
-
Garrido-Vásquez, P., & Rock, T. (2021). Judgments of truth are independently modulated by affect and repetition. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/qajkb
-
-
onlinelibrary.wiley.com onlinelibrary.wiley.com
-
Sloman, S. A. (2021). How Do We Believe? Topics in Cognitive Science, 0(2021), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/tops.12580
Tags
- lang:en
- pattern recognition
- is:article
- predictability
- knowledge
- causal reasoning
- representational language
- memory
- cognitive science
- information processing
- unfamiliar circumstance
- generalizability
- human thought
- sophisticated associative model
- representational scheme
- dual system of thinking
Annotators
URL
-
- Nov 2021
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
it was assumed that rational thought was value free it was just you know about what was true in the world and so 00:26:06 on and it's not because you're concerned with empathy and morality when you're thinking and and with emotion rational thought is really value-based 00:26:19 now whoa let's go back one there's a further view Descartes assumed that all rationality was the same for everybody that it was universal that what made us 00:26:34 human beings was being rational and logical and that therefore everybody had the same mode of reasoning now if that's true then all you have to do let's say 00:26:47 in politics is tell something somebody to facts and everybody will reason to the same conclusion right sure not true that is if enlightenment reason were 00:27:01 right that would happen it doesn't happen it turns out that it is not the case that all concepts are you are universal and that all of them are 00:27:13 accessible to everybody and then there's another view of you coming out of the postmodern thought that says no concepts are universal they're all arbitrary that's also false many concepts are 00:27:26 universal and many are not a very and it's an empirical question which is which and they vary from language to language and that's important you need to know that it is not the case that 00:27:41 everything with all thought is universal and it's not the case that that's all language particular or particular that is you need to know empirically what part is shared with other people who 00:27:53 speak other languages and come from other cultures and what part is not and that is an important empirical study so the big myth is this but there is some objective rational structure to the 00:28:07 world out there and that human reason can fit it directly and characterize it literally without frames or metaphors and reason about it adequately with formal logic alone that's just false the 00:28:21 world is real that is whatever it is our bodies and brains provide understandings of the world which depend on frames metaphors image schemas prototypes narratives all of those things and it is 00:28:35 that that permits us to create
Rational thought and emotions are entwined at the deepest level. Also, what Lakoff says about universals is very important as we consider how we unite and depolarize politics. We need to find the common denominators, but this is not such a simple task.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Manoochehri, M., Šrol, J., Asl, F. A., Mehdinasab, M., & Akhoundi, Z. (2021). Association of Mental Fatigue due to Long-term Restrictive Measures with Reasoning: A COVID-19 Study. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/4yme9
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Hoffman, R., Mueller, S., Klein, G., & Litman, J. (2021). Measuring Trust in the XAI Context. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/e3kv9
-
-
commons.wikimedia.org commons.wikimedia.org
-
It is difficult to know what to believe when human cognition can easily misrepresent reality.
-
- Oct 2021
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
What the world is seeing now, through the window provided by reams of internal documents, is that Facebook catalogs and studies the harm it inflicts on people. And then it keeps harming people anyway.
One of the flaws of Mark Zuckerberg's spectrum disorder is that he either has no sense of shame or his confirmation bias and loss aversion biases are incredibly large.
-
-
slate.com slate.com
-
There are many other more subtle biases of the evolved human brain—its tendency to focus on the thing that changes rather than the thing that’s constant,
Is there a name for this bias?
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. (2021, July 6). RT @mvankerkhove: I’m struggling with how best to stress how fragile the global situation is, so I’ll be blunt: Each week >2.6 million cas… [Tweet]. @SciBeh. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1412416348676820992
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Basol, M., Roozenbeek, J., & van der Linden, S. (n.d.). Good News about Bad News: Gamified Inoculation Boosts Confidence and Cognitive Immunity Against Fake News. Journal of Cognition, 3(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.5334/joc.91
-
-
www.cogsciwa.com www.cogsciwa.com
-
Www.cogsciWA.com. (n.d.). Www.CogsciWA.Com. Retrieved 4 October 2021, from https://www.cogsciwa.com/
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Covid: 37% of people have symptoms six months after infection | Coronavirus | The Guardian. (n.d.). Retrieved October 1, 2021, from https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/sep/28/covid-37-of-people-have-symptoms-six-months-after-infection?CMP=Share_iOSApp_Other
-
- Sep 2021
-
www.nicholascarr.com www.nicholascarr.com
-
Nicholas Carr explores cognitive science and media theory to understand how technology is change our brains through neuroplasticity.
Ezra Klein was in conversation with Richard Powers regarding his recent book, Bewilderment, exploring the way technology changes us by changing our environment. The medium is the message.
-
-
www.sheldrake.org www.sheldrake.org
-
The effects of spiritual practices are now being investigated scientifically as never before, and many studies have shown that religious and spiritual practices generally make people happier and healthier.
-
-
theconversation.com theconversation.com
-
Mixing science and art to make the truth more interesting than lies. (n.d.). Retrieved September 28, 2021, from https://theconversation.com/mixing-science-and-art-to-make-the-truth-more-interesting-than-lies-100221?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=bylinetwitterbutton
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xa84hA3OsHU
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Josh Cohen</span> in Aphantasia Video: Living without Mental Imagery (Wired) - Neuroscience, Psychology, and Health - Art of Memory Forum (<time class='dt-published'>09/19/2021 21:25:12</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
One last resource for augmenting our minds can be found in other people’s minds. We are fundamentally social creatures, oriented toward thinking with others. Problems arise when we do our thinking alone — for example, the well-documented phenomenon of confirmation bias, which leads us to preferentially attend to information that supports the beliefs we already hold. According to the argumentative theory of reasoning, advanced by the cognitive scientists Hugo Mercier and Dan Sperber, this bias is accentuated when we reason in solitude. Humans’ evolved faculty for reasoning is not aimed at arriving at objective truth, Mercier and Sperber point out; it is aimed at defending our arguments and scrutinizing others’. It makes sense, they write, “for a cognitive mechanism aimed at justifying oneself and convincing others to be biased and lazy. The failures of the solitary reasoner follow from the use of reason in an ‘abnormal’ context’” — that is, a nonsocial one. Vigorous debates, engaged with an open mind, are the solution. “When people who disagree but have a common interest in finding the truth or the solution to a problem exchange arguments with each other, the best idea tends to win,” they write, citing evidence from studies of students, forecasters and jury members.
Thinking in solitary can increase one's susceptibility to confirmation bias. Thinking in groups can mitigate this.
How might keeping one's notes in public potentially help fight against these cognitive biases?
Is having a "conversation in the margins" with an author using annotation tools like Hypothes.is a way to help mitigate this sort of cognitive bias?
At the far end of the spectrum how do we prevent this social thinking from becoming groupthink, or the practice of thinking or making decisions as a group in a way that discourages creativity or individual responsibility?
-
-
www.timeshighereducation.com www.timeshighereducation.com
-
A recent review of the evidence finds that when students are cognitively overloaded, they disengage more often, perform badly and learn less. You can help students stay focused by making your presentations less cognitively overloaded. So, shorten slides, reduce text, use diagrams, remove irrelevant images, progressively reveal content and stick to one idea per slide. Take a careful look at the materials you use and ask yourself: “What’s my main message? What distracts from that? How can I remove distractions?”
This feels related to some of the potential power of sketchnotes.
I'd like the reference to this particular research though.
-
-
www.propublica.org www.propublica.org
-
Billionaire business owners deployed lobbyists to make sure Trump’s 2017 tax bill was tailored to their benefit. Confidential IRS records show the windfall that followed.
@choppa1890 says "will read and get mad about one of these days"
With respect.....this learned attitude is the leading contributor to the problem with modern America. The quote reflects cognitive dissonance that is dealt with through a weak form of denial. @choppa1890 uses a mentally acceptable task (posting in Hypothesis) and 'avoidance', to resolve the dissonance. @choppa1890 can not allow him/herself to read the article, create knowledge and emotion. It's too much to think about so I will make a note in Hypothesis and move on!
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Inasaridze, K. (2021). Cognitive restructuring. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/82pwz
-
-
journals.sagepub.com journals.sagepub.com
-
Rutjens, B. T., van der Linden, S., van der Lee, R., & Zarzeczna, N. (2021). A group processes approach to antiscience beliefs and endorsement of “alternative facts.” Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 24(4), 513–517. https://doi.org/10.1177/13684302211009708
-
- Aug 2021
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
The Attack on "Critical Race Theory": What's Going on?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P35YrabkpGk
Lately, a lot of people have been very upset about “critical race theory.” Back in September 2020, the former president directed federal agencies to cut funding for training programs that refer to “white privilege” or “critical race theory, declaring such programs “un-American propaganda” and “a sickness that cannot be allowed to continue.” In the last few months, at least eight states have passed legislation banning the teaching of CRT in schools and some 20 more have similar bills in the pipeline or plans to introduce them. What’s going on?
Join us for a conversation that situates the current battle about “critical race theory” in the context of a much longer war over the relationship between our racial present and racial past, and the role of culture, institutions, laws, policies and “systems” in shaping both. As members of families and communities, as adults in the lives of the children who will have to live with the consequences of these struggles, how do we understand what's at stake and how we can usefully weigh in?
Hosts: Melissa Giraud & Andrew Grant-Thomas
Guests: Shee Covarrubias, Kerry-Ann Escayg,
Some core ideas of critical race theory:
- racial realism
- racism is normal
- interest convergence
- racial equity only occurs when white self interest is being considered (Brown v. Board of Education as an example to portray US in a better light with respect to the Cold War)
- Whiteness as property
- Cheryl Harris' work
- White people have privilege in the law
- myth of meritocracy
- Intersectionality
People would rather be spoon fed rather than do the work themselves. Sadly this is being encouraged in the media.
Short summary of CRT: How laws have been written to institutionalize racism.
Culturally Responsive Teaching (also has the initials CRT).
KAE tries to use an anti-racist critical pedagogy in her teaching.
SC: Story about a book Something Happened in Our Town (book).
- Law enforcement got upset and the school district
- Response video of threat, intimidation, emotional blackmail by local sheriff's department.
- Intent versus impact - the superintendent may not have had a bad intent when providing an apology, but the impact was painful
It's not really a battle about or against CRT, it's an attempt to further whitewash American history. (synopsis of SC)
What are you afraid of?
- racial realism
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Named after Soviet psychologist Bluma Zeigarnik, in psychology the Zeigarnik effect occurs when an activity that has been interrupted may be more readily recalled. It postulates that people remember unfinished or interrupted tasks better than completed tasks. In Gestalt psychology, the Zeigarnik effect has been used to demonstrate the general presence of Gestalt phenomena: not just appearing as perceptual effects, but also present in cognition.
People remember interrupted or unfinished tasks better than completed tasks.
Examples: I've had friends remember where we left off on conversations months/years later and we picked right back up.
I wonder what things effect these memories/abilities? Context? Importance? Other?
-
-
worrydream.com worrydream.com
-
you interpret the past as "the present, but cruder"
Like people who can't wrap their head around the idea that evolution has nothing to do with any kind of purpose to produce humans. (Even starting from the position that humans are the "end result" is fundamentally flawed.)
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Orticio, E., Martí, L., & Kidd, C. (2021). Social prevalence information is rationally integrated in belief updating. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/7gja2
-
-
-
Pillai, Raunak, and Lisa Fazio. “The Effects of Repeating False and Misleading Information on Belief.” PsyArXiv, August 3, 2021. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/z78xm.
-
-
-
Sulik, J., & McKay, R. (2021). Studying science denial with a complex problem-solving task [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/huxm7
-
- Jul 2021
-
-
Bressan, P. (2021). Strangers look sicker (with implications in times of COVID-19). PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/x4unv
Tags
- behavioural science
- psychological adaptation
- ingroup
- bias
- social science
- lang:en
- life science
- pathogen avoidance
- outgroup
- prejudice
- behavioural immune system
- facial resemblance
- framing
- infectious disease
- is:preprint
- family
- COVID-19
- cultural psychology
- cross-cultural psychology
- cognitive psychology
- emotion
- emotion regulation
- heuristic
- survival
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Jill Rosen </span> in Team finds brain mechanism that automatically links objects in our minds | Hub (<time class='dt-published'>07/24/2021 18:07:51</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
-
https://hub.jhu.edu/2021/07/09/how-the-mind-links-objects/
A study that quantifies association within the brain and indicates the region where it occurs.
-
-
lab6.com lab6.com
-
PDFs used to be large, and although they are still larger thanequivalent HTML, they are still an order of magnitude smaller than thetorrent of JavaScript sewage pumped down to your browser by mostsites
It was only 6 days ago that an effective takedown of this type of argument was hoisted to the top of the discussion on HN:
This latter error leads people into thinking the characteristics of an individual group member are reflective of the group as a whole, so "When someone in my tribe does something bad, they're not really in my tribe (No True Scotsman / it's a false flag)" whereas "When someone in the other tribe does something bad, that proves that everyone in that tribe deserves to be punished".
and:
I'm pretty sure the combination of those two is 90% of the "cyclists don't obey the law" meme. When a cyclist breaks the law they make the whole out-group look bad, but a driver who breaks the law is just "one bad driver."¶ The other 10% is confirmation bias.
-
-
www.scotthyoung.com www.scotthyoung.com
-
A top down view of some learning strategies to begin teasing out which may be better than others.
Are they broadly applicable or domain specific?
What learning methods and pedagogy piece are best and for which domains.
How can we balance learning and doing an overview of theory versus practice?
Which methods are better for beginners versus domain specific experts?
Which are better for overview versus creating new knowledge?
https://www.scotthyoung.com/blog/2021/07/13/against-the-real-thing/
-
Play may trump problem solving. When working on a problem without a specific goal, the student can try lots of things to figure out what works. In contrast, only one answer is needed to solve a problem with a single goal. A playful, exploratory mindset may map out the patterns of interactions better than a narrowly, solution-oriented perspective. As an example of this, Sweller asked students to solve some math problems. One group was asked to solve the problems for a particular variable, and the other group was asked to solve for as many variables as they could. The latter group did better later, which Sweller explained in terms of cognitive load.4
exploratory play >> problem solving
How does this compare to the creativity experience of naming white things in general versus naming white things in a refrigerator? The first is often harder for people, while the second is usually much easier.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Erlich, A., Garner, C., Pennycook, G., & Rand, D. G. (2021). Does Analytic Thinking Insulate Against Pro-Kremlin Disinformation? Evidence from Ukraine [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/4yrdj
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
Thoughts written down can be retrieved as-is. This conquers hindsight bias which makes you change your mind after the fact, pretending you knew it all along.
-
- Jun 2021
-
www.outsideonline.com www.outsideonline.com
-
Cognitive: Follow Your Interests, Do Deep-Focused Work
- find a flow activity
- 1-2 blocks undistracted work
-
- May 2021
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Agarwal, A. (2021). The Accidental Checkmate: Understanding the Intent behind sharing Misinformation on Social Media. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/kwu58
-
-
journals.plos.org journals.plos.org
-
As one of the authors recently pointed out [2], the cognitive demands on a person in a low-tech, paleolithic environment equal or exceed the cognitive loads placed on members of industrialized societies.
I'll have to bump up Tyson Yunkaporta's work on my reading list, particularly the cited text:
Yunkaporta T. Sand talk: how Indigenous thinking can save the world. Melbourne, Victoria: Text Publishing Company; 2019.
-
-
threadreaderapp.com threadreaderapp.com
-
Examples of this sort of non-logical behaviour used to represent identity can be found in fiction in:
- Dr. Seuss' The Butter Battle Book (Random House,1984) which is based on
- the war between Lilliput and Blefuscu in Jonathan Swift's 1726 satire Gulliver's Travels, which was based on an argument over the correct end to crack an egg once soft-boiled.
It almost seems related to creating identity politics as bike-shedding because the real issues are so complex that most people can't grasp all the nuances, so it's easier to choose sides based on some completely other heuristic. Changing sides later on causes too much cognitive dissonance, so once on a path, one must stick to it.
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Brewer, N. T., DeFrank, J. T., & Gilkey, M. B. (2016). Anticipated Regret and Health Behavior: A Meta-Analysis. Health Psychology : Official Journal of the Division of Health Psychology, American Psychological Association, 35(11), 1264–1275. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0000294
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Leblanc-Sirois, Y., Gagnon, M.-È., & Blanchette, I. (2020). Emotions, reasoning, and mental health as predictors of behavior during three phases of the COVID-19 pandemic. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/2p39h
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Greene, C., & Murphy, G. (2020). Can fake news really change behaviour? Evidence from a study of COVID-19 misinformation. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/qfnm3
-
-
-
Zabelina, D., Clay, J., & Upshaw, J. (2021). Imagination, anxiety, and loneliness during the COVID-19 pandemic. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/9aqbj
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Wischnewski, M., Bernemann, R., Ngo, T., & Krämer, N. (2021). Disagree? You Must be a Bot! How Beliefs Shape Twitter Profile Perceptions. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/8vyxr
-
- Mar 2021
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Such research drew from Baruch Fischhoff's work in 1975 surrounding hindsight bias, a cognitive bias that knowing the outcome of a certain event makes it seem more predictable than may actually be true.[5] Research conducted by Fischhoff revealed that participants did not know that their outcome knowledge affected their responses, and, if they did know, they could still not ignore or defeat the effects of the bias.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Hein, G., Gamer, M., Gall, D., Gründahl, M., Domschke, K., Andreatta, M., Wieser, M. J., & Pauli, P. (2021). Social cognitive factors outweigh negative emotionality in predicting COVID-19 related safety behaviors. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/5sbzy
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Levy, N. L., & Ross, R. M. (2020). The cognitive science of fake news [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/3nuzj
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Rahnev, D. (2020). Confidence in the Real World. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2020.05.005
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Szumowska, E., Czarnek, G., Dragon, P., & Keersmaecker, J. D. (2021). Multitasking and correction of false information. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/w5v4z
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Su, I., & Ceci, S. (2021, March 5). “Zoom Developmentalists”: Home-Based Videoconferencing Developmental Research during COVID-19. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/nvdy6
-
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
Cushing, E. (2021, March 8). Late-Stage Pandemic Is Messing With Your Brain. The Atlantic. https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2021/03/what-pandemic-doing-our-brains/618221/
-
- Feb 2021
-
link.aps.org link.aps.org
-
Wang, X., Sirianni, A. D., Tang, S., Zheng, Z., & Fu, F. (2020). Public Discourse and Social Network Echo Chambers Driven by Socio-Cognitive Biases. Physical Review X, 10(4), 041042. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.10.041042
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Schwartz, K. D., Cortens, D. E., McMorris, C., Makarenko, E., Arnold, P., Van Bavel, M., … Canfield, R. (2020, December 15). COVID-19 and Student Well-being: Stress and Mental Health during Return-to-School. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/mqpvn
-
-
www.schneems.com www.schneems.com
-
programmers can try to be aware of their configuration systems and the cognitive overhead they impose on people.
-
-
www.lambdatest.com www.lambdatest.com
-
every human has a defined cognitive load that the memory can process. Making anyone process more information than defined will result in cognitive overloading.
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
Centre for Cognition, Computation, & Modelling on Twitter. (n.d.). Twitter. Retrieved 20 February 2021, from https://twitter.com/BBK_CCCM/status/1359132159953559557
-
-
creativegood.com creativegood.com
-
UX is now "user exploitation."
The dark arts of dark patterns and exploiting cognitive biases.
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Perez Santangelo, A., & Solovey, G. (2020, November 9). Time to Shine: Reliable Response-Timing Using R-Shiny for Online Experiments. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/nuxdg
-
-
qz.com qz.com
-
Frame of reference has been manipulatedCrime statistics are often manipulated for political purposes by comparing to a year when crime was very high. This can expressed either as a change (down 60% since 2004) or via an index (40, where 2004 = 100). In either of these cases, 2004 may or may not be an appropriate year for comparison. It could have been an unusually high crime year.This also happens when comparing places. If I want to make one country look bad, I simply express the data about it relative to whichever country which is doing the best.This problem tends to crop up in subjects where people have a strong confirmation bias. (“Just as I thought, crime is up!”) Whenever possible try comparing rates from several different starting points to see how the numbers shift. And whatever you do, don’t use this technique yourself to make a point you think is important. That’s inexcusable.
This is an important point and when politicians are speaking it, they should cite their sources meticulously.
-
-
donaldrobertson.name donaldrobertson.name
-
When we gain cognitive distance from our own thoughts, it’s as though we’re taking off the spectacles and looking at them, rather than looking through them
-
- Jan 2021
-
-
Watched
[[Verna Myers]]: [[How to overcome our biases? Walk boldly toward them]] [[Ted Talk]]
Our biases can be dangerous, even deadly — as we've seen in the cases of Michael Brown in Ferguson, Missouri, and Eric Garner, in Staten Island, New York. Diversity advocate Verna Myers looks closely at some of the subconscious attitudes we hold toward out-groups. She makes a plea to all people: Acknowledge your biases. Then move toward, not away from, the groups that make you uncomfortable. In a funny, impassioned, important talk, she shows us how.
"Stare at awesome black people."
Look for discomfirming data
"Walk toward your discomfort."
When you see something, have the courage to say something. ie "We don't say those things anymore."
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.lesswrong.com www.lesswrong.com
-
Cognitive fusion isn’t necessarily a bad thing. If you suddenly notice a car driving towards you at a high speed, you don’t want to get stuck pondering about how the feeling of danger is actually a mental construct produced by your brain. You want to get out of the way as fast as possible, with minimal mental clutter interfering with your actions. Likewise, if you are doing programming or math, you want to become at least partially fused together with your understanding of the domain, taking its axioms as objective facts so that you can focus on figuring out how to work with those axioms and get your desired results.
Cognitive Fusion serves an important role
When you are driving a car, you want to be fused with its internal logic, because it will allow you to respond in the quickest possible way to threats. (I'm not sure if this is the same thing though)
-
-
www.verywellmind.com www.verywellmind.com
-
A cognitive bias is a systematic error in thinking that occurs when people are processing and interpreting information in the world around them and affects the decisions and judgments that they make.
The result of the heuristics we use.
-
-
-
“Cognitive Reframing” is a technique used in therapy where patients are taught to look at things from another perspective. This technique helps patients look at the same event with different points of view, and has been proven to help improve their self-talk and behaviour. We are, after all, made up of the stories we tell ourselves.
Cognitive Reframing - Technique to let patients look at situations from different perspectives.
- Helps with self talk and behavior
- Helps with narratives about ourselves
-
- Dec 2020
-
psycnet.apa.org psycnet.apa.org
-
Jarecki, J. B., & Wilke, A. (2018). Into the black box: Tracing information about risks related to 10 evolutionary problems. Evolutionary Behavioral Sciences, 12(3), 230–244. Retrieved from: https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037%2Febs0000123
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Cargnino. M., Neubaum. G., Winter. S., (2020) We're a Good Match: Selective Political Friending on Social Networking Sites. PSyarxiv. Retrieved from: https://psyarxiv.com/9dmgf/
-
-
www.scientificamerican.com www.scientificamerican.com
-
US, J. R. E., Christian Meissner,Deborah Goldfarb,Ian Jason Lee,The Conversation. (n.d.). New DIY Contact Tracing App Is Based on the Science of Memory. Scientific American. Retrieved December 10, 2020, from https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/new-diy-contact-tracing-app-is-based-on-the-science-of-memory/
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Corker, K. S., Arnal, J., Bonfiglio, D. B. V., Curran, P. G., Chartier, C. R., Chopik, W. J., Guadagno, R., Kimbrough, A., Schmidt, K., & Wiggins, B. J. (2020). Many Labs 5: Registered Replication of Albarracín et al. (2008), Experiment 7. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/qzspr
-
- Nov 2020
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Pennycook, G., & Rand, D. (2020). The Cognitive Science of Fake News. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/ar96c
-
-
www.roambrain.com www.roambrain.com
-
Cognitive Overhead (aka Cognitive Load): often the task of specifying formalism is extraneous to the primary task, or is just plain annoying to do.
This is the task that you're required to do when you want to save a note in Evernote or Notion. You need to choose where it goes.
-
-
-
A quick clarification — it’s important to note I’m differentiating “Diversity of Thought” from neurodiversity, which aims to make room for neurological differences (Dyslexia, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Autistic Spectrum, Tourette Syndrome, and others) and advocates for access to various communities often marginalized.
It's good to call out the distinction from [[neurodiversity]] from [[cognitive diversity]] and [[diversity of thought]]
When thinking of [[neurodiversity]] - there is also the intersectionality of being Black, a Person of Color, etc and being neurodiverse.
-
-
blog.thinkherrmann.com blog.thinkherrmann.com
-
4 Steps to Getting Started with Cognitive Diversity Don’t expect that bringing together a bunch of people with widely different backgrounds and experiences will be the miracle cure for all your business problems. Go beyond the surface to get the benefits of diversity of thought: Define cognitive diversity within your organization and measure it Provide the tools to make it practical and tangible Develop leaders who encourage cognitive diversity, facilitate it, and manage it Apply your awareness. of your team's cognitive diversity to think differently about stubborn challenges and tough problems
[[Cognitive Diversity]]
-
-
www.vox.com www.vox.com
-
A few years ago, there was a boom of articles called “If it happened there,” imagining how the American press would cover this-or-that story if it happened in another country. How would we cover the government shutdown if it happened in another country? The Ferguson protests? The Oregon militia siege? George Floyd’s murder? Mike Bloomberg? Slate’s Joshua Keating popularized the form, but other outlets, including Vox, deployed it. The intent was to use the tropes of foreign coverage to create a sense of what the literary critic Darko Suvin called “cognitive estrangement” — severing us from the familiarity and overconfidence that can dull our awareness of extraordinary events.
this is an interesting thought experiment
-
- Oct 2020
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Smith, A. M., Willroth, E. C., Gatchpazian, A., shallcross, amanda, Feinberg, M., & Ford, B. Q. (2020). Coping with Health Threats: The costs and benefits of managing emotions. [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/dn957
-
-
www-sciencedirect-com.libproxy.nau.edu www-sciencedirect-com.libproxy.nau.edu
-
In order to inform the development and implementation of effective online learning environments, this study was designed to explore both instructors' and students' online learning experiences while enrolled in various online courses. The study investigated what appeared to both support and hinder participants' online teaching and learning experiences.
The authors discuss the issue of community and engagement in online graduate programs. They carried out a small case study and used a Cognitive Apprenticeship Model to examine a successful program in Higher Education. They found that students feel too many online classes are just reading and writing, regurgitating rather than applying, and lack sufficient connection with the instructor and with other students, They recommend some strategies to fix that, but admit that more work is needed. 9/10
-
-
www-sciencedirect-com.libproxy.nau.edu www-sciencedirect-com.libproxy.nau.edu
-
We eventually hope to create affect-sensitive learning environments that respond constructively and effectively to boredom and confusion. When we do, we will have made significant progress towards improving students’ learning experiences, reducing problem behaviors such as gaming the system, managing students’ frustration and confusion in the face of impasses, and ultimately improving students’ learning.
Researchers studied students cognitive-affective states doing online learning in 3 separate, very different studies, among different student populations, ranging from 12-year-olds to college students. They found that, contrary to prior assumptions, frustration did not necessarily have negative learning outcomes. Boredom tended to last longest of the cognitive-affective states covered, led to the greatest attempts to game the system, and had the least successful learning outcomes. Confusion was sometimes beneficial and sometimes harmful. Therefore, online learning environments should be developed that guard against boredom and perhaps confusion, rather than frustration. 8/10
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
correspondent, N. D. S. (2020, October 9). “Brain fog”: The people struggling to think clearly months after Covid. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/oct/09/brain-fog-the-people-struggling-to-think-clearly-months-after-covid
-
-
Local file Local file
-
The stories added meaning that couldn’t be matched by facts and figures about the items for sale. Meaning can be very difficult to pull off in design, but sto-ries create cognitive fluency around meaning. Our minds love narratives because they love patterns; stories are like really well-packaged patterns. Beginning, middle, and end. Connect-ing that pattern to an object or action in your design can be achieved, in part, by making sure your design accommodates story—whether in the metaphorical sense of how the page is structured (i.e., the page has a clear beginning, middle, and end) or the more literal sense of actually making sure the design leaves room for text that tells a story.
This can also be leveraged to help improve one's memory.
-
If the original price is horizontally farther away on the page from the sale price (Fig 2.8), the customer is more likely to view it as a better deal, even if the dollar amounts do not change. We equate visual distance with fiscal distance (http://bkaprt.com/dcb/02-19/).
-
-
covid-19.iza.org covid-19.iza.org
-
IZA – Institute of Labor Economics. ‘COVID-19 and the Labor Market’. Accessed 6 October 2020. https://covid-19.iza.org/publications/dp13745/.
-
-
covid-19.iza.org covid-19.iza.org
-
IZA – Institute of Labor Economics. ‘COVID-19 and the Labor Market’. Accessed 6 October 2020. https://covid-19.iza.org/publications/dp13720/.
-
-
www.statnews.com www.statnews.com
-
Long after a Covid-19 infection, mental and neurological effects smolder. (2020, August 12). STAT. https://www.statnews.com/2020/08/12/after-covid19-mental-neurological-effects-smolder/
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Pfattheicher, Stefan, Michael Bang Petersen, and Robert Böhm. ‘Information about Herd Immunity and Empathy Promote COVID-19 Vaccination Intentions’, 30 September 2020. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/wzu6k.
-
- Sep 2020
-
behavioralscientist.org behavioralscientist.org
-
Behavioral Scientist. ‘Creating Citizen Choice Architects - By Ralph Hertwig & Samuli Reijula’, 28 September 2020. https://behavioralscientist.org/creating-citizen-choice-architects/.
-